Who Orders My Blood Tests
Your doctor typically orders blood tests for you during a physical, checkup, or an appointment intended to screen for a specific condition.
Its possible to order your own blood tests without a doctor through laboratories like LabCorp and Quest Diagnostics, but health insurance may not cover these tests.
While such blood tests may more accessible and convenient, it may be harder to interpret the results without a medical professional.
Some blood testing facilities may also not give you accurate results.
One infamous case of this is Theranos. The California biotechnology firm shut down in 2018 when an investigation uncovered lies and fraud around the accuracy of its private blood-testing technology.
Currently, litigation is underway against the founder and chief executive of the company, Elizabeth Holmes.
Fasting Blood Glucose Level
A glucose level below 11.1 mmol/L on a random blood sample does not rule out diabetes. A blood test taken in the morning before you eat anything is a more accurate test. Do not eat or drink anything except water for 8-10 hours before a fasting blood glucose test. A level of 7.0 mmol/L or more indicates that you have diabetes.
If you have no symptoms of diabetes but the blood test shows a glucose level of 7.0 mmol/L or more, the blood test must be repeated to confirm you have diabetes. If you do have symptoms and the blood test shows a glucose level of 7.0 mmol/L or more, the test does not need to be repeated. See the separate leaflets called Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes for more details.
Where Can I Get Blood Work Done
There are different locations that offer laboratory services that include blood work. Most hospitals contain a laboratory that you can visit to get tests done. Some laboratories will have walk-in options. Others may require an appointment.
Additional locations for blood testing may include:
- Private laboratories. Hospitals may use private labs to offload some testing from their own laboratories, or in cases when a specialized test is needed. Often, health insurance plans will require you to use a specific laboratory that is in their network for the test to be covered.
- Point-of care. This describes situations when you may need to get a blood test wherever you are receiving medical care. In routine scenarios, this typically
Results may take anywhere from a few hours to a few days to become available. Heres an overview of how long some common tests may take:
- complete blood count : 24 hours
- basic metabolic panel: 24 hours
- complete metabolic panel: 24 to 72 hours
- lipid panel: 24 hours
Timing can depend on the specific lab where you get tested, and how many tests you get done at once. If you order multiple tests, you may not get the complete results until all of the tests are completed.
Sometimes a lab will only release results to your doctor, who reviews them and then releases them to you.
You May Like: At What Blood Sugar Level Should I Take Insulin
What Does Glucose Do
Glucose is fuel for the human body.
When we eat food, the body breaks that food down into simpler substances that your cells, tissues, and organs use in the chemical processes that support life. The process of digestion helps turn complex carbohydrates into glucose. Fruits and dairy products also contain natural sugars that the body converts to glucose, and the body can use fat and protein to make glucose as well.
Inside the body, glucose is known as blood sugar because it is transported via the blood to all the cells of the body. Normal fasting blood sugar ranges between 70 to 99 mg/dL two hours after eating, a normal blood sugar level is less than 140 mg/dL. Higher-than-normal blood sugar levels indicate a problem with the bodys functioning.
Blood Glucose Levels And Diabetes

Your blood sugar level normally rises after you eat. Then it dips a few hours later as insulin moves glucose into your cells. Between meals, your blood sugar should be less than 100 milligrams per deciliter . This is called your fasting blood sugar level.
There are two types of diabetes:
- In type 1 diabetes, your body doesn’t have enough insulin. The immune system attacks and destroys cells of the pancreas, where insulin is made.
- In type 2 diabetes, the cells don’t respond to insulin like they should. So the pancreas needs to make more and more insulin to move glucose into the cells. Eventually, the pancreas is damaged and can’t make enough insulin to meet the body’s needs.
Without enough insulin, glucose can’t move into the cells. The blood glucose level stays high. A level over 200 mg/dl 2 hours after a meal or over 125 mg/dl fasting is high blood glucose, called hyperglycemia.
Too much glucose in your bloodstream for a long period of time can damage the vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to your organs. High blood sugar can increase your risk for:
Also Check: What Diabetic Testing Supplies Are Covered By Medicare
What Do The Results Of The Blood Glucose Test Mean
Normal fasting blood glucose — or blood sugar — is between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter or mg/dL for people who do not have diabetes. The standard diagnosis of diabetes is made when two separate blood tests show that your fasting blood glucose level is greater than or equal to 126 mg/dL.
However, if you have normal fasting blood sugar, but you have risk factors for diabetes or symptoms of diabetes, your doctor may decide to do a glucose tolerance test to be sure that you do not have diabetes.
Some people have a normal fasting blood sugar reading, but their blood sugar rapidly rises as they eat. These people may have impaired glucose tolerance. If their blood sugar levels are high enough, they may be diagnosed with diabetes.
How Is Blood Glucose Monitored
If youre diagnosed with diabetes, youll be asked to monitor your blood glucose levels daily to determine the amount of glucose in your blood. Your diabetes health care team will work with you to determine the best times during the day to test your blood glucose and to find the monitoring device that best suits your needs. There are many accurate blood glucose meters available, and theyre simple to operate. You prick your finger with a lancet and apply a drop of blood to a treated strip. A glucose meter then reads the strip and displays the value.
