Predictors And Role Of Metabolic Control
Dont Miss: How Lower Your Blood Sugar Fast
Treatment For Reducing The Severity Of Hypoglycemia
If the case of hypoglycemia is severe, there are a few treatment methods which can be employed:
- Feeding the patient high-calorie foods such as fruit juice, sugar water, glucose tablet can help. In total, there should be approximately fifteen grams of carbohydrates. The blood sugar should normalise within fifteen minutes of eating the carbs.
- In case the patient cannot eat or drink, visit a doctor at the earliest.
- During labour and delivery, it is vital to monitor blood sugar levels.
- In rare cases, tumours causing hormonal imbalance will need to be removed during the pregnancy.
Monogenic Diabetes In Pregnancy
Since pregnancy may be the first time in their lives that women undergo glucose screening, monogenic diabetes may be picked up for the first time in pregnancy. Monogenic diabetes first diagnosed in pregnancy should be suspected in the women with GDM who lack risk factors for GDM and type 1 diabetes and have no autoantibodies . A detailed family history can be very helpful in determining the likely type of monogenic diabetes. This is important because the type of monogenic diabetes influences fetal risks and management considerations. The most common forms of monogenic diabetes in Canada are maturity onset diabetes of the young 2 or MODY 3 . A history of family members with longstanding isolated elevated FBG with mild A1C elevations that do not progress to frank diabetes over a long duration is suggestive of MODY 2. During pregnancy, the usual phenotype for MODY 2 of isolated elevated FBG is not always seen, even though this phenotype may be present outside of pregnancy in the same woman . Fetal carriers of GCK mutations do not usually have macrosomia. Fetuses without the GCK mutation of mothers with GCK mutation are at increased risk of macrosomia. The best way to manage women with GCK mutation during pregnancy has yet to be established, but regular fetal growth assessment can aid in the establishment of appropriate glucose targets during pregnancy for women with documented or strongly suspected GCK mutations.
You May Like: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
About High And Low Blood Sugar
High blood sugar High blood sugar may result if there is too much sugar in your blood. To maintain a healthy pregnancy, blood sugars must be kept in a range between 60-120 mg/dl. Keeping your blood sugars within normal limits will help you prevent problems for you and your unborn baby.
How will I feel if my blood sugars are high?Signs and symptoms:
- Urinating often
If your blood sugar is not treated, you may get very sick with signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis. Signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis are similar to high blood sugar. These signs and symptoms are: feeling extremely thirsty, a need to empty your bladder often, dry skin, hunger, blurred vision, feeling drowsy and wounds that heal slowly. There is an increased risk of fetal loss with ketoacidosis and your baby end up with a lower IQ after birth.
Please notify your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
Low blood sugar Low blood sugar may result if you are taking medication to treat diabetes such as insulin if you forget to eat or exercise before eating or exercise more than usual.
How can I get low blood sugar?Causes:
- Not enough food or snack
- Skipping meals or snacks
How will I feel when I have low blood sugar?Signs and symptoms:
- Numbness or tingling around the mouth
What should I do if my blood sugar might be low?
The following foods have about 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates:
Donât Miss: Medicine From Canada For Diabetes
How Is Gestational Diabetes Treated

Fortunately, you can ward off the potential risks associated with diabetes in pregnancy by monitoring your blood sugar levels.
If youre diagnosed with GDM, doctors and researchers recommend the following:
- Monitor your blood sugar level several times a day. Check first thing in the morning to get your fasting rate and then an hour after you eat each meal to make sure your blood sugar stays in a healthy range . Most doctors recommend buying a diabetes kit, which includes needles to prick your finger and a little machine that reads your blood sugar. Its the most accurate way to tell how your body is processing various foods.
- Meet with a registered dietitian. He or she can help you review healthy food options and make a meal plan. Many women stick to their gestational diabetes eating style long after birth because itâs rich in nutrients and designed to keep your blood sugar stable.
- Keep a food log. After each meal, write down what you ate along with your blood glucose number. This helps you to better understand which foods are spiking your glucose levels so you can make adjustments going forward.
- Get moving. Go for a walk or take the stairs after a meal to lower your glucose levels.
Diet and exercise are often enough to control gestational diabetes but if they dont, your doctor may suggest that you take supplementary insulin to control it.
Supplementary insulin can be given in shots or through the oral drug glyburide .
Read Also: What Is A Diabetic Eye Doctor Called
What Are The Signs And Symptoms
Low blood sugar levels can cause many different symptoms. For starters, most women report feeling lightheaded, dizzy or even disorientated.
Some may also experience cold flashes, shakiness, and impaired gait. In some instances, unusual sweating may also occur spontaneously and for no apparent reason.
Some signs of low blood sugar can be challenging to connect to the condition as they may appear harmless or self-explanatory.
Dry lips and mouth is one such example. Women may also feel abnormal levels of thirst, even after drinking water.
