Sodiumglucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: A Case Study In Translational Research
Diabetes
Amber L. Beitelshees, Bruce R. Leslie, Simeon I. Taylor SodiumGlucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: A Case Study in Translational Research. Diabetes 1 June 2019 68 : 11091120.
Sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are the most recently approved class of diabetes drugs. Unlike other agents, SGLT2 inhibitors act on the kidney to promote urinary glucose excretion. SGLT2 inhibitors provide multiple benefits, including decreased HbA1c, body weight, and blood pressure. These drugs have received special attention because they decrease the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and slow progression of diabetic kidney disease . Balanced against these impressive benefits, the U.S. Food and Drug Administrationapproved prescribing information describes a long list of side effects: genitourinary infections, ketoacidosis, bone fractures, amputations, acute kidney injury, perineal necrotizing fasciitis, and hyperkalemia. This review provides a physiological perspective to understanding the multiple actions of these drugs complemented by a clinical perspective toward balancing benefits and risks.
Who Should Take An Sglt2 Inhibitor
Your doctor might suggest you try one of these kinds of SGLT2 inhibitors:
These drugs are pills that you generally take once a day before your first meal.
Before you try an SGLT2 inhibitor, your doctor will likely suggest you make changes in your lifestyle — like diet and exercise — as well as take a medication such as metformin.
Because SGLT2 inhibitors are a newer medication, there is limited information about their long-term safety. And they’re only able to lower blood sugar by a small amount, compared with other medications.
Your doctor might consider an SGLT2 inhibitor if:
- You already take several medications and your blood sugar is still not well-controlled
- There’s a medical reason you can’t take other diabetes medications
- You’re at risk for getting dangerously low blood sugar
The drugs can be an option if you’re uncomfortable with giving yourself insulin shots. Your doctor might also suggest them if you need to lose weight or lower your blood pressure.
Genitourinary And Perineal Infections
SGLT2 inhibitors increase glucose concentrations in urine, which creates a rich culture medium for bacteria, thereby increasing the risk of urinary tract infections . Glucosuria indirectly increases glucose concentrations on genital skin, which increases the risk of external genital infections, especially in women . While many SGLT2 inhibitorinduced genitourinary infections are minor and readily treated, infections can be recurrent and may exert a substantial adverse effect on quality of life. Indeed, mycotic genital infections are reported to affect as many as 510% of women with type 2 diabetes receiving SGLT2 inhibitors. Furthermore, the FDA has warned that some patients experience serious urosepsis or potentially life-threatening necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum . Fortunately, these serious infections are rare.
You May Like: Can Type 1 Diabetes Be Cured Permanently
Essential Effects Of Sglt2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 is the major transporter responsible for the reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation, is characterized by low affinity, high volume, as well as is predominantly expressed in the proximal tubules . By inhibiting SGLT2, SGLT2 inhibitors lower renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and reduce the renal threshold for glucose, thereby increasing urinary glucose excretion . This reduces HbA1c by approximately 0.61.0% . SGLT2 inhibitors increase sodium delivery to distal tubules through blocking SGLT2-dependent glucose and sodium reabsorption, which is thought to increase tube-ball feedback and decrease intraglomerular pressure. This may affect a variety of physiological functions, comprising reducing cardiac preload and afterload and downregulating sympathetic nerve activity . Metabolism is shifted to gluconeogenesis and ketosis, which are thought to have protective effects on the heart and kidneys . SGLT2 inhibitors can reduce glucotoxicity in renal tubular cells by reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation, and also reduce renal hypoxia by reducing tubular energy and oxygen demand .
Table 1 Clinical effects and risks of SGLT2 inhibitors
Reduction In Blood Pressure
Recent meta-analyses of clinical research that monitored ambulatory blood pressure show that SGLT2i therapy leads to a decline in systolic and diastolic blood pressure , over study durations of 412 weeks. The decrease in blood pressure is greater during the daytime than during the night , and the effect does not vanish with more prolonged therapy . The combined effects of SGLT2i on osmotic diuresis and natriuresis are postulated to play a major role in blood pressure lowering , although the effect of SGLT2i on the sympathetic nervous system may also contribute to the reduction in blood pressure . Interestingly, the antihypertensive effect remains unchanged regardless of the dose of SGLT2i , also indicating little correlation between the dose and the cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2i, as mentioned above. The effect of SGLT2i on blood pressure may also be independent of renal function and glycemic control .
Although SGLT2i reduce plasma volume and blood pressure, heart rate is not increased , probably implying that SGLT2i decrease the preload and afterload, with cardiac output maintained, or inhibit sympathetic nervous activity.
