Living With Type 1 Diabetes:
Life with type 1 diabetes poses lifelong challenges for every member of the family.
People with type 1 diabetes should:
- Test blood glucose levels three or more times per day and adjust their insulin through injections or an insulin pump.
- Ensure insulin doses are balanced with food intake and level of daily activity. People with type 1 diabetes may experience low and high blood sugar levels, which should be carefully monitored and managed.
While living with type 1 diabetes requires a certain amount of daily structure, newer pumps and insulin products have provided more flexibility in the management of this condition.
A healthcare provider can provide advice to help properly manage blood glucose levels.
Symptoms Signs Causes Of Levels Of High Blood Sugar In The Blood
High blood sugar or hyperglycemia is an abnormally high blood sugar level in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a hallmark sign of diabetes and prediabetes.
Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia include blurred vision, headaches, hunger, and …
The normal ranges for blood sugar levels in adults who do not have diabetes while fasting are 72-99 mg/dL. These ranges may increase to 80-130 mg/dL for those being treated for diabetes.
According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes should have
- blood sugar levels of 80-130 mg/dL before eating a meal , and
- less than 180 mg/dL about 1-2 hours after eating a meal
High blood sugar ranges for people who dont have diabetes begin at 140 mg/dL, while those being treated for diabetes have a high range beginning at 180 mg/dL.
An A1c Goal Of Between 7% And 8% Is Reasonable And Beneficial For Most Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
though if lifestyle changes can get that number lower, then go for it. For patients who want to live a long and healthy life and try to avoid the complications of diabetes, they will need to keep their blood sugars as normal as possible that means an A1c under 6.5%. However, studies show that using medications to achieve that goal significantly increases the risk of harmful side effects like hypoglycemia and weight gain. To live longer and healthier and avoid both the complications of diabetes as well as the risks of medications, theres this amazing thing called lifestyle change. This involves exercise, healthy diet, weight loss, and not smoking. It is very effective. Lifestyle change also can help achieve healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which in turn reduce the risk for heart disease. And heart disease is a serious and common complication of diabetes.
Lifestyle change should be the cornerstone of treatment for type 2 diabetes. The recommendations go on to say that for patients who achieve an A1c below 6.5% with medications, we should decrease or even discontinue those drugs. Doing so requires careful monitoring to ensure that the person stays at the goal set with his or her doctor, which should be no lower than 7%, for the reasons stated above.
Recommended Reading: Relationship Between Triglycerides And Blood Glucose
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
This test can be done in the lab or the healthcare providers office with a simple finger stickor your doctor may prescribe a meter and have you test regularly at home.
A fasting blood sugar level indicates what your blood sugar is when you havent eaten for at least 8 hours. For adults without diabetes, a normal fasting blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dL. A fasting blood sugar level of 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy.
When you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called glucose and sends that to your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells, which use it for energy.
When you have diabetes and donât get treatment, your body doesnât use insulin like it should. Too much glucose stays in your blood, a condition usually called high blood sugar. This can cause health problems that may be serious or even life-threatening.
Thereâs no cure for diabetes. But with treatment and lifestyle changes, you can live a long, healthy life.
Diabetes comes in different forms, depending on the cause.
