Symptoms Signs Causes Of Levels Of High Blood Sugar In The Blood
High blood sugar or hyperglycemia is an abnormally high blood sugar level in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a hallmark sign of diabetes and prediabetes.
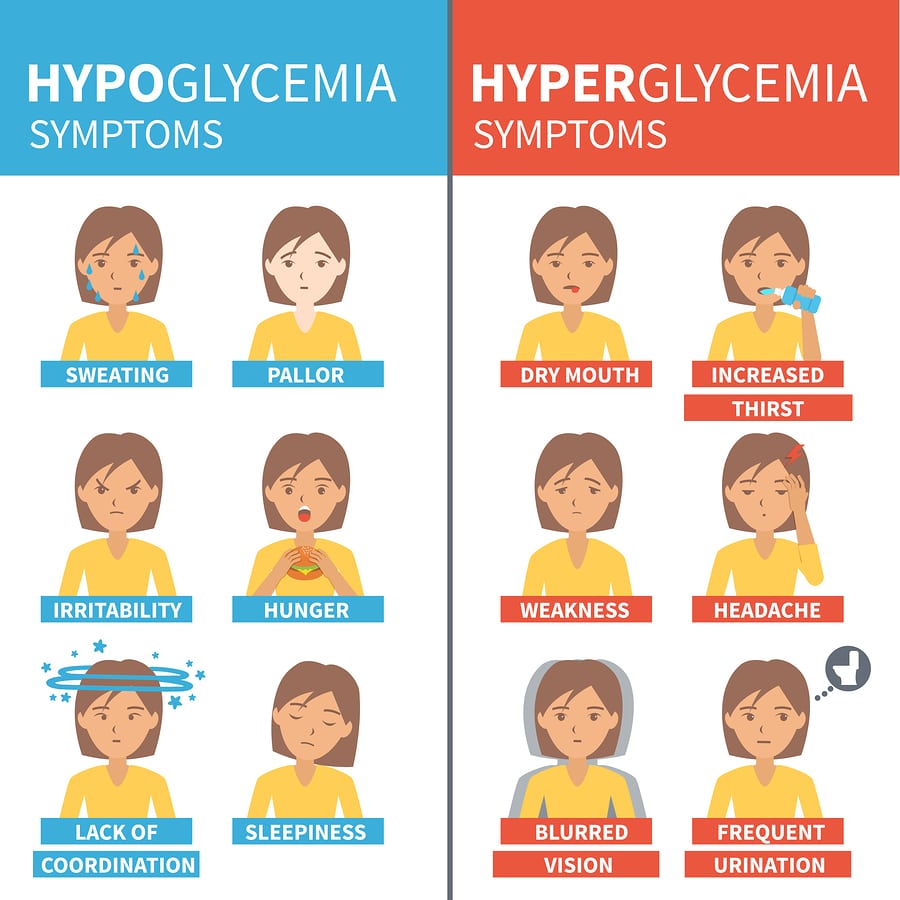
Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia include blurred vision, headaches, hunger, and …
The normal ranges for blood sugar levels in adults who do not have diabetes while fasting are 72-99 mg/dL. These ranges may increase to 80-130 mg/dL for those being treated for diabetes.
According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes should have
- blood sugar levels of 80-130 mg/dL before eating a meal , and
- less than 180 mg/dL about 1-2 hours after eating a meal
High blood sugar ranges for people who dont have diabetes begin at 140 mg/dL, while those being treated for diabetes have a high range beginning at 180 mg/dL.
What Are High Blood Sugar Levels
It is essential to address glucose levels in general. In persons without type 1 or type 2 diabetes, blood sugar levels generally range between 70 to 130 mg/dl.
It depends on the last time they ate a meal and the time of day. Normal blood glucose ranges in persons without any type of diabetes are:
- Fasting blood sugar in the morning before eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
- One hour after a meal 90 to 130 mg/dl
- Two hours after a meal 90 to 110 mg/dl
- Five or more hours after eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
In pregnant women, blood sugar levels tend to be lower. Harvard Health also confirms that a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 mg/dl after an eight-hour fast. Also, a person has diabetes if their blood sugar is 126 mg/dl or higher.
When it comes to hyperglycemia or high blood sugar, there are two kinds of problems. The first kind is fasting hyperglycemia, which is blood sugar higher than 130 mg/dl after not eating or drinking for eight hours.
The other kind is postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia, which happens when your blood sugar is higher than 180 mg/dl two hours after a meal. People without diabetes rarely have blood sugar higher than 140 mg/dl after a meal unless its a big one.
