High Blood Sugar: 13 Reasons Your Glucose Levels Are Rising
May 2, 2021
Itâs a fact of life that blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day. These ups and downs depend on a handful of factors, like when you wake up, what you eat, the medications you take, and how you manage stress. So, some variation is normal, to the point that you might not even notice it.
Ignoring blood sugar level changes altogether, though, means youâre ignoring a valuable marker of your health. Especially if you start to have new or unfamiliar symptoms like fatigue, thirst, or brain fog . Learning these symptoms and their causes will give you the tools to better understand your own body, then take the right actions for better long-term metabolic health.
I Feel Fine So I Dont Need To Test My Levels
Zanini points out that having high blood glucose can come as a surprise to anyone. âIt’s possible they didn’t notice any symptoms or were simply feeling ‘more tired than usual,ââ she says. âIt’s easy to attribute being tired to many other things. . .so this is why regular physicals with your healthcare provider are important.â The bottom line? Listen to your body, take note of symptoms as they arise, and consider monitoring your continuous glucose values.
How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Smart Insulin Pen
What Is High Blood Glucose
People who do not have diabetes typically have fasting plasma blood glucose levels that run under 100 mg/dl.
Your physician will define for you what your target blood glucose should be identifying a blood glucose target that is as close to normal as possible that you can safely achieve given your overall medical health. In general, high blood glucose, also called ‘hyperglycemia’, is considered “high” when it is 160 mg/dl or above your individual blood glucose target. Be sure to ask your healthcare provider what he or she thinks is a safe target for you for blood glucose before and after meals.
If your blood glucose runs high for long periods of time, this can pose significant problems for your long-term increased risk of complications, such as eye disease, kidney disease, heart attacks and strokes and more. High blood glucose can pose health problems in the short-term as well. Your treatment plan may need adjustment if the blood glucose stays over 180 mg/dl for 3 days in a row. It is important to aim to keep your blood glucose under control and treat hyperglycemia when it occurs.
- Increased thirst
- Slow healing cuts and sores
- Unexplained weight loss
- Too little exercise or physical activity
- Skipped or not enough diabetes pills or insulin
- Insulin that has spoiled after being exposed to extreme heat or freezing cold
- Stress, illness, infection, injury or surgery
- A blood glucose meter that is not reading accurately
What Are High Blood Sugar Levels
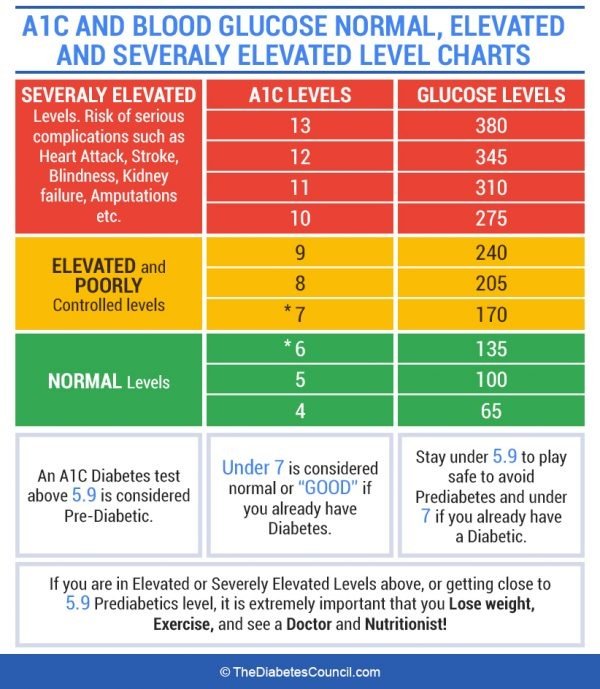
It is essential to address glucose levels in general. In persons without type 1 or type 2 diabetes, blood sugar levels generally range between 70 to 130 mg/dl.
It depends on the last time they ate a meal and the time of day. Normal blood glucose ranges in persons without any type of diabetes are:
- Fasting blood sugar in the morning before eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
- One hour after a meal 90 to 130 mg/dl
- Two hours after a meal 90 to 110 mg/dl
- Five or more hours after eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
In pregnant women, blood sugar levels tend to be lower. Harvard Health also confirms that a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 mg/dl after an eight-hour fast. Also, a person has diabetes if their blood sugar is 126 mg/dl or higher.
When it comes to hyperglycemia or high blood sugar, there are two kinds of problems. The first kind is fasting hyperglycemia, which is blood sugar higher than 130 mg/dl after not eating or drinking for eight hours.
The other kind is postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia, which happens when your blood sugar is higher than 180 mg/dl two hours after a meal. People without diabetes rarely have blood sugar higher than 140 mg/dl after a meal unless its a big one.
