Risk Of Bias Assessment
Two independent reviewers assessed the articles describing screening undertaken in a dental setting. Quality of the papers was assessed using a published and validated risk of bias assessment tool, the United States Preventative Task Force Criteria for Assessing Internal Validity of Individual Studies.
Keep Your Mouth Healthy And Happy
Treating gum disease may be able to help lower your blood sugar over time.
Regular dental visits are important to prevent problems. Follow your diabetes care schedule. Keep regular dental visits for professional cleanings, X-rays, and checkups. Ask your dentist how often you should have your teeth checked.
Keep regular dental visits for checkups and professional cleanings. Follow your diabetes care schedule to help stay on track.
Here are a few more important tips:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss your teeth at least once a day.
- Tell your dentist if you have diabetes.
- If your gums are red, swollen, or bleed easily, see your dentist. These may be signs of gum disease. Other signs include dry mouth, loose teeth, or mouth pain.
- If you smoke, quit. Smoking increases your risk of gum disease and can worsen your diabetes.
Osteonecrosis Of The Jaw
DM is an established risk factor for ONJ in general and medication-related ONJ . Microvascular complications impair blood circulation and hence bone nutrition and quality with reduced remodeling . DM also causes increased apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes and changes in immune cell function, promoting inflammation .
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Affect The Brain
Diabetes And Oral Fungal Infections
Oral thrush is a fungal infection. It is caused by an overgrowth of the yeast, Candida albicans, which lives in the mouth. Some conditions caused by diabetes such as high glucose in saliva, lowered resistance to infection and dry mouth can encourage the overgrowth of these fungi, leading to oral thrush.
Oral thrush causes uncomfortable, sometimes ulcerated white or red patches on the skin of the mouth. Good mouth hygiene and blood glucose levels in the target range can help to treat oral thrush. Your dentist can treat this condition by prescribing antifungal medications if needed.
Diabetes And Maintaining Good Oral Health
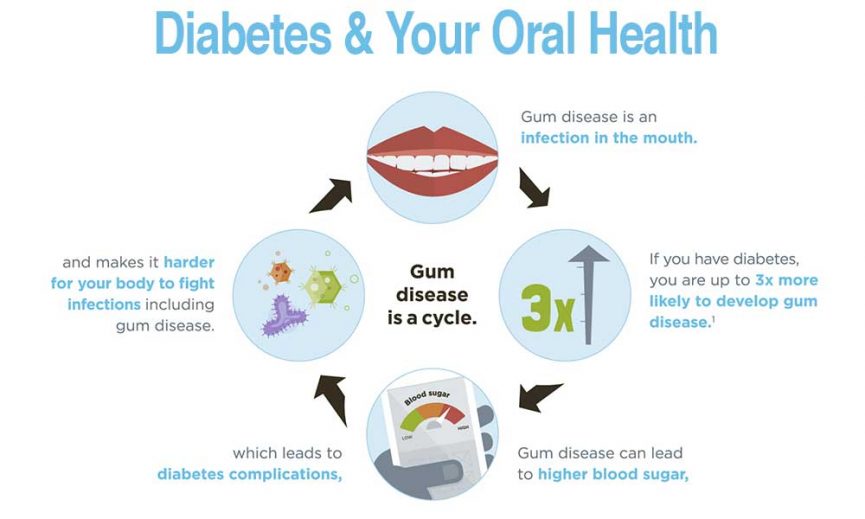
Research indicates that people with diabetes have a higher risk of oral health problems, including gum disease , thrush and dry mouth.
It is important for people living with diabetes to maintain excellent plaque removal every day through brushing regularly and using floss or small brushes for cleaning in-between the teeth. Good oral health can contribute to good general health.
Keeping good control of blood glucose levels, eating a healthy diet and quitting smoking can all help reduce your risk of dental health problems. You should also ensure your dentist knows about your diabetes and that you attend regular dental appointments.
In this section we will look at the recommended teeth cleaning techniques that can help you maintain healthy teeth and gums and lower the chance of oral and general health complications developing.