Key Points About Hyperglycaemia
| Seek urgent medical advice if you have high blood glucose and experience the following symptoms: |
These symptoms could be a sign of more serious complications of hyperglycaemia, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state, and you may need to be looked after in hospital. |
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes Diet
Problems Caused By High Blood Sugar
It’s not usually a serious problem if your blood sugar is sometimes slightly high for a short time.
But high blood sugar can cause serious problems if it stays high for a long time or gets to a very high level.
It can lead to:
- life-threatening conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis
If you have high blood sugar, your doctor or care team may ask you to test your blood or pee to check for ketones. A high level of ketones is a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis.
What Is High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of the blood pushing against the artery walls. Each time the heart beats, it is pumping blood into these arteries, resulting in the highest blood pressure when the heart contracts and is pumping the blood. High blood pressure, or hypertension, directly increases the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke . With high blood pressure, the arteries may have an increased resistance against the flow of blood, causing the heart to pump harder to circulate the blood.
Two numbers are used to measure blood pressure. The number on the top, the systolic pressure, refers to the pressure inside the artery when the heart contracts and is pumping the blood through the body. The number on the bottom, the diastolic pressure, refers to the pressure inside the artery when the heart is at rest and is filling with blood. Both the systolic and diastolic pressures are recorded as “mm Hg” .According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health , high blood pressure for adults is defined as:
-
140 mm Hg or greater systolic pressure and
-
90 mm Hg or greater diastolic pressure
NHLBI guidelines for prehypertension are:
-
120 mm Hg 139 mm Hg systolic pressure and
-
80 mm Hg 89 mm Hg diastolic pressure
NHLBI guidelines define normal blood pressure as follows:
-
Less than 120 mm Hg systolic pressure and
-
Less than 80 mm Hg diastolic pressure
Also Check: Should You Fast Before Glucose Test
High Blood Sugar Causes
You may be thinking that hyperglycemia can happen just from eating a super-sugary food, but its not really as simple as that. Sure, eating a lot of sugar or carbs can elevate your blood sugar level, but thats typically when your pancreas kicks into gear and creates insulin to move that glucose into cells throughout the body.
But when someone has diabetes, this finely tuned system gets thrown out of whack. In type 2 diabeteswhich accounts for 90% to 95% of diabetes in adults, according to the CDCthe body either cant make enough insulin or cant utilize insulin well, according to the NIDDK. If someone has prediabetes, their blood glucose will be higher than normal but not quite in the type 2 diabetes range yet, per the NIDDK. And in type 1 diabetes, the body does not make insulin or makes very little.
In any case, the result is extra sugar hanging around the bloodstream, making you feel like total crap in the short term and putting your health at risk in the long term.
How Is Hyperglycaemia Treated
If you experience hyperglycaemia regularly, speak to your doctor or diabetes care team. You may need to change your treatment or lifestyle to keep your blood glucose levels within a healthy range.
You may be advised to:
- adjust the foods you eat eg, avoid foods such as cakes or sugary drinks
- drink plenty of sugar-free fluids to help keep you well hydrated
- exercise more often even gentle, regular exercise such as walking can lower your blood sugar level
- if you use insulin, adjust your dose your healthcare team can give you specific advice about how to do this.
You may also be advised to monitor your blood glucose level more closely or test your blood or urine for substances called ketones .
Also Check: Type 1 Diabetes And Premature Ejaculation
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
must check their blood sugar levels daily with a glucose meter. This device takes a drop of blood, usually from a finger, and displays the sugar level within a few seconds.
People with type 1 diabetes will need to take insulin as their doctor recommends, usually several times a day.
Those with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes may need to change their diet and exercise habits. They may also need to take oral medications or insulin.
Various strategies hyperglycemia.
People should:
- Check their blood sugar levels as their doctor advises and take the correct amount of insulin if they have type 1 diabetes.
- Speak with a doctor or dietitian about which foods to eat or avoid, how much to eat, and how often.
- Take precautions to avoid infections, for example, through regular handwashing, as illness, such as a cold, can trigger an increase in blood sugar levels.
- Plan their food intake and exercise to balance blood sugar levels.
- Minimize stress as far as possible, for example, through exercise, getting enough sleep, and stress-reducing activities such as meditation or yoga.
