How And When To Ask For Support From Your Loved Ones
El Kawkgi says that having a chronic condition can take over many aspects of your life something that could cause you to feel isolated and overwhelmed. Asking for help when needed is a key part of living healthy with diabetes, he says. Recognizing signs that it is time to ask for help is the first step towards getting help.
If youre feeling signs of diabetes burnout, such as frustration and discouragement, you may need more help. This is a state of physical or emotional exhaustion that is caused by the continuous distress of having a chronic condition and the efforts to manage it, El Kawkgi says. When youre feeling burned out, you may feel less engaged with your treatment and less motivated to maintain a healthy lifestyle, he says. You may miss appointments, stop taking your medications, or even develop depression. El Kawkgi recommends talking to your healthcare provider and your support network of family and friends. Or you might benefit from sharing your experience with others who have diabetes.
If you arent close with friends or family, there are still plenty of ways to build a support network, El Kawkgi says. Healthcare providers can provide a listening ear and help point people with diabetes towards resources. These include the American Diabetes Associations nationwide Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support network and local support groups that include patients with diabetes, healthcare providers, and other members of the diabetes community.
When Should I Call My Doctor
Its important to monitor diabetes very closely if youre sick. Even a common cold can be dangerous if it interferes with your insulin and blood sugar levels. Make a sick day plan with your healthcare provider so you know how often to check your blood sugar and what medications to take.
Contact your provider right away if you experience:
- Confusion or memory loss.
- Nausea and vomiting for more than four hours.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
- Severe pain anywhere in your body.
- Trouble moving your arms or legs.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body doesnt make enough insulin and cant use sugar the way it should. Sugar, or glucose, builds up in your blood. High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications. But Type 2 diabetes is manageable. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help you manage your blood sugar. You may also need medication or insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you should monitor your blood sugar at home regularly and stay in close communication with your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/25/2021.
References
What Should A Type 2 Diabetes Meal Plan Include
Ask your healthcare provider or a nutritionist to recommend a meal plan thats right for you. In general, a Type 2 diabetes meal plans should include:
- Lean proteins: Proteins low in saturated fats include chicken, eggs and seafood. Plant-based proteins include tofu, nuts and beans.
- Minimally processed carbohydrates: Refined carbs like white bread, pasta and potatoes can cause your blood sugar to increase quickly. Choose carbs that cause a more gradual blood sugar increase such as whole grains like oatmeal, brown rice and whole-grain pasta.
- No added salt: Too much sodium, or salt, can increase your blood pressure. Lower your sodium by avoiding processed foods like those that come in cans or packages. Choose salt-free spices and use healthy oils instead of salad dressing.
- No added sugars: Avoid sugary foods and drinks, such as pies, cakes and soda. Choose water or unsweetened tea to drink.
- Non-starchy vegetables: These vegetables are lower in carbohydrates, so they dont cause blood sugar spikes. Examples include broccoli, carrots and cauliflower.
Don’t Miss: Insulin Pen Cost Without Insurance
Learn How To Live With Diabetes
It is common to feel overwhelmed, sad, or angry when you are living with diabetes. You may know the steps you should taketo stay healthy, but have trouble sticking with your plan over time. This section has tips on how to cope with your diabetes,eat well, and be active.
Cope with your diabetes.
- Stress can raise your blood sugar. Learn ways to lower your stress. Try deep breathing, gardening, taking a walk, meditating, working on your hobby, or listening to your favorite music.
- Ask for help if you feel down. A mental health counselor, support group, member of the clergy, friend, or family member who will listen to your concerns may help you feel better.
Eat well.
- Make a diabetes meal plan with help from your health care team.
- Choose foods that are lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Eat foods with more fiber, such as whole grain cereals, breads, crackers, rice, or pasta.
- Choose foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, bread and cereals, and low-fat or skim milk and cheese.
- Drink water instead of juice and regular soda.
- When eating a meal, fill half of your plate with fruits and vegetables, one quarter with a lean protein, such as beans, or chicken or turkey without the skin, and one quarter with a whole grain, such as brown rice or whole wheat pasta.
Be active.
Know what to do every day.
Talk to your health care team.
- Ask your doctor if you have any questions about your diabetes.
- Report any changes in your health.
How Diabetes Tech Can Help With Hypo Worry

If hypos are a worry, the healthcare team may mention use of a Flash Glucose Monitor or a Continuous Glucose Monitor . This is a small sensor worn on the back of the upper arm which sends blood sugar readings night and day to a mobile app. It connects to one or more mobile phones. So even if you don’t live with someone, you can keep an eye on their blood sugar levels. A CGM also has an alarm which can be set up to go off if someone’s blood sugar goes too low. This would send an alert to your mobile.