Recommended Reading: Blood Testing Meters For Diabetes
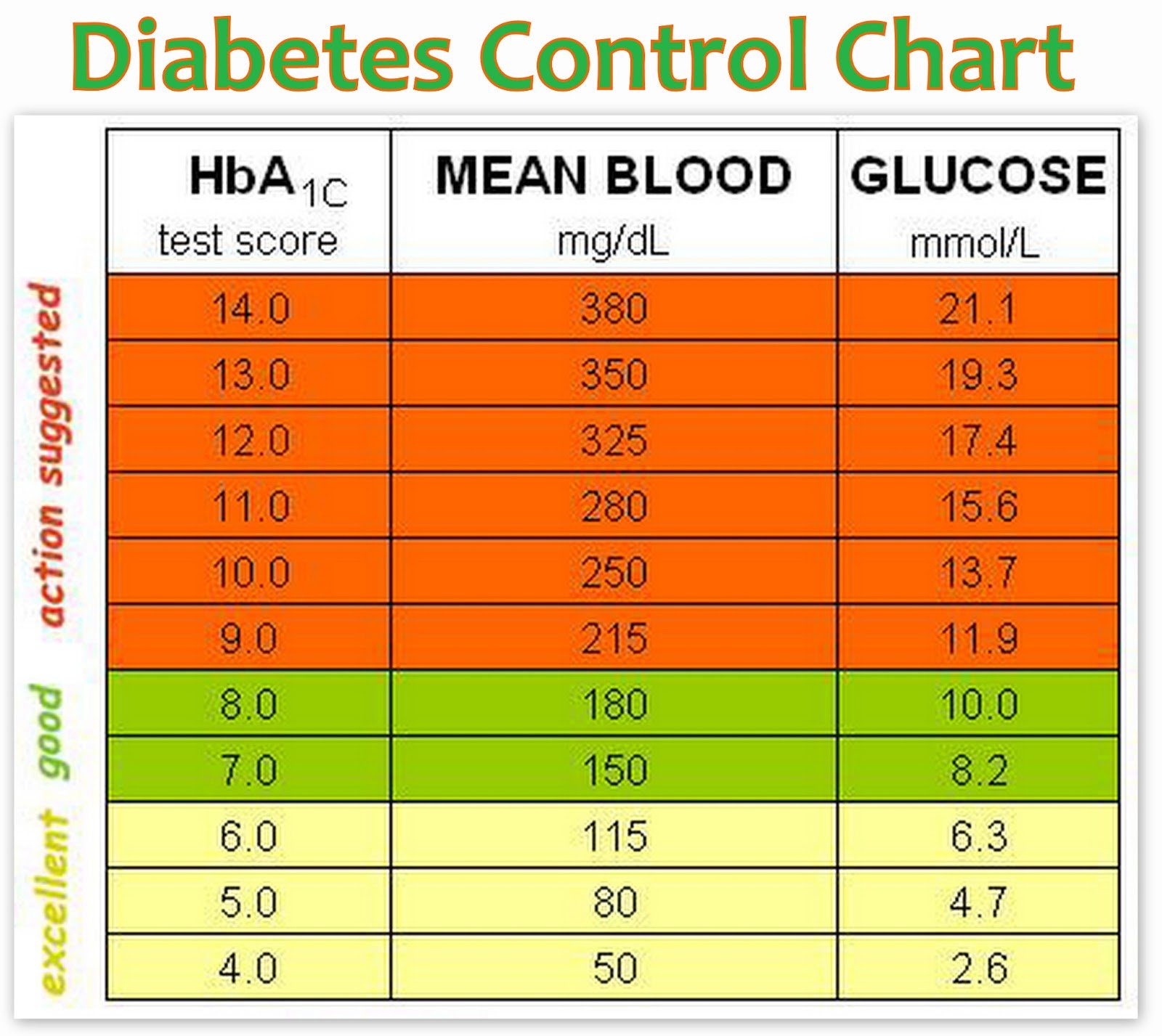
Diabetes Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Before sharing the diabetes blood sugar levels chart, we want to OVER EMPHASIZE the importance of you gaining the best control of your blood sugar levels as you possibly can. Just taking medication and doing nothing else is really not enough.
You see, people are often not fully informed about why it is so crucial to do, because if you already have a diabetes diagnosis, then you are already at high risk for heart disease and other vascular problems.
Maybe youve been better informed by your doctor but many people we come across havent. So if thats you, its important to know that during your pre-diabetic period, there is a lot of damage that is already done to the vascular system. This occurs due to the higher-than-normal blood sugar, thats what causes the damage.
So now that you have type 2 diabetes, you want to prevent any of the nasty complications by gaining good control over your levels.
Truly, ask anyone having to live with diabetes complications and theyll tell you its the pits!
You DO NOT want it to happen to you if you can avoid it.
While medications may be needed, just taking medication alone and doing nothing is really not enough!
Why is it not enough even if your blood sugars seem reasonably under control?
Not only are my readings now within normal range, Im also down over 20 pounds and feeling so much better. Thank you.