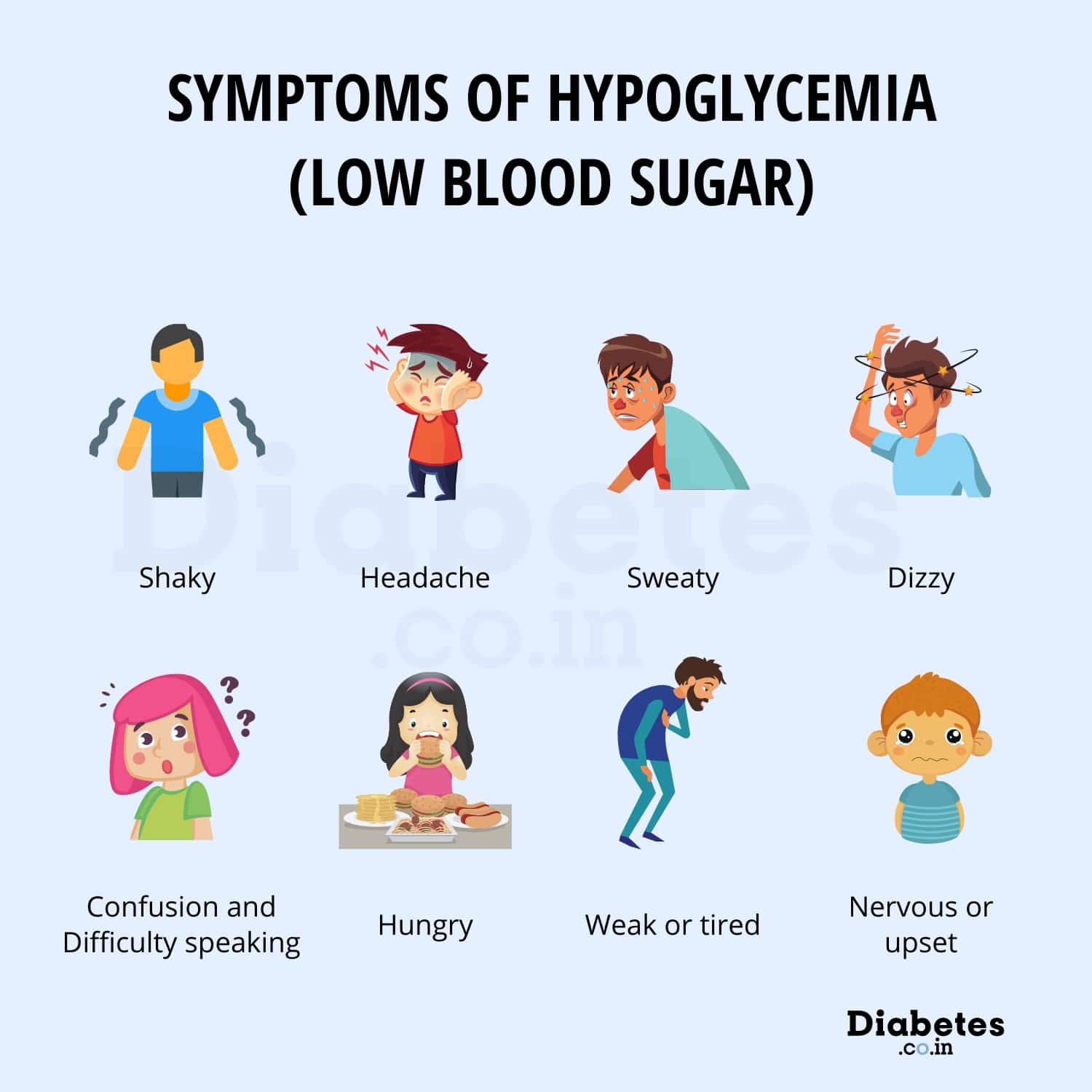
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can occur when a person:
- has certain medical conditions
- does a lot of exercise
- skips meals or eats too little
It can also be a side effect of diabetes medicines. Taking too much insulin can result in low blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
- feeling weak or shaky
- fast heart rate, or palpitations
- consult doctor regularly
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
You May Like: Diabetes Secondary To Sleep Apnea
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Blood glucose levels can be measured at any time, for example, when someone fasts , before they eat, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating, is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
How To Effectively Manage High Blood Sugar
While diabetes is a dangerous disease, it is often possible to manage it and control blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the symptoms of high blood sugar is critical. When blood glucose levels are high, a person must take appropriate action. This is the case with both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
The patient should start by discussing the high blood sugar level with their doctor. The doctor will be able to perform a few tests to give them a better view of the patients diabetes.
It also helps the doctor determine what type of diabetes the patient has. This may be type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes in some cases. Patients also need to be aware that insulin resistance can develop into diabetes. Thus, if the patient is insulin resistant, they need to take action.
There are medications that can help. Some drugs help to ensure there is enough insulin in the body. Others rather have a direct effect on blood sugar levels. This can help to reduce the risk of a blood sugar spike. Failure to manage high blood sugar levels can lead to dangerous problems, such as diabetic coma.
A healthy diet is also critical for a person with diabetes. Carbohydrate counting is important, and you should learn what an appropriate portion size is for you. Meals should be balanced to avoid low blood sugar levels and a spike in blood glucose. It is also important that you take your medication with food.