Recommended Reading: Is 162 Blood Sugar High
Low Blood Glucose: Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can occur when blood glucose drops below normal levels or drops too quickly. Your blood glucose level is too low if it is under 70 mg/dL.
Hypoglycemia can be caused by:
- A combination of these factors
- Being more active than usual
- Drinking alcohol
- Eating at the wrong time for the medications you take
- Skipping or not finishing meals or snacks
- Taking too much diabetes medication
You can have hypoglycemia without any symptoms. That makes it important to check your blood glucose levels regularly. When hypoglycemia does cause symptoms, they can include:
Causes Of High Blood Sugar
The leading causes of high blood sugar or hyperglycemia include:
Diet: Glucose comes from food, so what you are eating causes high blood sugar. Carbohydrates are the most common culprit as they are broken down into glucose very quickly in the body. High-sugar foods, high-fat foods, and processed foods also cause blood glucose spikes and should be replaced with healthier options.
Stress: When you are stressed, more stress hormones and chemicals are released, which drives blood sugar levels up too. If the stress is only temporary, this is not a serious issue, but if you experience chronic stress or an anxiety disorder, you may experience high blood sugar levels more often.
Metabolic Syndrome: These are a collection of conditions that occur at the same time and increase your risk for type 2 diabetes. High blood pressures, excess fat around the waist, and high cholesterol or triglycerides are examples of these conditions. When these occur in the body together, your risk for diabetes increases as does your blood sugar and the risk for potential complications.
Physical Inactivity: A lack of physical activity contributes to elevated blood sugar. When you are physically active each day, insulin works more efficiently, and your blood sugar can be maintained.
Read Also: Non Insulin Drugs For Diabetes
Postprandial Or Reactive Hyperglycemia
This type of hyperglycemia occurs after eating .
During this type of hyperglycemia, your liver doesn’t stop sugar production, as it normally would directly after a meal, and stores glucose as glycogen.
If your blood glucose level 1-2 hours after eating is above 180mg/dL, that signals postprandial or reactive hyperglycemia.
However, it’s not just people with diabetes who can develop hyperglycemia. Certain medications and illnesses can cause it, including beta blockers, steroids, and bulimia. This article will focus on hyperglycemia caused by diabetes.
Why Do Blood Sugars Matter In Diabetes
A key part of managing diabetes involves checking blood sugars, or glucose levels.
In type 1 diabetes , a persons pancreas does not produce the insulin they need. In type 2 diabetes , the body may not make or use insulin correctly anymore.
For either T1D or T2D, ensuring glucose levels stay as level as possible is the goal. Sometimes insulin or diabetes medications are used based on the type of diabetes and personal needs. Many factors affect glucose levels, including food, exercise, insulin, medications, stress, etc.
Glucose level targets may vary for everyone based on their unique needs.
You May Like: Glucerna Vs Boost For Diabetics
Yoga For Diabetes: Here Are 5 Asanas To Maintain Your Blood
Even though chia seeds are not something children will eat willingly, this is something that will be really beneficial for them. We can check out some interesting ways to include chia seeds in their diet. Healthy fats, vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants are abundant in chia seeds. According to one of the studies published in Diabetes Care, chia seeds can help lower blood sugar levels. Additionally, it lowers the risk of heart disease in type 2 diabetic individuals.
5. Yogurt
Consuming yogurt with live bacteria may aid in fighting off the disease. Additionally, a wonderful source of protein is yogurt. Live microorganisms known as probiotics aid in the defense against all types of harmful bacteria. By raising the quantity of virus-fighting cells, they also aid in the battle against the disease.
Pro tip: Diabetic children should avoid processed meats because they are high in fat and salt. Additionally, it is important for them to exercise at their home through body-weight exercises or yoga and practice breathing on a regular basis. Evidence suggests that nutritious foods can help to curb sugar spikes and improve insulin resistance which may eventually lead to less dependence on medications.
Disclaimer: Tips and suggestions mentioned in the article are for general information purposes only and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Please consult a doctor before starting any fitness regime or medical advice.
What Factors Affect Blood Sugar
You can guess that carbohydrate intake and insulin production are at least partly responsible for your blood sugar levels. But the list is much longer — almost every lifestyle choice you make can affect your blood sugar. Here’s just a partial list.
- Exercise can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to lower blood sugar for up to 48 hours.
- Alcohol intake increases insulin production, causing low blood sugar.
- Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar, because your body wants access to energy in order to escape what it perceives as a dangerous situation.
- Medications, especially statins and diuretics, can raise blood sugar. Statins are used to treat cholesterol, and diuretics for high blood pressure.
- Diet is a major player in blood sugar. Eating too many simple carbs at once can cause levels to skyrocket, while protein intake leads to a slower increase in blood sugar.
- Dehydration raises blood sugar, because with less water in your body the glucose concentration will be higher.