Excessive hunger can also be apparent. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Either hyperglycemia too high or hypoglycemia too low blood sugar during pregnancy is dangerous both for mother and her baby. If left untreated, both conditions can be harmful and increase the risk of some pregnancy complications.
Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are more likely to occur in pregnant women with gestational diabetes or women who already have diabetes before pregnancy. Even sometimes both conditions also can occur in pregnant women without diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Don’t Miss: 1000 Calorie Diabetic Diet Plan
Signs And Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
As sugar is the source of energy for many of the bodys metabolic processes, low blood sugar will cause several symptoms to manifest. Some of them include:
- Weakness, tiredness, and fatigue can make you exhausted and cranky.
- It becomes harder to think with clarity.
- The body begins to sweat and shake uncontrollably often.
- You might experience irregularity or an increase in your heart rate.
- Your vision might become blurry and unclear.
- Tired even after a good nights sleep
- Difficulty in waking up in the morning
What Does It Mean To Have Low Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the bodys main source of energy. The body gets glucose primarily by metabolizing the carbohydrates in food. The hormone insulin helps move glucose out of the bloodstream and into the cells, where it is used for energy.
But people with diabetes either dont produce enough insulin or cant use it effectively, according to the Mayo Clinic. Without sufficient insulin action, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, causing high blood sugar. As a result, many people with diabetes need to take medications to bring their blood sugar back to a healthy level. But taking too much of this medication can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low.
Read Also: Signs Of Blood Sugar Too High
What Causes Low Blood Sugar Pregnancy
This condition is due to insulin resistance, hormonal changes, and the increased demands of pregnancy on the body. Gestational diabetes can also cause low blood sugar, particularly in women who take diabetes medication or who do not eat enough. An estimated 9.2 percent of pregnant women experience gestational diabetes.
The Dl On Diabetes And Hypoglycemia
Having type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes increases your chances of hypoglycemia, compared to someone who is pregnant but not diabetic. This is because your already fluctuating insulin levels have a new factor to deal with: pregnancy hormones.
Even if you arent taking medication for your diabetes, you may still experience hypoglycemic episodes. For this reason, you should eat a balanced diet and carefully monitor your blood sugar throughout your pregnancy.
Signs of hypoglycemia during pregnancy are similar to what a non-pregnant person with low blood sugar may experience . Symptoms may include:
- tingling around the mouth
Once your blood sugar rises, these conditions typically disappear. The symptoms of severe hypoglycemia can be even more serious if left untreated. It can cause seizures, convulsions, or even loss of consciousness.
Read Also: How Can Diabetes Be Managed
After Youve Given Birth
Most peoples blood sugar levels return to normal after delivery, but your doctor will likely check them during the postpartum period. Thats because having gestational diabetes has some long-term effects, increasing your overall risk of:
- High blood pressure.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Type 2 diabetes.
In fact, about 10% of people with gestational diabetes have Type 2 diabetes without knowing it, and about half of people with gestational diabetes will have Type 2 diabetes in 10 years.
That means its especially important for your primary care physician to monitor your blood sugars and for you to try your best to take control of your health, Dr. Zanotti says. Being as healthy as you possibly can be will go a long way toward helping reduce your risk.
How To Treat Someone Who’s Unconscious Or Very Sleepy
Follow these steps:
They may need to go to hospital if they’re being sick , or their blood sugar level drops again.
Tell your diabetes care team if you ever have a severe hypo that caused you to lose consciousness.
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Cause Depression
Who Is More Prone To Hypoglycemia
Pregnant women who are most prone to hypoglycemia in the following conditions:
- A pregnant woman is more prone to hypoglycemia during the end of the first trimester, especially between 8 and 16 weeks of pregnancy.
- If you frequently fall sick during pregnancy, it can lead to hypoglycemia.
- A history of low blood sugar or hypoglycemic attacks can also lead to hypoglycemia.
How To Treat A Low Blood Sugar Level Yourself
Follow these steps if your blood sugar level is less than 3.5mmol/L or you have hypo symptoms:
You do not usually need to get medical help once you’re feeling better if you only have a few hypos.
But tell your diabetes team if you keep having hypos or if you stop having symptoms when your blood sugar level is low.
Also Check: Type 1 Diabetes And Premature Ejaculation
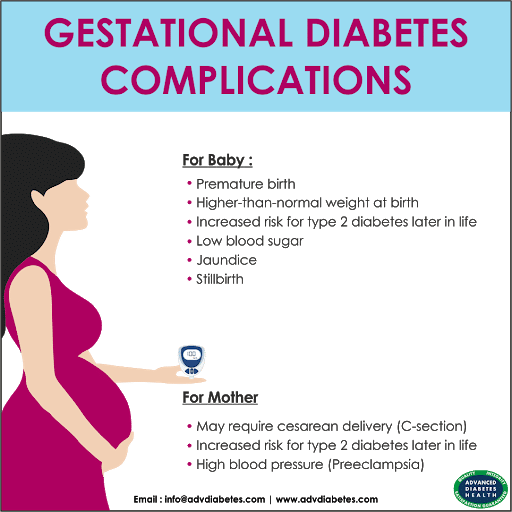
What Are The Risks Of Having Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes can cause problems for both you and your baby.