Don’t Miss: Three P’s Of Diabetes
Hyperglycemia/dm And Oral Health Mutually Affect Each Other
While type 1 DM is due to no or insufficient insulin production affecting about 5% of patients with DM, type 2 DM is a syndrome characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin production, insufficient insulin uptake, or both . About 463 million adults suffer from DM, with 700 million expected by the year 2045 . An additional 374 million people have prediabetes and are at risk of developing T2DM .
Systemic hyperglycemia causes complications such as retinopathy nephropathy neuropathy heart, peripheral arterial, and cerebrovascular disease obesity, cataracts erectile dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease . Regardless of DM type, it is the hyperglycemia, not the diagnosis of DM per se, that leads to several oral complications and oral health-related decreased quality of life .
These oral manifestations are described, followed by any effects in the opposite direction.
For succinct brevity, DM is used for any type of diabetes or hyperglycemia and the comparison group is non-traditionally omitted. For example, in the sentence People with DM have greater xxxx, the comparison than people without DM is implicit, but not shown.
Diabetes Teeth And Gums
People with diabetes who have irregular blood glucose levels have a higher risk of tooth problems and gum disease than people without diabetes. This is because they have lowered resistance to infection and may not heal as easily.
If you are living with diabetes, you need to pay particular attention to your oral health and dental care, as well as keeping your blood glucose levels in the target range. Visit your dentist every 6 to 12 months for advice about how to keep your teeth and gums healthy.
Diabetes is a common condition in Australia, affecting around 1.8 million people . The first signs and symptoms of diabetes can occur in the mouth, so paying attention to your oral health and speaking to your doctor or dental practitioner about any changes can also lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Don’t Miss: Latest News On Type 1 Diabetes Cure
Type 2 Diabetes And Oral Health
The link between type 2 diabetes and oral health
Diabetes affects your bodys ability to utilize glucose, or blood sugar, for energy. Diabetes can cause many complications. These include nerve damage, heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and even blindness. Another common health complication is gum disease and other oral health problems.
According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes are at higher risk for gingivitis, gum disease, and periodontitis . Diabetes affects your ability to fight off bacteria that can cause gum infections. Gum disease can also affect the bodys blood sugar control.
Diabetes is associated with increased risk for thrush, a type of fungal infection. Additionally, people with diabetes are likely to have a dry mouth. This has been associated with increased risk for mouth ulcers, soreness, cavities, and dental infections.
Dental Treatment In Dm
Non-surgical periodontal treatment consisting of scaling and root planing , or deep cleaning, home oral hygiene instruction, and maintenance follow-up visits can be performed in any dental office by dental hygienists or dentists and improves the periodontal health status also in DM . However, advanced cases need treatment by periodontists or other especially skilled clinicians. Adults with DM and periodontitis manage to incorporate new, effective oral hygiene measures into daily life and frequent tooth brushing is negatively associated with incident DM .
Also Check: What Is The Best Meal Replacement For Diabetics
More Than A Sweet Tooth
If the sugar level is high in your blood, its high in your saliva too. Bacteria in plaque, a sticky film, use sugar as food. Some of this bacteria can cause tooth decay, cavities, and gum disease. If the tooth is not treated, it can also lead to tooth loss.
Gum disease can be more severe and take longer to heal if you have diabetes. If you have gum disease, your diabetes may be harder to manage.
Heres a quick look at how diabetes can take its toll on your oral health:
- You may have less saliva, causing your mouth to feel dry.
- Your gums may become inflamed and bleed often .
- Infections in your mouth can take longer to heal.
Oral Health Disease Risk Factors
Aside from inadequate personal and professional dental care, there are a number of other factors that you should be aware of if you have type 2 diabetes. The importance of controlling blood glucose levels deserves additional emphasis.
Blood sugar control should serve as the cornerstone of any type 2 diabetes disease prevention strategy, including the prevention of oral health problems. This requires careful monitoring of blood glucose levels and the adoption of a diabetes friendly diet and lifestyle.
Smoking is a risk factor for developing oral health problems even if you dont have type 2 diabetes. Nevertheless, the possibility of developing serious oral disease is significantly higher for the type 2 diabetes population.
Needless to say, eliminating smoking and relying on a dental care professional to treat potential oral health care problems during the early stages of the disease process is highly recommended.