Other surprising factors can affect your blood sugar, like a sunburn or gum disease, so if you’re dealing with a blood sugar issue and can’t figure out what’s causing your spikes and dips, talk to a healthcare professional.
Don’t Miss: How To Increase Glucose Levels
Tests For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests. Youll probably be tested between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes , your doctor may test you earlier. Blood sugar thats higher than normal early in your pregnancy may indicate you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than gestational diabetes.
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
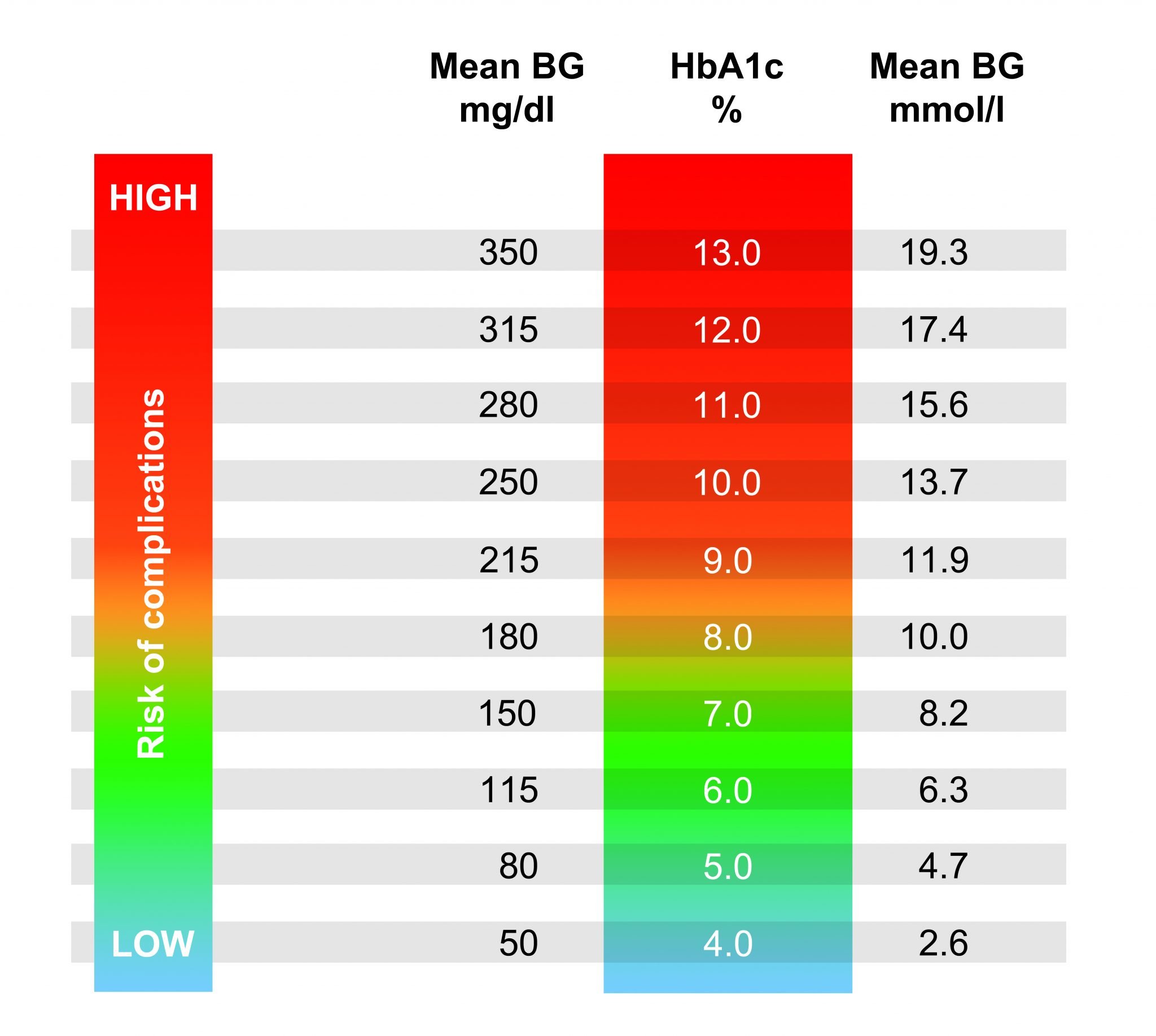
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
Recommended Reading: Can Urgent Care Treat Diabetes
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome : When Hyperglycemia Becomes Severe For People With Type 2 Diabetes
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome is very rare, but you should be aware of it and know how to handle it if it occurs.
HHNS is when your blood glucose level goes way too highyou become extremely hyperglycemic. HHNS affects people with type 2 diabetes.