When your bodys insulin supply cant keep up, extra glucose stays in your blood, and your baby receives more sugar than it needs, which is then stored in their body as fat, Dr. Chapa explains.
Possible outcomes include:
- Higher chance of a cesarean delivery, also known as a C-section.
- Increased risk of preeclampsia, a serious blood pressure condition.
- Likelihood of delivering a larger-than-average baby .
- Slightly higher risk of fetal and neonatal death.
Babies born to mothers with diabetes need their blood sugar levels monitored after birth, Dr. Chapa adds. Low blood sugars can result in newborn babies from mothers with any type of diabetes, and this can lead to problems for your baby, including seizures.
Prevalence Of Hypoglycemia Diagnosis In Pregnancy
Hypoglycemia in pregnancy is very common. Having type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes increases your risk of hypoglycemia during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes occurs in up to 10% of pregnant women in the United States. Up to 71% women with type 1 diabetes develop hypoglycemia at some time during pregnancy.
Read Also: How Often Does Medicare Pay For Diabetic Foot Care
After You Have Low Blood Sugar
If your low blood sugar was mild , you can return to your normal activities once your blood sugar is back in its target range.
After you have low blood sugar, your early symptoms for low blood sugar are less noticeable for 48 to 72 hours. Be sure to check your blood sugar more often to keep it from getting too low again, especially before eating, physical activity, or driving a car.
If you used glucagon because of a severe low , immediately call your doctor for emergency medical treatment. If you have had lows several times close together , you should also tell you doctor. They may want to change your diabetes plan.
Some Of The Reasons Might Include:
You May Like: Can Low Blood Sugar Cause You To Blackout
Also Check: Blood Glucose Higher In Morning
Gestational Diabetes And Low Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
As well we know, gestational diabetes is a term used to call diabetes that only develops and occurs during pregnancy. In other words, this kind of diabetes will go away on its own after childbirth .
While some women with gestational diabetes dont need to take insulin replacement to help their blood glucose control, others do.
The decision of whether or not you should take insulin during pregnancy is closely dependent on how well you can control your blood glucose level. If it increases significantly , you may be asked to take insulin therapy. For more guidance about this issue, ask your doctor!
Placenta tends to produce more pregnancy hormones as the pregnancy progresses. And this can bring a greater effect for the performance of insulin produced by placenta in regulating the amount of glucose in the bloodstream.
In some pregnant women, the insulin sensitivity or the quantity of insulin produced by pancreas is not enough to control their blood sugar level as their pregnancy progresses. As a result, they may develop gestational diabetes!
To respond this situation, doctor may prescribe some glucose-lowering drugs or insulin replacement to help cope with the problem. The prescribed insulin dosage is usually based on the blood glucose log of each patient.
Here are some checklists to remember when youre going with your insulin therapy:
What Causes Diabetes During Pregnancy
Some women have diabetes before they get pregnant. This is called pregestational diabetes. Other women may get a type of diabetes that only happens in pregnancy. This is called gestational diabetes. Pregnancy can change how a womans body uses glucose. This can make diabetes worse, or lead to gestational diabetes.
During pregnancy, an organ called the placenta gives a growing baby nutrients and oxygen. The placenta also makes hormones. In late pregnancy, the hormones estrogen, cortisol, and human placental lactogen can block insulin. When insulin is blocked, its called insulin resistance. Glucose cant go into the bodys cells. The glucose stays in the blood and makes the blood sugar levels go up.
Read Also: What Is High Glucose Levels
Risk Factors For Developing Diabetes During Pregnancy
There is an increased risk of diabetes during pregnancy if:
- The woman is overweight
- There is a family history of diabetes
- The woman is from an ethnic minority
- There is previous history of the birth of a large baby
There is a routine antenatal test used to measure glucose levels in urine however it has been noted it is relatively unreliable for diagnosing diabetes.
Therefore blood sugar levels are checked between 26 and 30 weeks of gestation. This is done of two separate occasions using one of two tests, either the fasting glucose test or the random glucose test. In addition to this if there are any abnormal results of these tests or there is a family history of diabetes, or a woman is regarded as obese she will be offered a glucose tolerance test.
Often with gestational diabetes, the woman is advised to take a number of steps to change their diet and exercise habits to ensure the best possible pregnancy.
It is reportedly advisable to increase participation in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, yoga and pilates. In addition to this it is advisable to eat regular meals watching the amount of fat being eaten, remembering it is controlling the amount of fat not cutting it out of the diet completely.
Also reducing the amount of salt in the diet and ensuring that plenty of fruit and vegetables are included in the diet.