Glucose monitors don’t replace finger-prick testing, but you don’t have to do so many of them.
Guidelines on who may be eligible for a free CGM
Don’t Miss: Freestyle Libre Type 2 Diabetes
Focus 2 Your Lifestyle
What you think the lifestyle of a diabetic patient would be like? Some serious diet plans and always peeping into their medicines. But on the contrary, this does not apply to all.
All the diabetic patients can enjoy fully by maintaining good health and heart with keeping all the phases balance in life.
It addition, managing your diabetes with medical interventions, you must monitor the following aspects of your lifestyle carefully.
Nutrition
Sugar levels can be controlled at a good rate once the foods are going to contain the required nutritional balance.
Diet is an integral part, and following a healthy diet will keep you healthier in terms of your disease.
Not skipping your meals and having a regular intake of diabetes-friendly nutrient foods like salmon, beans, and egg yolks will go a long way.
Also, taking care of your health by reading the labels with attention to detail about what you about to consume a good habit to add to your lifestyle.
Make sure you avoid saturated, fatty, and processed foods. Eat greener and fresh food.
Tip: While our Type 2 Diabetes Food List provides a generalized food recommendation for type 2 diabetes, depending on your specific diabetes challenges, you may need to stick with Diabetic Gastroparesis Food List or Reactive Hypoglycemia Diet and Food List. The key is to stay away from Diabetes Food Myths and to follow our Tips if you experience blood sugar drops.
Exercise
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
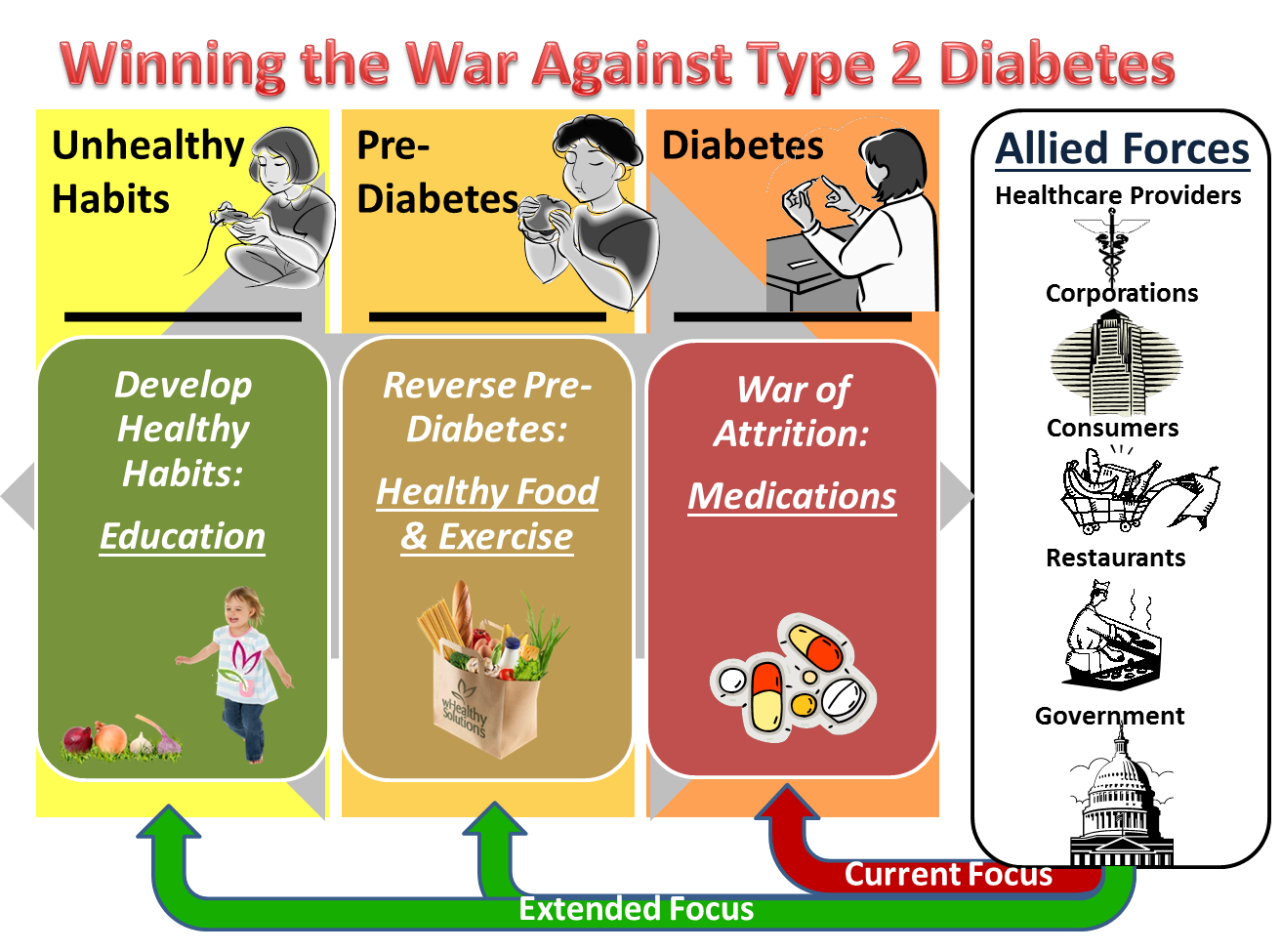
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that acts like a key to let blood sugar into the cells in your body for use as energy. If you have type 2 diabetes, cells dont respond normally to insulin this is called insulin resistance. Your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Eventually your pancreas cant keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
Recommended Reading: Can Diabetics Eat Activia Yogurt
You May Need Medicines
If diet and exercise are not enough, you may need to take medicine. It will help keep your blood sugar in a healthy range.