HHNS is most likely to occur when you’re sick, and elderly people are most likely to develop it.
It starts when your blood glucose level starts to climb: when that happens, your body will try to get rid of all the excess glucose through frequent urination. That dehydrates your body, and you’ll become very thirsty.
Unfortunately, when you’re sick, it’s sometimes more difficult to rehydrate your body. For example, it might be difficult to keep fluids down.
When you don’t rehydrate your body, the blood glucose level continues to climb, and it can eventually go so high that it could send you into a coma.
To avoid hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome, you should keep close watch on your blood glucose level when you’re sick .
Talk to your health care professional about having a sick-day plan to follow that will help you avoid HHNS.
You should also be able to quickly recognize the signs and symptoms of HHNS, which include:
-
Extremely high blood glucose level
How Does High Blood Sugar Affect The Body
Monitoring your blood sugar is essential if you have diabetes. Symptoms will get worse if treatment is not provided, and serious health complications can arise as a result. The signs of high blood sugar to look for include fatigue, blurred vision, and headaches along with:
- Frequent urination and thirst: Excess sugar in the blood is passed through the kidneys and into urine. This draws more water into the urine which means more frequent urination. High glucose levels cause thirst even when you are drinking enough fluids.
- Weight loss: Elevated blood sugar levels over time can lead to unexplained weight loss as a result of cells not getting the glucose they need. As a result, they start burning fat instead.
- Numbness: High blood sugar can cause tingling and numbness in the extremities. It is important to note that this is a complication of long-term diabetes and uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
Don’t Miss: Good Snacks To Eat For Low Blood Sugar
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
This test involves the administration of a syrupy liquid after 8 hours of fasting. The liquid contains about 75 grams of glucose. Also, the blood glucose level is measured 2 hours after administration of this liquid.
- Normal: Values less than 140 ml/dL
- Prediabetes: Values between 140 ml/dL
- Diabetes: Values more than 200 mg/dL
Out of all these tests, any two values over 200 mg/dL need medical attention.
Blood Sugar Level Charts For Those With Diabetes
Normal blood sugar levels, for those with diabetes, will vary depending on someones age and the time of day. For example, when fasting, blood sugar levels are often in the target goal range. The type of food eaten will impact blood sugar levels in different ways. A meal with a lot of carbohydrates will raise blood sugar quicker than a meal that contains carbohydrates, protein, and fat . Blood sugar will rise after a meal, but will start to return to normal levels in several hours.
Lets take a look at what blood sugar levels should be, in those with diabetes, based on their age.
Don’t Miss: Normal Glucose Range For Diabetics
When To Go To The Er
High blood sugar can be very concerning because your body can start burning fat for energy instead of blood glucose.
This can cause conditions such as DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome . These conditions are medical emergencies and can be fatal if left untreated.
DKA is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes. Its rare in people with type 2 diabetes, but can occur.
Symptoms that can indicate you should go to the emergency room include:
- ketones in your urine, as diagnosed using a urine dipstick test
High blood sugar levels can cause a fluid imbalance in the body and can cause the blood to become acidic in a manner that doesnt support life.
Medical treatments for these conditions include administering intravenous insulin on a continuous basis and IV fluids to correct dehydration.
Summary
High blood sugar can become a medical emergency. Go to the ER if you suspect DKA or HHS.
If Your Child Is Suffering From Diabetes Help Them Become Aware Of What Foods They Need To Eat To Manage Their Blood Sugar Levels
India TV Lifestyle Desk Follow us on
Diabetes is a very common problem among adults, but its prevalence among children has witnessed a rise in recent times. Lifestyle choices and poor eating patterns, this condition has been observed to increase in children and teenagers. As a result, those who have diabetes need to watch what they consume very carefully. This World Diabetes Day, lets take a look at how to manage blood sugar levels in children and help them beat Type 2 diabetes.
Foods high in fiber can help reduce inflammation in the body, boost the immune system, and regulate blood sugar levels. A recent study found that drinking a small amount of whey protein before meals can help people with type 2 diabetes control their blood sugar levels.
Also Check: What Is The Correct Reading For Diabetes
Symptoms Of Blood Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of blood sugar levels differ depending on if it is high or low. To determine which way the blood sugar have moved, the symptoms for each are typically:
| High Blood Sugar Symptoms | |
| Slow healing wounds | Turning pale |
If symptoms are left untreated, more extreme circumstances can happen such as fainting, weakness, disorientation, vomiting and dehydration. When you notice symptoms, usually more than one at one time, it is advised to see a doctor right away.
It is important to get the right treatment so that you can return to a healthy normal blood sugar level and inhibit it from occurring again.
Treatment methods vary from the severity of the blood sugar level, whether it is high or low and if the patient has existing medical conditions, such as diabetes. Here are ways in which blood sugar levels can be treated: