Inconsistent Highs & Lows
Sometimes you may get a lower or higher blood glucose reading than usual and you may not be able to figure out the reason. When you are sick with a virus or flu, your blood glucose levels will nearly always go up and you may need to contact your doctor. There are a number of other common causes for blood glucose levels to increase or decrease. These include:
- Food time eaten, type and amount of carbohydrate for example: bread, pasta, cereals, vegetables, fruit and milk
- Exercise or physical activity
- Other medications
- Blood glucose checking techniques.
Contact your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator if you notice that your blood glucose patters change or are consistently higher or lower than usual.
What Causes High Morning Blood Sugars
Two main culprits prompt morning highs: the dawn phenomenon and waning insulin. A third, much rarer cause, known as the Somogyi effect, may also be to blame.
The occasional morning high will have little impact on your A1C, a measure of your average blood sugar levels over time that indicates how well managed your diabetes is. But if those highs become consistent, they could push your A1C up into dangerous territory.
Why Checking Your Blood Sugar Is Crucial
Monitoring your blood sugar helps your doctor determine if your diabetes treatment plan is working or if your medication needs adjusting. It can also help you make decisions about what to eat and when to be physically active, per the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . Blood sugar thats too high, referred to as hyperglycemia, or too low, known as hypoglycemia can cause health problems such as dizziness, confusion, blurred vision, and even coma.
The only way to know your blood sugar level is to test it frequently, says Erin Palinski-Wade, a registered dietitian and certified diabetes educator in private practice and author of 2 Day Diabetes Diet based in New York City. You cannot always feel spikes and crashes in blood sugar, so getting into the habit of testing can help you to understand how your body responds to certain foods, exercise, and stress to help you best manage your diabetes.
Staying on top of your blood sugar levels may reduce your risk for long-term diabetes complications, too, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These include heart disease, vision loss, kidney disease, and nerve problems.
The good news: A patient with well-controlled type 2 diabetes whos treated with metformin may only need to check their glucose a few times a week or month, says Dr. Kohlenberg.
Recommended Reading: Type 2 Diabetes Nerve Damage
Do Your Blood Sugar Levels Drop When You Sleep
Yes, people with diabetes may experience a blood sugar level that drops when they sleep. This is largely due to a phenomenon called the dawn effect.
This doesn’t always happen and it’s not something that everyone experiences but as time goes on, our bodies will tell us which pattern is best for it: whether we should eat before bed or not. It’s important to experiment with what works best for our individual needs – if eating before bed causes our blood sugar to drop too low, then we’ll know that it’s best to avoid eating for the hours leading up to bed to keep your blood sugar under control.
If we do experience a drop in blood sugar levels, there are some strategies that may help us either prevent or treat it. Some people will take insulin before going to bed if they know their blood sugar is too high others might drink juice or eat cereal with milk before bedtime when they know they have low blood sugar during the night.
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Levels
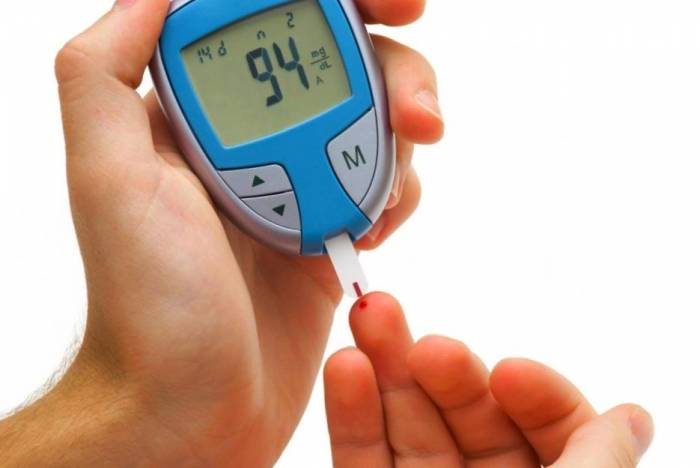
Refer to your blood glucose meters instructions on how to monitor your blood glucose levels.
Your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator will help you decide how many checks are needed and the levels to aim for. When and how often you should check your blood glucose levels varies depending on each individual, the type of diabetes and the tablets and/or insulin being used. Blood glucose levels are measured in millimoles per litre of blood .
Keeping a record of your blood glucose levels can be very helpful for you and your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator. You can keep a diary or use a mobile phone app or website to record your levels.