One of the leading causes of dry mouth is medication. The National Institutes of Health has identified no less than 400 medications that may cause dry mouth. The long list includes medications commonly prescribed to type 2 diabetics.
These medications are typically prescribed for the purpose of alleviating diabetes related complications such as neuropathy and nerve pain. Make sure you ask your doctor whether your medications are likely to cause dry mouth.
Your dentist may even prescribe an oral rinse to reduce symptoms. Sugar free lozenges can also be helpful.
Don’t Miss: What To Give A Diabetic When Blood Sugar Is Low
Why Are People With Diabetes More Likely To Develop Oral Health Problems
The link between diabetes and oral health problems is high blood sugar. If blood sugar is poorly controlled, oral health problems are more likely to develop. This is because uncontrolled diabetes weakens white blood cells, which are the bodys main defense against bacterial infections that can occur in the mouth.
Just as studies have shown that controlling blood sugar levels lowers the risk of major organ complications of diabetes such as eye, heart, and nerve damage so to can diabetes protect against the development of oral health problems.
Dental Hygiene Diabetes And Heart Problems
Diabetes can lead to excess cholesterol building up in the bloodstream, raising the risk of heart disease.
A number of studies have shown that people with gum disease may have a higher risk of heart disease. Bacteria and inflammation in the gums may escape into the blood system and cause blockages in the blood vessels, which reduce blood flow to the heart.
More research is being carried out to further investigate the effect of gum disease on the heart.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Someone With Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms Of Gum Disease
Please see your dentist immediately if you notice any signs and symptoms of gum disease, including:
- red, swollen, tender, bleeding gums
- a persistent discharge coming from the gums
- gums that are loose and pull away from the teeth
- a bad taste or bad breath
- loose teeth this can change the feel of your bite when your teeth are placed together or may make dentures fit differently
- spaces opening up between your teeth.
Neuropathy Consequencies In The Oral Cavity
A common complaint among DM patients is burning mouth syndrome, an orofacial neurosensory disorder of unknown cause, characterized by a bilateral burning sensation of the oral mucosa usually in the absence of clinical and laboratory findings. Management of burning mouth syndrome should have an interprofessional approach to improve patients well being and quality of life. The treatment protocol for xerostomia is frequently used for the treatment of burning mouth syndrome, allowing for the palliative care of the symptoms.
Taste detection is determined hereditarily, but it can be influenced also by occurrence of neuropathy. This sensory dysfunction can inhibit the ability to maintain a proper diet and can lead to poor glycemic control. Taste impairment has also been associated with the development of obesity, and it has been reported during the course of diabetes. The use of oral hygiene devices may be impaired by peripheral neuropathies and by diabetic retinopathy, which may impair daily oral hygiene. The use of an electric toothbrush as well as other alternative hygiene methods and a strict dental maintenance schedule are important in the long-term oral health of these patients.
Recommended Reading: How To Use Insulin Pump Video
Types Of Dental Problems
Mouth problems linked to your diabetes can mean:
- tooth decay
- infection in the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth
- dry mouth
- irritated and sore mouth, meaning you might have difficulty wearing dentures
- tooth loss
- abscesses.
The early signs of mouth problems are things like redness, soreness and bad breath. If you notice these, dont ignore them and make an appointment with your dentist. Getting the right treatment early can prevent severe infections, tooth loss and other complications down the road.
Symptoms To Watch For
You should call your dentist if you:
- Have bleeding or sore gums
- Get infections often
- Have bad breath that won’t go away
Controlling your diabetes will go a long way toward protecting your teeth and gums. And that, in turn, will also help you manage your diabetes.