There are many diabetes medicines that work in different ways to help control your blood sugar. Many people with type 2 diabetes need to take more than one medicine to control their blood sugar. You may take medicines by mouth or as a shot . Certain diabetes medicines may not be safe if you are pregnant. So, talk to your doctor about your medicines if you’re thinking of becoming pregnant.
If medicines don’t help you control your blood sugar, you may need to take insulin. Insulin must be injected under the skin. You’ll receive special training to learn how to give yourself injections. Most people find that insulin injections are easier than they thought.
Focus 4 Diabetes Monitoring
Depending on the severity of diabetes, there is a possibility you might be observing some of the rare symptoms of diabetes, indicating your pancreas is not working effectively. Instead, it might be producing enough insulin, but that insulin might be struggling to convert into energy easily, so it might leave behind as high blood sugar.
Regardless of the scenario, a proper diabetes management care plan can be referred to by your medical and nursing team of experts will help in monitoring your blood sugar and A1C levels, which you make improvements to your lifestyle with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and mindfulness.
To prevent complications and hurdles that will lead to risking your health, it is highly recommended maintaining a chart of diabetic management so you can keep track of your blood glucose levels closer to the target range that diverges between 4 to 6 mmol/L.
From your doctors point of view, it is also important as a part of your nursing care plan, you daily monitor your sugar levels and keep a record of it. That will allow the doctor to identify how your body systems respond to prescribed tablets and whether they work for you in a way helping to convert your blood glucose into energy.
Tip: This is what we think about Smart Dario Glucose Meter.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
- Extreme thirst
Actions
- Monitor and record blood sugar levels and diabetes symptoms as you experience them.
Monitor any hypoglycemic events too.
Sign of hypoglycemia
- Running pulse
Read Also: What Foods Should A Diabetic Eat To Lose Weight
Favorite Resource For Diet Advice
Giving up some of the foods you once loved is arguably the biggest bummer about receiving a diabetes diagnosis. But with this Harvard-affiliated organizations expert diet guidance, you dont have to.
For more on “bad” foods you can eat in a diabetes diet, check out our article “5 ‘Bad’ Diabetes Foods You Can Enjoy in Moderation.”
Want to get involved? The IDF, which reaches 168 countries, makes it easy with their advocacy network page. Youll find different organizations that you can work with to help propel diabetes research, legislation, and awareness.
How To Learn More About Diabetes
- Take classes to learn more about living with diabetes. To find a class, check with your health care team, hospital, or area health clinic. You can also search online.
- Join a support group in-person or online to get peer support with managing your diabetes.
- Read about diabetes online. Go toNational Diabetes Education Program.
Recommended Reading: Best Insoles For Diabetic Neuropathy
The Importance Of Self
Diabetes can contribute to long-term damage or failure of different organs especially in the eyes, kidneys, heart, nerves and blood vessels, according to the American Diabetes Association. Therefore, self-care is necessary to limit potential organ damage, and it can reduce the likelihood of hospitalizations and ER visits for patients.
A study published in the Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders concluded that the following seven self-care practices help patients with diabetes avoid hospital visits and serious health complications:
- Healthy eating
- Developing healthy coping skills
- Practicing risk-reduction behaviors
The above strategies have been positively correlated with blood sugar control, fewer complications and overall improved of quality of life. However, there are several other recommendations that are often overlooked.
Dr. Tracie Kirkland, professor at the USC Suzanne Dworak-Peck School of Social Work Department of Nursing, regularly treats patients with diabetes in Houston, Texas, and suggests several clinically proven strategies that patients can practice at home after discussing with a provider.