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Low blood sugar, also called hypoglycemia, is what happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. People who take insulin may have low blood sugar if they take too much insulin or mistime the insulin dose in relation to food, or if they exercise more than usual when there is fast-acting insulin on board .
Your healthcare provider will tell you when and how to check blood sugar, and when and how to treat low blood sugar. A low blood sugar is generally considered to be less than 70 mg/dL. A dangerously low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL.
Low blood sugar can also be caused by many things including certain medications or combinations of medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:
- Lightheadedness
If your blood sugar is low you might start to feel some of the first signs of hypoglycemia like dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating. The only way to know for sure if your blood sugar is low is to test it with a glucose meter or monitor it with a continuous glucose monitor such as the Dexcom G6.
If your blood sugar is low , a general rule of thumb is to consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbs to raise your blood sugar levels and avoid further symptoms, according to the American Diabetes Association . Your healthcare provider will give you a plan for what to do in case of low blood sugar that is specifically designed for you.
Read Also: Best Glucose Meter For Dogs
Is A1c Supposed To Be The Same As My Blood Sugar Average
A1C measures your average blood sugar over the past 3 months.
You can have your A1C measured with a blood draw in your doctors office or lab. Some doctors can also perform a fingerstick blood test to check your A1C level.
When sugar enters your bloodstream, it binds to a protein called hemoglobin. People with high blood sugar have a higher percentage of the hemoglobin protein coated with sugar. Your A1C result will give you an indication of what percentage of your hemoglobin is bound to sugar.
- Standard : Less than 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.5%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
In general, the ADA and other clinical guidelines for people with diabetes is that you should work closely with your diabetes care team to determine whats best for your A1C goal. Generally, clinicians advise for an A1C of being safely 7.0%, though that can vary depending on ones individual care plan.
Its important to keep in mind that A1C levels do not reflect all of the nuances of ones diabetes management, meaning it doesnt always reflect your glucose variability, meaning that A1C doesnt offer insight into high or low blood sugars, and it can be manipulated if your blood sugars fluctuate regularly.
As a result, many diabetes professionals have moved away from considering the A1C the sole gold standard for someones diabetes management. Instead, they use that A1C in addition to time in range figures, showing how often your glucose levels are in your individualized target range.
Ideal Blood Sugar Levels For Type 2 Diabetes
In this post, we talk about the ideal blood sugar levels for type 2 diabetes. Blood sugar levels or blood glucose levels is the amount of blood sugar in your body. When you understand the normal blood sugar level ranges you can better manage your diabetes. The ranges stated on this post are as recommended by the National Institute for Clinical Excellence . However, your target range as advised by your doctor or health professional may be different.
For most healthy people, the normal blood sugar levels are:
- Fasting : between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L
- 2 hour after eating: Up to 7.8 mmol/L
Also Check: Medicare Part D Insulin Coverage
High Blood Glucose Levels
Consistently high blood sugar levels are part of a condition called hyperglycemia.
People with poorly controlled diabetes, Cushings syndrome, and some other illnesses often experience hyperglycemia. People taking oral steroids may also experience hyperglycemia while taking this medication.
Hyperglycemia normally develops when there is not enough insulin in the body, or when the cells become less sensitive to insulin.
Without insulin, glucose cannot enter cells, and it builds up in the bloodstream.
Common symptoms of hyperglycemia can include:
If the kidneys and liver do not work correctly, breaking down and excreting medication from the body becomes harder.
Excessive insulin production or supplementation can lead to hypoglycemia. Some tumors can cause low blood sugar, as they produce chemicals similar to insulin. A tumor may also consume so much glucose that it does not leave enough for the rest of the body.
People who undergo gastric bypass surgery might also experience hypoglycemia, as they will be able to take in less food than they were able to before surgery.
Nesidioblastosis, a rare condition involving the enlargement of beta cells, often results in an overproduction of insulin. Beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas.
What To Do When Your Blood Sugar Is High Or Low
High blood sugar can harm you. If your blood sugar is high, you need to know how to bring it down. Here are some questions to ask yourself if your blood sugar is high.