If you have diabetes, keep an eye out for these oral health conditions — especially if you’ve already reached the half-century mark.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus
What The Research Says
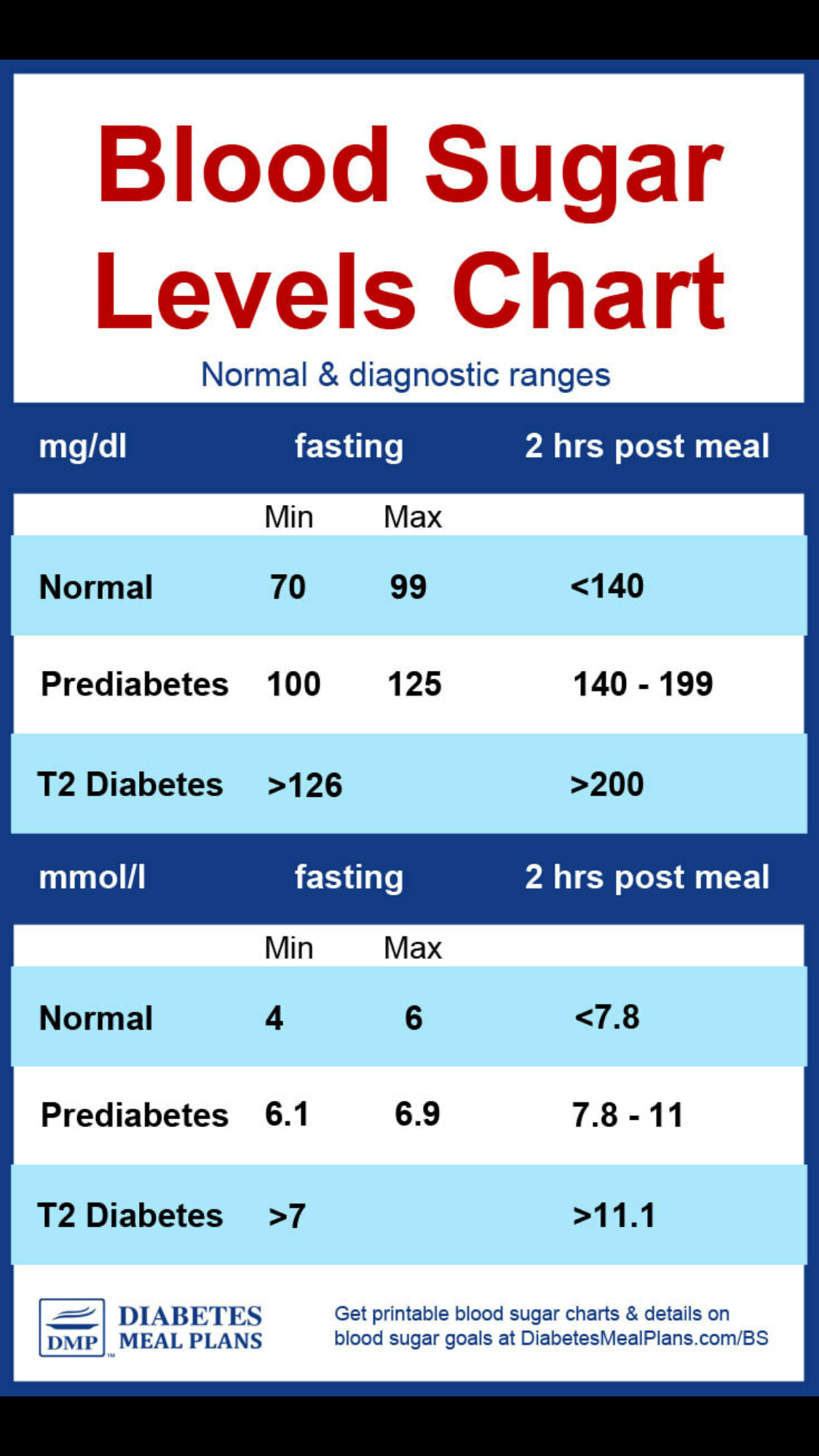
A 2013 study published in the journal BMC Oral Health looked at 125 people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers measured factors including missing teeth, the incidence of periodontal disease, and the amount of reported dental bleeding.
The study found that a combination of the longer people had diabetes, the higher their fasting blood glucose, and the higher their hemoglobin A1C , the more likely they were to have periodontal disease and dental bleeding.
Those who did not report careful self-management of their condition were more likely to have missing teeth than those who did work to control their blood sugar levels.