Read Also: How To Treat Diabetes Insipidus
How Can I Prevent Hyperglycaemia
To reduce your risk of severe or prolonged hyperglycaemia:
- monitor your blood glucose level regularly
- be careful with what you eat be particularly aware of how snacking and eating sugary foods or carbohydrates can affect your blood glucose levels
- stick to your management plan take diabetes medicines as and when directed
- be as active as possible getting regular exercise can help stop your blood glucose level rising, but you should check with your doctor first if you’re taking diabetes medication, as some medicines can lead to hypoglycaemia if you exercise too much.
- take extra care when you’re ill see our page on having a diabetes sick day plan.
How Do I Measure Blood Sugar
If you have diabetes, you probably already keep a watchful eye on your blood sugar through the use of a continuous glucose monitor or a blood sugar meter . Blood sugar measurement is also typically included in routine lab work for people without diabetes — your physician will usually order a glycated hemoglobin test, which measures your average blood sugar over the past two to three months.
Say your A1C test comes back with no sign of diabetes — constantly measuring your blood sugar can still be helpful. For instance, some people experiment with using a CGM to see how their body responds to different types of food. However, it’s good to note that this is a fairly cost-intensive way of figuring out your nutrition, and writing down a food diary that includes how you felt after each meal will also help you figure out what to eat.
Check out these blood sugar monitors if you’re looking for recommendations on how to keep track of your levels at home.
Don’t Miss: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Cost
How Is High Blood Sugar Diagnosed
There are different kinds of blood tests that can diagnose hyperglycemia. These include:
- Random blood glucose: this test reflects the blood sugar level at a given point in time. Normal values are generally between 70 and 125 mg/dL, as discussed earlier.
- Fasting blood glucose: This is a measurement of blood sugar level taken in the early morning before eating or drinking anything since the night before. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are less than 100 mg/dL. Levels above 100 mg/dL up to 125 mg/dL suggest prediabetes, while levels of 126 mg/dL or above are diagnostic of diabetes.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: this is a test that measures blood glucose levels at given time points after a dose of sugar is consumed. This test is most commonly used to diagnose gestational diabetes.
- Glycohemoglobin A1c: is a measurement of glucose that is bound to red blood cells and provides an indication of blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
What Causes Hyperglycemia
Your diet may cause you to have high blood sugar levels, particularly if you have diabetes. Carbohydrate-heavy foods such as breads, rice, and pasta can raise your blood sugar. Your body breaks these foods down into sugar molecules during digestion. One of these molecules is glucose, an energy source for your body.
After you eat, glucose is absorbed into your bloodstream. The glucose cant be absorbed without the help of the hormone insulin. If your body is unable to produce enough insulin or is resistant to its effects, glucose can build up in your bloodstream and cause hyperglycemia.
Hyperglycemia can also be triggered by a change in your hormone levels. This commonly happens when youre under a lot of stress or when youre feeling ill.
Hyperglycemia can affect people regardless of whether they have diabetes. You may be at risk of hyperglycemia if you:
- lead a sedentary or inactive lifestyle
- have a chronic or severe illness
- are under emotional distress
- use certain medications, such as steroids
- have had a recent surgery
If you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels may spike if you:
- dont follow your diabetes eating plan
- dont use your insulin correctly
- dont take your medications correctly
Also Check: How To Control Type Two Diabetes With Diet
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
This test can be done in the lab or the healthcare providers office with a simple finger stickor your doctor may prescribe a meter and have you test regularly at home.
A fasting blood sugar level indicates what your blood sugar is when you havent eaten for at least 8 hours. For adults without diabetes, a normal fasting blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dL. A fasting blood sugar level of 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
Diabetes And High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is twice as likely to strike a person with diabetes than a person without diabetes. Left untreated, high blood pressure can lead to heart disease and stroke. In fact, a person with diabetes and high blood pressure is four times as likely to develop heart disease than someone who does not have either of the conditions. About two-thirds of adults with diabetes have blood pressure greater than 130/80 mm Hg or use prescription medications for hypertension.
Read Also: When Does Long Acting Insulin Peak
High Blood Sugar Levels
If you have diabetes, you can find out if your blood sugar level is high by having a blood sugar test.
You may have regular tests by your care team or GP surgery, or you may have tests you can do at home.
| Type of test | High level |
|---|---|
| Test done by a health professional to check your blood sugar level over the last 2 or 3 months | 48 mmol/mol or over |
| Test done by a health professional after not eating for a few hours | Over 7 mmol/L |
| Home test done after waking up or before eating | Over 7 mmol/L |
| Home test done at any other time | Over 11 mmol/L |