How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
Continue Learning About Diabetes
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
What Should My Blood Sugar Be When I Wake Up
Checking your blood sugar first thing in the morning is important. In fact, fasting blood sugar readings really help you determine how to approach the rest of your day. You have to take steps considering how low or high your fasting blood sugar is, and understand how to set your morning target and what to do to achieve it. Let’s find out more about it.
Also Check: Type One Diabetes Cure Research
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
How To Manage After

Get medicine that works for you.The right insulin or medication program can make a big difference. In general, to cover after-meal spikes, those that kick in quickly and for a short time are a better choice than ones that work slowly over a long period. Your doctor can explain your options.
Keep blood sugar in check before meals. That way, even if it goes up after you eat, it won’t be so dramatic.
Watch what you eat. Limit sweets, white bread, rice, pasta, and potatoes. They tend to trigger post-meal spikes.
The type of fat you eat may play a role, as well. One study shows you may be able to curb blood sugar spikes after you eat if you skip foods with lots of butter and choose a meal made with a little olive oil instead.
Eat breakfast every morning. Even when you’re in a hurry to get out the door, don’t be tempted to skip it. A study shows that folks with diabetes who don’t eat breakfast get higher blood sugar spikes after lunch and dinner.
The ideal morning meal? It might just be one that’s packed with protein. A small study shows that when people ate a 500-calorie breakfast that was 35% protein, their post-meal blood sugar levels were lower than those who started their day with high-carb food. But check with your doctor to see what’s right for you.
Go for an after-dinner walk. It’s a healthy habit for everyone, but if you have diabetes, it’s also a good way to burn extra glucose from a meal.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: What Is The Average A1c For Type 2 Diabetes
Checking Your Blood Sugar
Your meals, medicine, and exercise all revolve around your blood sugar. So youâll need to test it regularly.
Your doctor will tell you how many times to do it each day. It’ll depend on the kind of diabetes you have and how much insulin or other medicine youâre taking.
If youâre taking insulin several times a day, you may need to do a test before each meal and before you go to bed.
If youâre taking long-acting insulin, you may only need to test before breakfast and before dinner.
If youâre taking other medicine but not insulin, you may not need a test every day.
Keep extra-close watch on your blood sugar if you do vigorous exercise. Physical activity can affect your level for hours even the next day. You may need to check your blood sugar before, during, and after each workout.
Show Sources
Joslin Diabetes Center: âDiabetes and Scheduling: Starting a Routine,â âOral Diabetes Medications Summary Chart.â
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âManaging Diabetes,â âDiabetes Diet, Eating, and Physical Activity.â
Kaiser Permanente: âWhat to Eat, How Much, and When,â âAction Plan for Healthy Eating.â
Mayo Clinic: âDiabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar,â âDiabetes,â âBlood sugar testing: Why, when and how.â
Food & Nutrition: âMeal Times and Diabetes: Whatâs the Connection?â
Medicare.gov: âYour Medicare Coverage: Nutrition therapy services .â
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Your blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are a measurement that show how much glucose you have in your blood. Glucose is a sugar that you get from food and drink. Your blood sugar levels go up and down throughout the day and for people living with diabetes these changes are larger and happen more often than in people who dont have diabetes.
You can check your sugar levels yourself by doing a finger-prick test, by using a flash glucose monitor or with a continuous glucose monitor . You can do this a number of times a day helping you keep an eye on your levels as you go about your life and help you work out what to eat and how much medication to take. Find out your ideal target range.
But not everyone with diabetes needs to check their levels like this. Youll need to if you take certain diabetes medication. Always talk to your healthcare team if youre not sure whether thats you theyll give you advice on whether to check them yourself and how often.
And theres also something called an HbA1c, which measures your average blood sugar level from the previous few months. Everyone with diabetes is entitled to this check.
High blood sugar levels increase your risk of developing serious complications. However you manage your diabetes, stay in the know about your blood sugar levels.
Also Check: How To Lower Fasting Glucose
How Long After Eating Does Blood Sugar Return To Normal
The blood sugar level falls back to a normal level around 1-2 hours after taking food. During this time digestion slows down and the sugar is absorbed by the tissue.