Diabetes And Oral Health: Summary Of Current Scientific Evidence For Why Transdisciplinary Collaboration Is Needed
- 1School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States
- 2Centre for Oral Health Outcomes and Research Translation , Western Sydney University, Liverpool, NSW, Australia
- 3Drug Health Services, South Western Sydney Local Health District , Cabramatta, NSW, Australia
This Perspective provides a brief summary of the scientific evidence for the often two-way links between hyperglycemia, including manifest diabetes mellitus , and oral health. It delivers in a nutshell examples of current scientific evidence for the following oral manifestations of hyperglycemia, along with any available evidence for effect in the opposite direction: periodontal diseases, caries/periapical periodontitis, tooth loss, peri-implantitis, dry mouth , dysbiosis in the oral microbiome, candidiasis, taste disturbances, burning mouth syndrome, cancer, traumatic ulcers, infections of oral wounds, delayed wound healing, melanin pigmentation, fissured tongue, benign migratory glossitis , temporomandibular disorders, and osteonecrosis of the jaw. Evidence for effects on quality of life will also be reported. This condensed overview delivers the rationale and sets the stage for the urgent need for delivery of oral and general health care in patient-centered transdisciplinary collaboration for early detection and management of both hyperglycemia and oral diseases to improve quality of life.
You May Like: Freestyle Libre For Type 2 Diabetes
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that acts like a key to let blood sugar into the cells in your body for use as energy. If you have type 2 diabetes, cells dont respond normally to insulin this is called insulin resistance. Your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Eventually your pancreas cant keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
What Oral Health Problems Are Associated With Diabetes
People with diabetes face a higher risk of:
- Dry mouth: Uncontrolled diabetes can decrease saliva flow, resulting in dry mouth. Dry mouth can further lead to soreness, ulcers, infections and tooth decay.
- Gum inflammation and periodontitis: Besides weakening white blood cells, another complication of diabetes is that it causes blood vessels to thicken. This slows the flow of nutrients to and waste products from body tissues, including the mouth. When this combination of events, the body loses its ability to fight infections. Since periodontal disease is a bacterial infection, people with uncontrolled diabetes might experience more frequent and more severe gum disease.
- Poor healing of oral tissues: People with uncontrolled diabetes do not heal quickly after oral surgery or other dental procedures because blood flow to the treatment site can be damaged.
- Thrush: People with diabetes who frequently take antibiotics to fight various infections are especially prone to developing a fungal infection of the mouth and tongue. The fungus thrives on the high glucose levels in the saliva of people with uncontrolled diabetes. Wearing dentures can also lead to fungal infections.
- Burning mouth and/or tongue: This condition is caused by the presence of thrush.
Read Also: Once A Week Shot For Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes And Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is caused by an infection that destroys the bone surrounding and supporting your teeth. This bone holds your teeth into your jawbone and allows you to chew comfortably. Bacteria and food debris called dental plaque contribute to gum disease.
If left on teeth and gums, plaque hardens to form calculus or tartar. The plaque and calculus irritate the gums around teeth so they become red, swollen and bleed. As gum disease progresses, this also affects the underlying bone which is eventually lost. Teeth become loose and may fall out by themselves or may need to be removed.
Gum disease is more common and more severe in people with suboptimal blood glucose levels. This is because they generally have lower resistance to infection and reduced healing capacity.
It is important to look after your oral health and control your blood glucose levels to prevent gum disease. Treating gum disease helps to improve blood glucose levels in people living with diabetes, and people with blood glucose levels in the target range respond very well to dental treatment.
Type 2 Diabetes And Your Oral Health
Type 2 diabetes can make it difficult for your body to control blood glucose levels and ward off bacterial infections that cause dental disease. People with diabetes are particularly susceptible to developing a dry mouth and a fungal infection called thrush.
Dry mouth can lead to soreness, cavities, missing teeth, periodontal disease, mouth ulcers, oral infections and dental bleeding.
Research findings indicate that oral health disease correlates highly with elevated blood glucose levels. The higher your hemoglobin A1C result, a test that measures the average blood glucose level over a three-month period, the higher your risk of developing periodontal disease is destined to be.
As you might expect, type 2 diabetics that emphasize blood glucose level control, personal dental hygiene and regular professional dental care are more likely to avoid oral health problems.
Read Also: Is Equal Good For Diabetics