You May Like: Can You Get A Cdl With Diabetes
Sodiumglucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors And The Short
Diabetes Care
Devin Abrahami, Helen Tesfaye, Hui Yin, Seanna Vine, Blánaid Hicks, Oriana H.Y. Yu, Lysanne Campeau, Robert W. Platt, Sebastian Schneeweiss, Elisabetta Patorno, Laurent Azoulay SodiumGlucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and the Short-term Risk of Bladder Cancer: An International Multisite Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 1 December 2022 45 : 29072917.
To determine whether sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, compared with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, are associated with an increased risk of early bladder cancer events.
We conducted a multisite, population-based, new-user, active comparator cohort study using the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink, Medicare fee-for-service, Optums de-identifed Clinformatics Data Mart Database , and MarketScan Health databases from January 2013 through December 2020. We assembled two cohorts of adults with type 2 diabetes initiating 1) SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1RAs and 2) SGLT2 inhibitors or DPP-4 inhibitors. Cox proportional hazards models were fit to estimate hazard ratios and 95% CIs of incident bladder cancer. The models were weighted using propensity score fine stratification. Site-specific HRs were pooled using random-effects models.
Sglt2i Use And Its Guideline
In Australia, the Therapeutic and Goods Administration , has currently approved two SGLT2i use in Australia: dapagliflozin and empagliflozin . Canagliflozin was delisted from the Pharmaceutical Benefit Scheme in 2015 due to pricing issue . The use of SGLT2i is recommended to combine with metformin in treating T2DM patients, as well as considered use in diabetic patients with cardiovascular diseases or at least two cardiovascular risk factors . SGLT2i has the greatest therapeutic effect in those with preserved renal function, with declining efficacy as Glomerular Filtration Rate decreases .
In the United States of America, the Food and Drug Administration has authorised the use of four SGLT2 inhibitors including canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin and ertugliflozin in treating T2DM patients. Recent guidelines by American Diabetes Association state that patients with high-risk or pre-existing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, or pre-existing kidney disease, or heart failure, we recommended SGLT2i as part of the glucose-reducing regimen irrespective of HbA1c control .
In the United Kingdom and the European Union, SGLT2 inhibitors are approved as an add-on therapy for patients having high blood glucose levels despite being on metformin and insulin. They are, however, not recommended to be prescribed for patients with CKD due to decreased efficacy .
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Diabetes 2
Funding Support And Author Disclosures
Dr Echouffo-Tcheugui was supported by National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant K23 HL153774. Dr Selvin was supported by National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant K24 HL152440. Dr Selvin has received payments from Wolters Kluwer for chapters and laboratory monographs in UpToDate on measurements of glycemic control and screening tests for type 2 diabetes.
-
Virani S.S., Alonso A., Aparicio H.J., et al.”Heart disease and stroke statistics2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association”. Circulation2021 143:e254-e743.
Sglt2 Inhibitors’ Role Of Primary Prevention Beyond Diabetes
Apart from well-documented benefit in diabetic patients as a monotherapy or add-on therapy, more recent evidence demonstrated that SGLT2i reduced major adverse cardiovascular events and hospitalisation for heart failure . SGLT2i showed benefits on delaying the onset and worsening of renal complications by lowering serum creatinine, reducing albuminuria, and decreasing mortality associated with renal disease . The cardiovascular and renal benefits seem to be unrelated to glycaemic control, making SGLT2i the most recommended class of medications for diabetic patients with significant cardiovascular or renal risks. These significant findings would postulate the potential primary preventive benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in terms of cardiovascular outcomes. This postulation has been substantiated in a recent review with Metformin, which has been showed to have potential primary preventive role in reducing cardiovascular events in the healthy and non-diabetic elderly . In non-diabetes patients with heart failure, SGLT2i has shown positive impact on weight and blood pressure .
Taken together, evidence is mounting for reviewing the literature of SGLT2i use in both diabetic and non-diabetic population , so as to substantiate our postulation of its potential primary preventive role in reducing events in healthy adults.
Table 2. Summary of SGLT2i preventive effects in DM and Non-DM patients.
Also Check: Sell Unused Diabetic Test Strips
Glycemic Control And Attenuation Of Glucotoxicity
Clinical studies in patients with T2DM have suggested that SGLT2i, as compared with placebo, decrease HbA1c by 0.61.0% in the presence of different background therapies . Although it remains controversial whether SGLT2i can be combined with insulin to treat type 1 diabetes mellitus because of safety issues, recent meta-analyses of clinical trials have demonstrated a reduction in HbA1c levels of approximately 0.4% in patients with T1DM . The antihyperglycemic effect of SGLT2i depends on urinary glucose excretion and, in patients with CKD, the effect is thus diminished as eGFR decreases . In the CREDENCE trial, the blood glucose lowering effect weakened over time, whereas the cardiovascular benefits did not , indicating that glycemic control does not account for the cardiorenal benefits of SGLT2i.