Monitoring blood glucose and making appropriate changes offers a more independent, self-sufficient approach to diabetes management. Research indicates that complications associated with diabetes may be reduced if blood glucose levels are kept near normal. Blood glucose monitoring can help you:
- Make changes in your daily diet, medications or activity
- Identify low blood glucose levels
- Control blood glucose during illness
Continuous glucose monitoring technology uses a wearable or implantable sensor to monitor blood sugar levels and communicate data via a phone app or receiver-style device. Personal CGM devices are considered the standard of care for patients with Type 1 diabetes and are increasingly common for those with Type 2 diabetes. CGM technology allows patients to view their results in real time and for those results to be shared with their doctor.
You May Like: What Is In Insulin Shots
Tests For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests. Youll probably be tested between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes , your doctor may test you earlier. Blood sugar thats higher than normal early in your pregnancy may indicate you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than gestational diabetes.
Causes Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst the liver and muscles produce some glucose, most comes from the foods we eat. Food and drinks that are high in carbohydrates are most impactful on blood sugar level. What we eat provides us most of the nutrients our body needs and sometimes, does not need. That is not to say that food is a major cause of blood sugar level increasing or decreasing too dramatically.
Typically, if a person has health conditions or poor nutrition, this will lead to a spike or decline in blood sugar level. The causes differ from high to low blood sugar levels and are as follows:
Read Also: What Are The Best Frozen Meals For Diabetics
Why It Is Done
Blood glucose tests are done to:
- Check for prediabetes and diabetes.
- Monitor treatment of diabetes.
- Check for diabetes that occurs during pregnancy .
- Determine if an abnormally low blood sugar level is present. A test to measure blood levels of insulin and a protein called C-peptide may be done along with a blood glucose test to determine the cause of hypoglycemia.
What Should My Blood Sugar Level Be When I Wake Up
These are goal levels, according to The Joslin Diabetes Center:
- Under 100 mg/dl if you do not have diabetes.
- 70 to 130 mg/dl if you have diabetes.
The dawn effect can often lead to a high morning measurement in diabetes. This is your bodys tendency to get ready for the day by raising blood sugar by increasing levels of counter-regulatory hormones the ones that counteract insulin as in normal blood sugar. For people with diabetes, you do not have the capacity to counterbalance this rise in blood sugar, so levels can be dangerously high.
Ways to lower your morning blood sugar value include:
- Eating dinner earlier
- Checking your medications making sure you are taking them properly and asking your doctor if they are correct
- Going for a walk after dinner
Recommended Reading: What Week Is The Glucose Test In Pregnancy
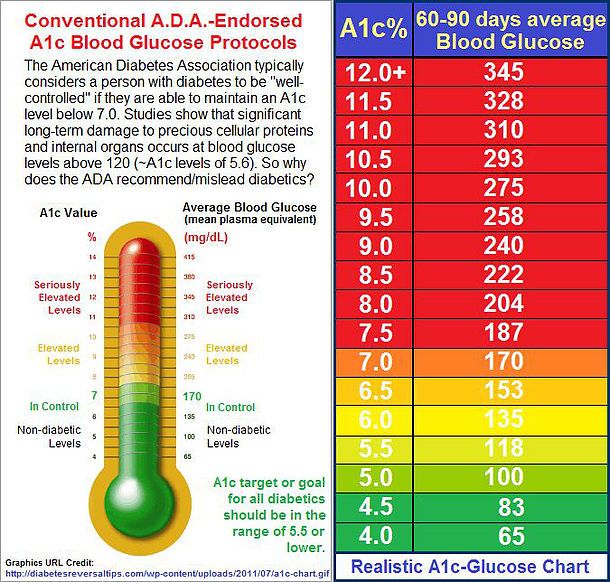
A1c Blood Sugar Tests
The A1C test measures the percentage of glucose bound hemoglobin in a persons blood.
According to The National Institutes of Health , this gives a general picture of a persons blood glucose levels over the past 23 months .
Abnormal A1C test results do not necessarily mean a person has diabetes. A doctor will confirm these findings with another blood glucose test.
The doctor may recommend running more tests, such as blood work, to rule out other conditions that can affect blood sugar levels.
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose level, is the level of sugar/glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a simple version of sugar which comes from the food we eat. Therefore, the more food you consume with high sugar levels over a period of time, will typically increase your blood sugar level.
Glucose comes from the foods we eat and its sugar content. When a person consumes a food with high sugar content, that is turned into glucose. The glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream with the support of insulin. This is then distributed between the bodys cells and used as energy.
Foods high in glucose include most carbohydrates and a handful of proteins and fats. Most foods contain glucose as it is simply a natural sugar that occurs in most dietary forms. However, it is carbohydrates that contain the most sugar and 100% of it turns into glucose, through the process mentioned above, once consumed. The concentration of glucose present in the blood will determine your blood sugar level.