In diabetics, there can be a sudden spike in blood sugar after eating causing headache, dizziness and discomfort. This is called a post-prandial reaction. Normally, taking prescribed insulin medication can help mediate this problem.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Recommended Reading: Average Age Of Type 2 Diabetes
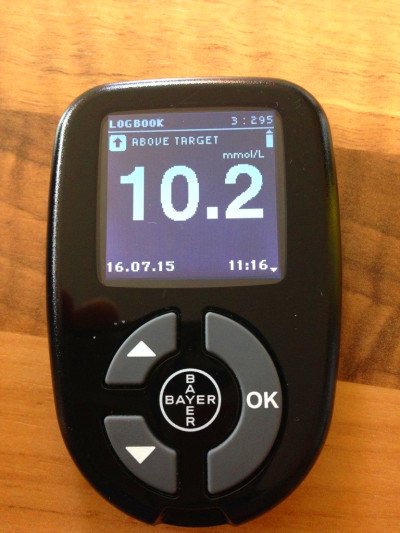
Blood Sugar Testing At Home
A person can test their blood sugar levels at home.
In most cases, doctors ask people to measure fasting blood sugar immediately upon waking and before they have anything to eat or drink. It may also be appropriate to test blood sugar before eating or 2 hours after a meal, which is when blood sugar returns to normal levels.
The right time to test depends on treatment goals and other factors. For example, most people with diabetes do not need to test between meals unless they are using a diabetes drug that can lower blood sugar. Other people may test between meals if they feel their sugar levels may be low.
Since people with type 1 diabetes do not make any insulin, they need to test their blood sugar levels several times a day so they can adjust their insulin doses.
A person will test blood sugar levels by:
- preparing the testing strip and glucose monitor to be ready for the blood sample
- using an alcohol swab to clean the testing area, which is usually the side of a fingertip
- lancing the testing area and bracing against a firm surface to help resist the impulse to pull away
- squeezing the testing area around the wound to maximize blood flow
- squeezing a drop of blood onto the test strip
- putting the strip into the monitor
- recording the time, blood sugar reading, and recent food intake in a log
Whats A Blood Sugar Spike And Why Do They Happen
Postprandial spikes are temporary high blood sugars that occur soon after eating. It is normal for the blood sugar to rise a small amount after eating, even in people who do not have diabetes. However, if the spike is too high, it can affect your quality of life today and contribute to serious health problems down the road.
The reason blood sugar spikes is a simple matter of timing. In a non-diabetic, consumption of carbohydrate results in two important reactions: the immediate release of insulin into the bloodstream, and production of a hormone called amylin which keeps food from reaching the intestines too quickly. In most cases, the after-meal blood sugar rise is barely noticeable.
However, in people with diabetes, the situation is like a baseball player with very slow reflexes batting against a pitcher who throws 98 mph fastballs: the timing is not good. Rapid-acting insulin that is injected at mealtimes takes approximately 15 minutes to start working, 60-90 minutes to peak, and four hours or more to finish working. And dont forget about the amylin hormone effect. In people with diabetes, amylin is either produced in insufficient amounts or not at all. As a result, food digests even faster than usual. The combination of slower insulin and faster food can cause blood sugar to rise absurdly high soon after eating. This is followed by a sharp drop once the mealtime insulin finally kicks in.
Don’t Miss: Best Vitamin C Supplement For Diabetics
Right Before Lunch Or Dinner
Checking your blood sugar before your next meal can tell you two things:
- How well your body and/or medication dosages handled your last meal
- How well your body and/or medication dosages handled your blood sugar in the last few hours without food being digested.
Keep in mind that some meals take longer to digest than others. High-fat meals that are also high in carbohydrates can take many hours to digest, affecting your blood sugar for many hours, too.
A high blood sugar level before lunch or dinner could suggest:
- What you ate or drank at your last meal was more than your body could handle on your current diabetes management regimen.
- Your body may need some extra help from a diabetes medication.
- Your current diabetes medications may need a change in dosage.
- Your current diabetes medication may not be the right fit for you.
- Its time to try a different type of diabetes medication.
- Your overall insulin production or insulin resistance level has changed and your body needs more support from a new or current medication.
A low blood sugar level before your next meal could suggest:
- Youre getting too much of a certain diabetes medication .
- Your insulin sensitivity or insulin production has improved, which means your medication dosages need to be adjusted by your healthcare team.
Talk to your healthcare team about making any adjustments to your diabetes regimen to help you achieve your blood sugar goals.