Because urinary glucose levels are elevated, the most common adverse event of SGLT2i is genital infections, with a higher incidence in females than in males . SGLT2i generally do not lead to hypoglycemia , unless combined with drugs that cause hypoglycemia, such as sulfonylureas .
Sglt2is Demonstrate Profound Impact On Heart Failure: Is The Restoration Of Anabolic/catabolic Cycling A Novel Path To Treatment Of Alzheimer’s Disease
Gluconeogenesis/ketogenesis is activated to maintain critical circulating glucose and ketone levels to ensure adequate fuel availability for the brain. This ultimately requires increased catabolism of circulating, gluconeogenic AAs to supply carbon for glucose production, as well as increased FAO to supply the ATP required for gluconeogenesis. Acetyl-CoA formed as a result of increased FAO directly contributes to ketone body formation through ketogenesis, an effect observed in both diabetic and non-diabetic subjects treated with an SGLT2i . Increased ketogenesis indirectly indicates activation of gluconeogenesis as ketogenesis occurs as a result of competition for oxaloacetate carbons between gluconeogenesis and acetyl-CoA entry into the Krebs cycle . Importantly, these alterations also take place in non-diabetic patients as exemplified by the DAPA-HF study , where there was no observed effect on circulating glucose levels as EGP fully compensated for the urine glucose loss.
Don’t Miss: Can Walking Lower Blood Sugar
Eligibility And Response To Sodium
Editorial Comment
Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Welch Prevention Center for Prevention, Epidemiology and Clinical Research Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Welch Prevention Center for Prevention, Epidemiology and Clinical Research Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 are the transporter molecules available in the proximal tubule. The majority of glucose reabsorption by the kidneys is influenced with the activity of SGLT2 inhibitors.91 One of the potential treatment options for the management of T2DM is SGLT2 inhibitor. A natural agent, phlorizin, inhibited SGLT1 and SGLT2 nonselectively,92 reversed insulin resistance, and normalized the concentration of plasma glucose in a diabetic animal model, and thus the SGLT2 inhibitors caught the attention of researchers.93 Phlorizin is already proven as SGLT2 inhibitor. But, this agent could not be a drug candidate due to poor absorption after oral administration, and the formation of phloretin by metabolism. Phloretin is a GLUT1 inhibitor, which may cause diarrhoea and nausea.94 Thus several SGLT2 inhibitors have been synthesized whose basic structures are related to phlorizin to overwhelm the limitations of phlorizin. These SGLT2 inhibitors are in clinical development for the treatment of T2DM.
Efficacy
Safety
Shylaja Srinivasan, … Kathleen M. Giacomini, in, 2018
Also Check: What Is Worse Diabetes 1 Or Diabetes 2
Reductions In Bp And Weight
Several RCTs of SGLT2 inhibitors have evaluated changes in systolic BP and weight as secondary endpoints. In RCTs that compared SGLT2 inhibitors with placebo, SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced SBP by approximately 3 to 5 mmHg and weight by roughly 4 to 6 pounds.5-7 Positive effects on weight and BP also were seen in RCTs comparing SGLT2 inhibitors with other antidiabetic agents.8
The BP-lowering effect is most likely due to osmotic diuresis, which is believed to contribute to the initial weight loss as well. Gradual weight loss is thought to be caused by a reduction in adipose tissue as well as calorie loss through glycosuria.8 These additional benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors are theorized to contribute to positive CV outcomes accordingly, a number of trials are investigating the CV benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors.
Amelioration Of Endothelial Dysfunction And Vascular Stiffness
Arterial stiffness is strongly associated with hypertension, cardiovascular events, HF, and death , and endothelial dysfunction plays a vital role in the development of coronary artery disease and HF . Many clinical studies have shown that short-term therapy with SGLT2i mitigates aortic stiffness and improves endothelial function. One study , however, did not show such benefits, presumably because of differences in design and settings between this and the other studies. A study investigating the effects of long-term treatment is in progress and should further confirm the vascular benefits .
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Glucose Levels
Who Are Sglt2 Inhibitors Suitable For
SGLT2 inhibitors may be suitable for people with type 2 diabetes that have high blood glucose levels despite being on a medication regimen such as metformin and insulin.
SGLT2 inhibitors are not recommended for prescribing to people with kidney disease as kidney disease prevents the drug from working sufficiently well.
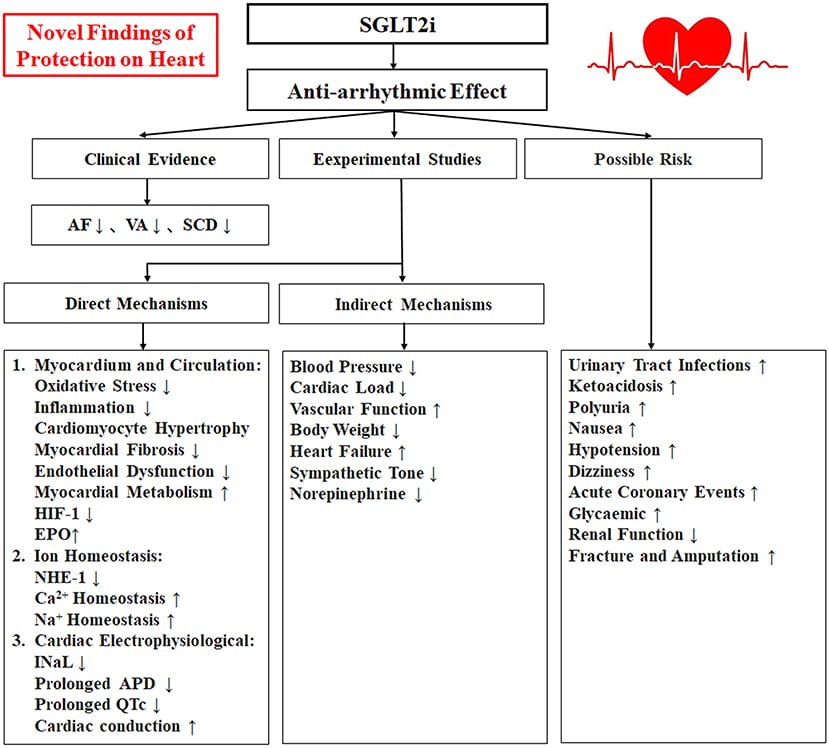
Cardiovascular Protection Mechanisms Of Sglt2i
The cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2i are mediated by multiple direct and indirect mechanisms that are interwoven and interactional . These mechanisms improve many aspects of the cardiovascular system, including hemodynamics, metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation.
Fig. 2
Cardiovascular protection mechanisms of SGLT2i. SGLT2i directly increase natriuresis and glycosuria, leading to a spectrum of secondary beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. Inhibition of the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger and protection of renal function mediated by SGLT2i may also, to some extent, play a beneficial role. These effects jointly contribute to the cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2i, especially the reduced risk of hospitalization for heart failure
You May Like: Why Is Keto Diet Bad For Diabetics
Sglt2i Safety And Adverse Events
There are numerous reports of potential safety issues associated with the use of SGLT2i including the rare but serious adverse events of diabetic ketoacidosis and necrotising fasciitis of the perineum. The report regarding the possible heightened risk of lower limb amputation and fracture with SGLT2i is conflicting.
Genital Infection Or Urinary Tract Infection
Both retrospective studies and meta-analyses have indicated that SGLT-2 inhibitors cause genital infections at a higher risk than other antidiabetic drugs . Safety analysis indicated a continued increase in the risk of genital infections associated with SGLT-2 inhibitors .
Genital fungal infections adverse events have been associated with higher rates of canagliflozin, with a minority leading to treatment discontinuation . Empagliflozin has a higher risk of genital infection or urinary tract infection than placebo, metformin, or sitagliptin . Increased rates of genital infections were more commonly reported in patients receiving empagliflozin in EMPA-REG OUTCOME and EMPEROR-Reduced trials . Common adverse reactions commonly reported with dapagliflozin in DURATION-8 included urinary tract infections . Genital infections leading to treatment discontinuation or considered serious adverse events in DECLARETIMI 58 were more common in the dapagliflozin group . In VERTIS MONO, the incidence of female genital fungal infections was notably higher in the ertugliflozin group than in the placebo or metformin group. In men, the 15 mg group was significantly higher compared with placebo/metformin . In VERTIS SITA2, compared with placebo , female and male subjects receiving ertugliflozin had a higher incidence of genital fungal infections .
You May Like: Most Accurate Blood Sugar Monitor
Sglt2 Inhibitors For Diabetes
SGLT2 inhibitors are called gliflozins. They lead to a reduction in blood glucose levels, and therefore have potential use in the treatment of type II diabetes. Gliflozins enhance glycemic control as well as reduce body weight and systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The gliflozins canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin may lead to euglycemic ketoacidosis. Other side effects of gliflozins include increased risk of Fournier gangrene and of genital infections such as candidal vulvovaginitis.
| Normal |
| All tests and analysis from |
Model organisms have been used in the study of SLC5A2 function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called Slc5a2tm1aWtsi was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program â a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disease to interested scientists. Male and female animals underwent a standardized phenotypic screen to determine the effects of deletion. Twenty-two tests were carried out on homozygous mutant mice and one significant abnormality was observed: males displayed increased drinking behaviour.