Here is a quick video explaining Blood sugar levels chart :
Your blood sugar level can either be low, normal or high. Depending on what you eat and health conditions, it will vary from person to person. Here is a breakdown of how your blood sugar works and how low or high blood sugar levels happens:
Recommended Reading: Is Raisin Bran Cereal Good For Diabetics
What Is Glucose Used For
Consistent blood sugar levels in your bloodstream power your cells, maintain your energy, and ensure that your body functions properly.
Your pancreas, an organ in your abdomen, helps monitor your blood glucose. Your blood sugar levels rise every time carbs are digested, which signals certain cells in your pancreas to release insulin into your blood. These cells monitor blood sugar levels every few seconds.
Insulin then guides the glucose into your fat, liver, and muscle cells so that it can be used for energy. Once glucose moves to these cells, your blood sugar levels return to a normal level between meals.
During the process where insulin helps glucose move from the bloodstream to cells, your blood sugar levels drop. The pancreas can tell when this is taking place and slows down insulin production. This in turn slows down the amount of glucose entering your cells.
When everything is working normally, this careful process ensures that you are getting the right amount of energy to power your cells.
One of the most important roles glucose plays is providing the main source of energy for your brain. Having too much or too little glucose can negatively impact the brain’s ability to function and can lead to memory problems and poor attention, as well as other cognitive issues.
Types Of Glucose Tests
Several different glucose tests are commonly performed for screening and diagnosis.
Although glucose tests most often use blood or urine samples to test for and monitor diabetes, they can also be performed on samples of cerebrospinal fluid or joint fluid. Abnormal levels of glucose in the CSF or synovial fluid can be due to viral, bacterial, or fungal infections and other conditions.
If you have abnormal results on a glucose test, your doctor may want to repeat the test or have you take a different type of glucose test to confirm the results. The type of glucose test your doctor may recommend, how often its given, when and where you will receive the test, and whether you will need additional testing will depend on your unique situation.
Also Check: What Is A Fast Acting Insulin
Ive Recently Been Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes Will I Need To Monitor My Glucose Levels Every Day
Your healthcare practitioner will discuss with you whether you need to monitor your glucose levels. Not everyone with type 2 diabetes needs to monitor their glucose levels every day, especially if they are able to manage their diabetes and glucose levels with diet and exercise.
However, some people with type 2 diabetes must check their blood glucose levels, sometimes several times a day. This may be done using a glucose meter. You would place a drop of blood from a skin prick onto a glucose strip and then insert the strip into the glucose meter, a small machine that provides a digital readout of the blood glucose level. Alternatively, some people may use a continuous glucose monitoring device.
Your healthcare practitioner will give you guidelines for how high or low your blood sugar should be at different times of the day. By checking your glucose regularly, you can see if the diet and medication schedule you are following is working properly for you.
The Casual Plasma Glucose Test For Diabetes
The casual plasma glucose test is another method of diagnosing diabetes. During the test, blood sugar is tested without regard to the time since the person’s last meal. You are not required to abstain from eating prior to the test.
A glucose level greater than 200 mg/dL may indicate diabetes, especially if the test is repeated at a later time and shows similar results.
You May Like: Managing Your Type 2 Diabetes
What Are Blood Glucose Tests Used To Diagnose
Glucose testing is primarily done to diagnose or manage type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Diabetes is a condition that causes your blood glucose levels to rise.
The amount of sugar in your blood is usually controlled by a hormone called insulin. But if you have diabetes, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or the insulin produced doesnt work properly. This causes sugar to build up in your blood.
If left untreated, chronically elevated levels of blood sugar can lead to other serious conditions including kidney disease, blindness, and heart disease.
In some cases, blood glucose testing may also be used to test for hypoglycemia. This condition occurs when the levels of glucose in your blood are too low, usually lower than 70 milligrams per deciliter .
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes if they take too much of their medication, like insulin, exercise more than usual, or skip a meal. Less commonly, hypoglycemia can be caused by other underlying conditions or medications.
Doctors consider very low blood sugar to be a medical emergency, as it can lead to seizures, coma, and even death.
Risks Of High Glucose
There are two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks and destroys the pancreatic cells that make insulin. In type 2 diabetes, your body cannot make enough needed insulin or use it properly. This is the most common form of diabetes.
Diabetes can cause hyperglycemia. Blood glucose levels higher than 130 mg/dL while fasting or higher than 180 mg/dL two hours after eating indicate hyperglycemia. Additionally, a level of blood glucose higher than 200 mg/dL anytime is considered hyperglycemia.
Blood sugar levels that are too high can:
- Cause more frequent urination as the kidneys try to pass excess blood glucose through urine
- Increases a persons thirst, which increases the risk of dehydration
Severe low blood sugar can lead to more serious issues like feeling very weak, difficulty walking, and blurry vision. It can also lead to seizures, or involuntary movements and possibly a loss of consciousness.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetes Make You Lose Your Eyesight
What Are The Usual Treatments For Diabetes
For type 2 diabetes, which is the most common type of diabetes, losing excess weight, eating a healthy diet that is high in fiber and restricted in carbohydrates, and getting regular amounts of exercise may be enough to lower your blood glucose levels. In many cases, however, medications may be necessary to achieve the desired glucose level. With type 1 diabetes , insulin injections several times a day are necessary. See the article on Diabetes for more on treatment.