- Are you eating too much or too little? Have you been following your diabetes meal plan?
- Are you taking your diabetes medicines correctly?
- Has your provider changed your medicines?
- Is your insulin expired? Check the date on your insulin.
- Has your insulin been exposed to very high or very low temperatures?
- If you take insulin, have you been taking the correct dose? Are you changing your syringes or pen needles?
- Are you afraid of having low blood sugar? Is that causing you to eat too much or take too little insulin or other diabetes medicine?
- Have you injected insulin into a firm, numb, bumpy, or overused area? Have you been rotating sites?
- Have you been less or more active than usual?
- Do you have a cold, flu, or another illness?
- Have you had more stress than usual?
- Have you been checking your blood sugar every day?
- Have you gained or lost weight?
Recommended Reading: Freestyle Precision Neo Blood Glucose Test Strips
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieve closer to normal blood sugar levels.
If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
How Do Blood Glucose Levels Compare With Hba1c Readings
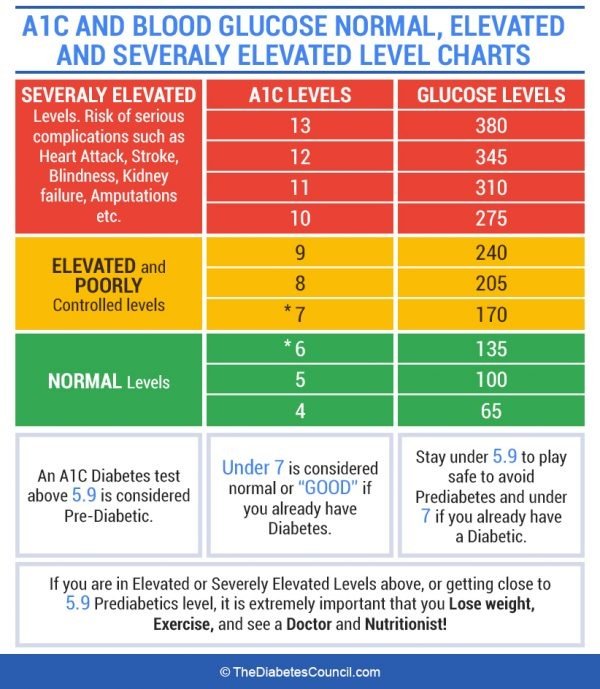
The table on the right shows how average blood sugar levels in mmol/L would be translated into HbA1c readings , and vice versa.
It is important to note that because blood glucose levels fluctuate constantly, literally on a minute by minute basis, regular blood glucose testing is required to understand how your levels are changing through the day and learning how different meals affect your glucose levels.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Diabetes Permanently
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person’s needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals. A general guideline is:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
In general, before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
What Is Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
Also Check: Do Expired Blood Glucose Test Strips Read High Or Low
New Recommendations For Hba1c Targets For Type 2 Diabetes: Warranted Or Short
Hemoglobin A1c has been a standard test of long-term average blood glucose control for patients with type 2 diabetes for more than a decade, and blood levels above accepted thresholds are used to diagnose both pre-diabetes and diabetes . While it is uniformly accepted that higher HbA1c levels are associated with greater risk of complications from diabetes, as well as the incidence of other diseases, the targets for reducing this biomarker in people with existing diabetes remain open to debate. In particular, aggressive pharmaceutical therapy increases both side effects and costs, which need to be considered when assessing the net benefits accrued from meeting specific HbA1c targets.
Recently the American College of Physicians published less stringent treatment goals than those advocated by the American Diabetes Association , resulting in an open debate between these two trusted medical organizations. As you might expect, this is of considerable interest to us at Virta as we strive to help our patients achieve even lower HbA1c values than either of these organizations recommend.
In other words, the method used to get to a specific HbA1c level will significantly affect the resulting risk-benefit ratio, and thus the appropriate targets will differ depending on the chosen method of treatment. So here, in detail, is how we at Virta justify setting an HbA1c target reflecting better blood glucose control than what is advocated by either the ACP or the ADA.
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- s: Stop smoking or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
You May Like: Diabetes Blood Sugar Level Tester