Attending annual eye exams: Seeing an ophthalmologist regularly is part of maintaining good eye care and can help catch early signs of retinopathy a condition characterized by blurred vision or partial blindness caused by damage to blood vessels in the eye.
Causes And Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition that involves high blood glucose or blood sugar.
The pancreas makes insulin, a hormone that enables cells to take glucose from the bloodstream for energy. In type 2 diabetes, the cells do not respond normally to insulin, called insulin resistance. As a result, the pancreas makes more insulin in an attempt to get glucose inside the cells.
After some time, the pancreas cannot keep up, and blood sugar increases, which leads to prediabetes and diabetes.
Symptoms frequently develop over several years, including:
- tiredness
- numbness or tingling in hands or feet
- weight loss without trying
Read Also: Best Fruit Drinks For Diabetics
Look Out For The Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
If a person with diabetes experiences a major drop in his or her blood sugar from their insulin or diabetes medications, this can be dangerous and lead to life-threatening problems such as seizure or becoming unconscious . So its important for people around them to be aware of the signs of low blood sugar.
Watch out for fatigue, weakness, shakiness, pale skin, sweating, hunger, irritability, dizziness, and nervousness or anxiety.
They can get confused or seem to have brain fog, Dr. Kirkman says.
If you see this happening, try to encourage the person to test his or her blood sugar if they can. If needed, offer something to help boost blood sugar, like orange juice, bread or fruit . Make sure to stick around to see if the person is starting to feel better once blood sugar levels are back within normal range. If symptoms persist, especially if they become worse, seek immediate medical attention.
If you offer the person a snack or drink and they do not respond to your encouragement to eat or drink it, thats a sign that its probably beyond your ability to help them. If they look like they are going to pass out or have a seizure, its best to call 911, Dr. Kirkman says.
There is also an emergency injection or nasal spray called glucagon, which raises low blood sugar. Family members or roommates can be trained to use glucagon, but typically casual friends wouldnt know how to do this. When in doubt, call for help.
Blood Glucose Targets In The Elderly
Generally, blood glucose targets in the elderly are the same as other adults with diabetes:
- A1C: less than 7.0%
- Fasting blood glucose : 4.0 to 7.0 mmol/L
- Blood glucose two hours after eating a meal: 5.0 to 10.0 mmol/L
However, in elderly people who are described as frail, their blood glucose targets are different from the general population with diabetes. Frail elderly people are described as those who suffer from three or more of the following conditions:
In the frail elderly, blood glucose levels two hours before eating a meal are a better gauge of diabetes control than A1C or post-meal blood glucose levels. The recommended fasting blood glucose for the frail elderly is 5.0 to 12.0 mmol/L.
For more information about blood glucose, click here.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is An Insulin Shot
High Dose Steroids And Diabetes
Often, high dose corticosteroids such as dexamethasone are prescribed to relieve pain or pressure from tumours in people towards the end stages of life. Some corticosteroids can cause blood glucose levels to rise because they dont allow the body to use insulin properly.
When steroids are used short term, the need for treatment is less likely because as the dose of steroids reduce, so too will their effect on insulin resistance. If steroids are used in high doses or for a long period of time, it is important to monitor blood glucose levels. If an anomaly is detected, it should be reported to the GP and a corrective dose of insulin may be given if necessary. It is important to keep monitoring the levels over a short period of time as a random high can occur. The patients specialist diabetes team will supervise and check for this.
For people who require long-term steroids, an appropriate diabetes medication may be beneficial. The regime will depend on the persons needs and the dose of steroids being taken. If the steroid dose reduces, it may be necessary to review the insulin dose too. Remember that aiming for normal blood glucose levels can be unrealistic in people receiving end of life care as dietary intake varies or reduces.
Understanding Diabetes And Blood Sugar
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition characterized by hyperglycemia also known as high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is caused by the bodys inability to create or absorb the proper amount of insulin, a hormone that regulates the amount of sugar in the blood, which is called glucose.
There are three common forms of diabetes:
Type 1: Most often occurring children, whose bodies create little to no insulin, Type 1 diabetes forces people to rely on insulin injections that move the bodys sugar, or glucose, from the bloodstream to the cells. Only 5 percent of diabetes patients have Type 1.
Type 2: The most common form of diabetes has historically occurred in adults though in recent years an increase in pediatric diagnoses has alarmed health care providers. People with Type 2 diabetes have developed an insulin resistance, meaning the body does not absorb insulin easily. Their high blood sugar levels can go undetected for years if symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, headaches and fatigue arent reported early on.
Prediabetes: This condition indicates an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes during adulthood. Patients diagnosed with prediabetes have high blood sugar or polyuria . However, the symptoms of prediabetes can be easily confused with other health complications, so its critical for adults to get tested.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Erectile Dysfunction