You May Like: Why Does A Diabetic Need Insulin
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
Monitor Your Alcohol Intake
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, drinking is considered âto be in the moderate or low-risk range for women at no more than 3 drinks in any one day and no more than 7 drinks per week. For men, it is no more than 4 drinks a day and no more than 14 drinks per week.â
If you still find your glucose levels are low, try cutting the NIAAAâs recommendation in half .
Don’t Miss: Hope For Type 1 Diabetes Cure
What Hba1c Do I Aim For
The goal for most people with diabetes will be in the 6.5-7 percent range however this may need to be higher for some people including children and the elderly. Your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator can help you decide on a target that is both appropriate and realistic for your individual circumstances.
Try Changing Your Exercise Timing
Your body only has two major storage pools for glucose: the muscles and the liver. Late evening exercise â particularly if it is long in duration or high-intensity â can significantly deplete those stores. Combined with inadequate re-fueling, some people can experience hypoglycemia the following morning.
Read Also: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
Other Tips For Checking:
- With some meters, you can also use your forearm, thigh, or fleshy part of your hand.
- There are spring-loaded lancing devices that make sticking yourself less painful.
- If you use your fingertip, stick the side of your fingertip by your fingernail to avoid having sore spots on the frequently used part of your finger.
What Is Normal Blood Glucose
There is no one blood glucose level that defines a person as normal. The table of blood glucose levels below gives the appropriate values at different times and in different states, according to the American Diabetes Association. For example, insulin-dependent diabetics often use an upper limit of 7 mmol/L or 140 mg/dL, while non-insulin-dependent diabetics may aim for less than 6 mmol/L or 108 mg/DL.
The blood glucose levels range between less than 100-180 mg/dL for adults from 20 years or older. Depending on your age this may vary.
- Fasting: Less than 5.6 mmol/L or 100 mg/DL
- Before meal: 3.9-7.2 mmol/L or 70-130 mg/DL
- 1-2 hours after eating: Less than 10 mmol/L or 180 mg/DL
- Bedtime: 5.6-7.8 mmol/L or 100-140 mg/DL
Be aware that the above numbers might be different for everyone depending on your doctor’s recommendations.
Recommended Reading: Cauliflower Pizza Crust For Diabetics
Check Your Blood Sugar Levels Before Sleeping
Checking your blood sugar levels before sleeping is a good idea to make sure you’re not going low. If you are using a glucose meter try to avoid going to bed with hypoglycemia. If you have a continuous glucose monitor make sure you review the
It might take some practice but eventually, this routine could become natural and we’ll be able to have an accurate representation of what our body needs without having to even think about it.
If any numbers seem high at all – don’t hesitate to check with your doctor as soon as possible so they can help you figure out how best to get them under control. We want those numbers right where they should be!
Why Is It So Important To Check My Blood Levels