The Best Healthcare Options To Prevent Diabetes
Health care is expensive. Canada spent an estimated $253.5 billion in 2018, and as the cost of health care increases, so does the cost to you. Pre-existing medical conditions, family history, and BMI are all factors that increase the cost of health care. These factors also increase your risk of diabetes, so you must be covered.
Of course, as a Canadian, you are entitled to some free and subsidized health care, which is great. But many people opt for private healthcare and for diabetes prevention this can be very useful. If youâre shopping around for private healthcare, itâs important to choose the right package.
Basic health insurance will usually cover health care, medical services, and prescriptions, but they tend to lack customizations. If you opt for a premium/guaranteed health insurance you have the bonus of a custom plan based on your needs if you are worried about your risk of diabetes this is like gold dust.
Private healthcare plans can cover the cost of many expenses related to diabetes such as blood tests, blood sugar monitors, specialist referrals, hospital stays, and much more! The most important thing to note about private health care is that it covers costs for preventative care, not just treatment for diseases.
You May Like: How To Counter Low Blood Sugar
Recommended Reading: Low Carb Meal Plan For Diabetics Type 2
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
There are two types of blood sugar levels that may be measured. The first is the blood glucose level we get from doing finger prick blood glucose tests. These give us a reading of how high our levels are at that very point in time.
The second is the HbA1c reading, which gives a good idea of our average control over a period of 2 to 3 months. The target blood glucose levels vary a little bit depending on your type of diabetes and between adults and children.
Where possible, try to achieve levels of between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and under 8.5 mmol/L after meals. The target level for HbA1c is under 48 mmol/mol .
Research has shown that high blood glucose levels over time can lead to organ and circulation damage.
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous.
Your doctor may give you different targets. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets.
FREE blood glucose level chart
You May Like: How Much Sugar Should You Have On Keto
Low Blood Glucose Levels
Hypoglycaemia is when your blood glucose level below is too low . This can occur when on insulin injections or medications that make the pancreas produce more insulin. This is why it is important to know how your medication works. If unsure, ask your healthcare professional or Pharmacist how your medication works and if it could cause hypoglycaemia.
Signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
- Excessive sweating
- Change from normal behaviour e.g. unusually aggressive or tearful
Low blood glucose levels can be caused by:
- Delayed or missed meal/snack
- Eating less starchy food than usual
- Being more activity than usual
- Taking too much insulin or diabetes tablets
- Drinking too much alcohol or drinking alcohol without having starchy food
Treating a low blood glucose level
Treat immediately with 15-20grams of fast acting carbohydrate
- 170ml of Lucozade
- 200ml of smooth orange juice
- 4-5 GlucoTabs, 5-6 dextrose tablets or 4 jelly babies
- Non-diet fizzy drink Regularly check label of product since some manufactuerers are planning to reduce the sugar content of their drinks due to Soft Drinks Industry Levy
After 5-10 minutes if blood glucose level is still below 4 mmol/l, repeat one of the above. Once blood glucose is 4 mmol/l or higher then have something to eat such as:
- A slice of bread
- Two plain biscuits or crackers
- Or your usual meal if it is due.
If unconscious, nothing should be given by mouth and paramedics should be called.
Also Check: Healthy Sugar Levels For Diabetics
Everyday Health: Testing Too Soon After Eating
This is the kind of website that, on the surface, doesnt seem to have any credibility in the medical field at all! But they do have a Wellness Advisory Board that includes a number of MDs and PhDs.
Anyway, Im citing an article of theirs that was written by some lady who is not a doctor and peer-reviewed by another who is a doctor. So heres what they say:
Testing too soon after youve had a meal or a snack will give you results that are probably too high. The solution for better diabetes control: Test fasting blood sugar, and test every time before you eat. Wait two hours after eating to get the best reading.
Source: Everyday Health | 7 Blood Sugar Testing Mistakes to Avoid
Here is yet another source that says to wait 2 hours after eating before you check your glucose.
But heres the best part!
Wait two hours after eating to get the best reading.
The BEST reading? When it comes to goddam diabetes and glucose numbers, best generally means lowest. But I dont think thats what theyre saying.
Im gonna assume that by best they mean the result that most accurately reflects what effect a meal has had on your blood sugar.
That is what I have to ASSUME. Because they didnt say that specifically. Why? Who the f**k knows.
All right, so there you have it! Four different sources, three of which recommend testing glucose 2 hours after you eat, and one that punts the issue to your doctor.
To review:
For me, 2 hours is 2 long.