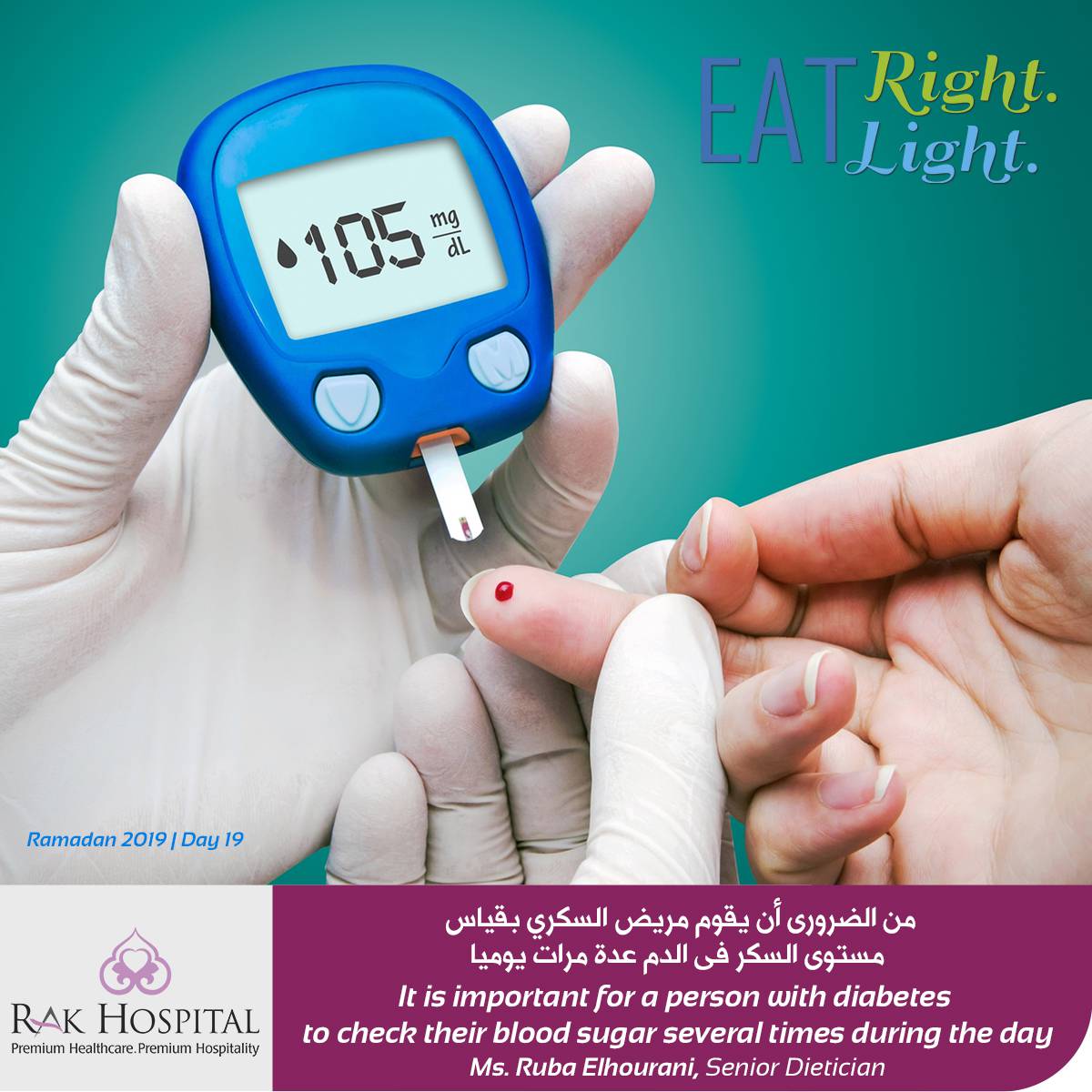
Regular checking and recording of your blood glucose level can reinforce your healthy lifestyle choices as well as inform you of your response to other choices and influences.
Importantly, blood glucose level pattern changes can alert you and your health care team to a possible need for a change in how your diabetes is being managed.
You May Like: What Does High Blood Sugar Feel Like
What Are The Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
Most people have symptoms of low blood sugar when their blood sugar is less than 70 mg/dL. When your blood sugar is low, your body gives out signs that you need food. Common early symptoms of low blood sugar include the following:
- Feeling weak
Late symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- Feeling confused
- Being unable keep your mind on one subject
- Numbness in your mouth and tongue
- Passing out
How To Treat Someone Who’s Having A Seizure Or Fit
Follow these steps if someone has a seizure or fit caused by a low blood sugar level:
Tell your diabetes care team if you ever have a severe hypo that caused you to have a seizure or fit.
Read Also: Low Blood Sugar High Blood Pressure
Check Your Blood Glucose Levels
For many people with diabetes, checking their blood glucose level each day is an important way to manage their diabetes. Monitoring your blood glucose level is most important if you take insulin. The results of blood glucose monitoring can help you make decisions about food, physical activity, and medicines.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. You get a drop of blood by pricking the side of your fingertip with a lancet. Then you apply the blood to a test strip. The meter will show you how much glucose is in your blood at the moment.
Ask your health care team how often you should check your blood glucose levels. Make sure to keep a record of your blood glucose self-checks. You can print copies of this glucose self-check chart. Take these records with you when you visit your health care team.
Wheres The Health Benefit In This
Is there any evidence of benefit if people without diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels with CGMs? Theres little published research to help answer this question.
The best study I could find found nothing particularly surprising: among 153 people who didnt have diabetes, about 96% of the time blood sugar levels were normal or nearly so. In fact, many of the abnormal levels were considered implausible or a mistake. Another small study looked at sedentary individuals without diabetes who were overweight or obese. Participants completed a counseling session about the effects of physical activity on blood sugar and used a CGM device and an activity tracker for 10 days. Afterward, they reported feeling more motivated to exercise.
But I could find no published study suggesting that monitoring translates into improved health. Well, wait: one maker of a CGM device posted a study on its website reporting better blood sugar results among healthy people using their product. However, the study wasnt published in a peer-reviewed medical journal, it lacked details that would allow critical evaluation, and it examined what seem to be arbitrary ranges of blood sugar values, not actual health outcomes such as heart disease, nerve damage, or hospitalizations.
You May Like: Dialysis And Diabetes Diet Plan
How To Use A Blood Glucose Meter:
- After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter.
- Use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood.
- Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result.
- Your blood glucose level will appear on the meter’s display.
Note: All meters are slightly different, so always refer to your user’s manual for specific instructions.
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Before a meal.
- Two hours after a meal.
- At bedtime.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
Don’t Miss: Sourdough Bread Good For Diabetics
What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1C is a lab test. It indicates an average blood glucose reading for the last 90 days. It is done when you find out you have diabetes, and every 3 months after that at clinic visits. A person without diabetes has a Hemoglobin A1C of less than 5.6%.
|
Target Hgb A1C is 7.5% for all children and adults with diabetes. |
The chart below shows the Hemoglobin A1C result compared with the blood glucose number.
Structured Blood Glucose Testing

Structured testing supports your routine or daily testing by giving you deeper, more targeted data to work from. It can help you determine if you’re in a safe range and problem-solve around how the things you do are connected to your blood sugar. You simply perform additional tests over a short period at specific times of day.
Structured blood glucose testing can help you:
- Discover how to best use your numbers
- See how certain activities can affect on your blood sugar levels
- Problem-solve around highs and lows
- Identify blood sugar patterns
- Work with your healthcare team decide if any adjustments are needed in your insulin therapy or other areas of your diabetes management
Pattern management: If you find that your A1C result is rising in spite of your best efforts, or if you don’t feel as well as you’d like, talk with your healthcare professional about the Accu-Chek 360° View tool. This simple paper tool helps you track your blood sugar over 3 days, so you and your doctor can quickly identify patterns that can guide adjustments to your treatment plan. As a result, you may be able to feel better and lower your A1C.2
Before-and-after testing: You may also decide to try the Accu-Chek Testing in Pairs tool. This easy-to-use, printable tool helps you see changes in your blood glucose with before-and-after testing. In just 7 days, you can see the effect a specific meal, exercise or other event has on your blood sugar.
Recommended Reading: Drug Assistance Programs For Insulin
Types Of Diabetes And Their Major Causes
Diabetes is mainly of 3 types, type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, and with all 3 types of diabetes, the body is either not able to produce enough insulin or unable to use the insulin that it makes, leading to high blood sugar levels.Type 1 Diabetes usually starts in childhood and carries on for life. Type 1 Diabetes occurs when the patients pancreas stops making insulin. The causes of Type 1 Diabetes are:
- Family History and Genetics: A person having a close relative with Type 1 Diabetes usually has a high chance of getting the condition himself. So, it is imperative for every child with a parent or a sibling having Type 1 Diabetes to undergo a screening test for Type 1 Diabetes.
- Pancreatic Diseases: Persons with diseased pancreas may acquire Type 1 Diabetes because the pancreas may fail to produce insulin needed to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
- Infections or Illnesses that Cause Damage to the Pancreas: Viral infections such as German measles, mumps, and rotavirus may cause damage to the beta cells of the pancreas which produce insulin and lead to the development of Type 1 Diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes occurs when the body develops insulin resistance and is not able to make use of the insulin produced by the pancreas, leading to uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Type 2 Diabetes usually affects adults, but it can occur in individuals of any age. The main causes of Type 2 Diabetes include:
Symptoms Of A Low Blood Sugar Level
A low blood sugar level can affect everyone differently. You’ll learn how it makes you feel, although your symptoms may change over time.
Early signs of a low blood sugar level include:
- sweating
- a fast or pounding heartbeat
- becoming easily irritated, tearful, anxious or moody
- turning pale
If a low blood sugar level is not treated, you may get other symptoms, such as:
- weakness
- unusual behaviour, slurred speech or clumsiness
- feeling sleepy
- seizures or fits
- collapsing or passing out
A low blood sugar level, or hypo, can also happen while you’re sleeping. This may cause you to wake up during the night or cause headaches, tiredness or damp sheets in the morning.
Read Also: Best Diet For Type One Diabetes
What Are The Target Ranges
Blood glucose targets are individualized based on:
- duration of diabetes
- conditions a person may have
- cardiovascular disease or diabetes complications
- hypoglycemia unawareness
- individual patient considerations
The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A1C targets differ based on age and health. Also, more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.
- A1C: Less than 7%A1C may also be reported as eAG: Less than 154 mg/dL
- Before a meal : 80130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after beginning of the meal *: Less than 180 mg/dL