What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is a sugar that moves through the bloodstream and provides energy to all the cells in the body. It is one of your babys most important sources of energy.
Babies with normal blood glucose levels have all the energy they need for healthy growth and development. However, in rare cases, blood glucose levels can fall too low and cause a baby to become sick.
What Is Neonatal Hypoglycemia
Neonatal hypoglycemia occurs in between 1 and 3 of every 1000 births, making it the most common metabolic issue among newborns. The condition refers to a newborn baby with low blood sugar levels following birth. Among healthy newborns, its actually quite normal for blood sugar to dip right after a baby enters the world. However, when glucose concentrations drop in the first 24 hours of life, your infant may be diagnosed with neonatal hypoglycemia.
Without treatment, chronic low blood sugar could be associated with neurological damage and result in developmental issues. However, medical professionals are trained to closely monitor for symptoms of neonatal hypoglycemia and intervene quickly, which can drastically reduce the risk of complications.
How To Avoid Low Blood Sugars
Antenatal hand expression
If you are reading this leaflet before your baby is born because it has already been identified that your baby may be at risk of low blood glucose, you may want to consider expressing some breast milk before your baby is born. This can be beneficial to supporting your babys blood glucose level regardless of whether you plan to breastfeed your baby or not. This is because it is thought that breast milk helps to activate the babys response mechanisms which supports them when their blood sugars drops.
Research shows that if there are no other risk factors, expressing breast milk from 36 weeks in to your pregnancy should be safe for you and your baby.
You will be shown how to hand express your milk and provided with syringes in which to collect it. The milk can then be labelled and stored in your own freezer ready to bring in when baby is born.
If you are interested in doing this please see your Midwife for further support and information.
Skin-to-skin contact
Skin-to-skin contact with your baby on your chest helps keep your baby calm and warm and helps to encourage your babys natural instincts to feed. During initial skin-to-skin contact, your baby should wear a hat and be kept warm with a blanket or towel.
Keep your baby warm
Put a hat on your baby until they are able to maintain their own temperature effectively and then remove. Your Midwife will be able to guide you with this.
Feed as soon as possible after birth
Express your milk
Also Check: How Do People Get Type 1 Diabetes
Breast Milk Helps To Treat Hypoglycemia In Newborns
Within a week after the birth, the babys body can store glucose in the liver. Therefore, it helps the baby to cope with the transition from the womb to the world. Mothers first milk is a rich and creamy substance called Colostrum. It has special enzymes that help your baby release the stored glucose from the liver. The liver of premature babies does not get enough chance to store glucose. They are, therefore, more prone to hypoglycemia. Breast milk helps in regulating blood sugar and treat hypoglycemia.
Babies That Are At Higher Risk Of Developing Hypoglycemia
low blood sugar in newborn babies is most commonly found when the mother has diabetes.
- Babies who are premature or who are a very low birth weight are at higher risk.
- A smaller twin has a higher risk of becoming a low blood sugar baby.
- Babies with colds or respiratory problems after birth.
- Mothers who had long labors.
- Babies who are under stress during delivery.
- Babies who get too cold after birth and are not allowed skin on skin contact.
- Mothers who are given intravenous fluids containing glucose.
Don’t Miss: Safe Male Enhancement Pills For Diabetics
Severe Low Blood Sugar
As your low blood sugar gets worse, you may experience more serious symptoms, including:
- Having difficulty walking or seeing clearly.
- Acting strange or feeling confused.
- Having seizures.
Severe low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL. Blood sugar this low may make you faint . Often, youll need someone to help you treat severe low blood sugar.
People with diabetes may experience low blood sugar as often as once or twice a week, even when managing their blood sugar closely. Knowing how to identify and treat it is important for your health. Learn how to treat low blood sugar.
Complications Of Hypoglycemia In Newborns
Hypoglycemia means that an infant does not have enough sugar in their blood to provide adequate energy to fuel their body or brain. There is ongoing scientific debate about the precise level at which this is likely to cause harm.
Transient hypoglycemia that resolves quickly is unlikely to be harmful. However, hypoglycemia that is severe and sustained or that remains untreated may cause serious complications.
Read Also: Blood Sugar 160 After Eating
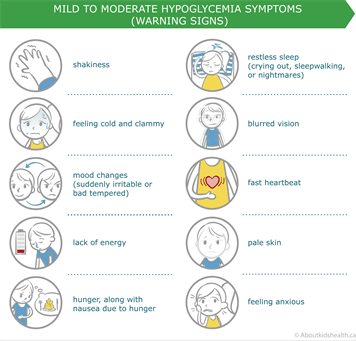
What Are The Signs Of Hypoglycemia In Newborns
Symptoms of neonatal hypoglycemia arent always recognizable, especially early on. As a result, most hospitals perform blood glucose tests at a babys birth and then at specific intervals. However, if symptoms are present, they may include:
- Weak or floppy muscles
- Blueish or white discoloration of skin and lips
- Not interested in eating
- Low body temperature
If blood sugar continues to drop or remains low for several days, symptoms will be more severe. Fortunately, neonatal hypoglycemia is treatable. However, problems can result in lasting brain damage when there isn’t prompt treatment. Doctors and nurses who identify symptoms must act quickly. Treatments may include medications, giving sugar gel, or using formula to supplement breastfeeding.
Who Should Be Screened
Glucose screening is recommended for infants in the following categories who are at increased risk for pathological hypoglycemia:
- Born to mothers with gestational diabetes or diabetes mellitus
- Large for gestational age
- Small for gestational age
Checking at least one glucose level is also recommended for infants with clinical signs consistent with hypoglycemia:
- Tremors, jitteriness, irritability
- Poor suck, refusal to feed
Don’t Miss: How To Use Insulin Glargine Injection
Going Home With Your Baby
It is recommended that your baby stays in hospital for at least 24 hours after birth. After that, if your babys blood glucose is stable and they are feeding well, you will be able to go home.
Before you go home, make sure you know how to tell if your baby is getting enough milk. A member of staff will explain the normal pattern of wet and dirty nappies and the changing colour of babys stools. For further information, if you are breastfeeding, see How you and your midwife can recognise that your baby is feeding well .
It is important to make sure that your baby feeds well at least 8 times every 24 hours. However, there is no need to continue waking your baby to feed every 2 to 3 hours as long as they have at least this number of feeds, unless this has been recommended for a particular reason. Instead you can now start to feed your baby responsively. Your midwife will explain this t o you.
If you are bottle feeding, make sure you are not over-feeding your baby. Offer the bottle when they show feeding cues and observe for signs that they want a break. Do not necessarily expect your baby to finish a bottle let them take as much milk as they want.
Once you are home, no special care is needed, however as with all newborn babies, you should continue to look for signs that your baby is well, and seek medical advice if you are worried at all.
Treatment Options For Hypoglycemia In Newborns
Treatment for neonatal hypoglycemia is designed to correct low blood glucose levels. This can be as simple as extra feedings of breastmilk or formula, oral sugar gel, or an intravenous sugar solution and a stay in the NICU. Typically, interventions continue until your baby can maintain safe blood sugar levels, which can last for hours or days after birth. Medications are also available for use in rare cases.
Learning that your baby has a medical issue can understandably be scary, but neonatal hypoglycemia typically isn’t something to worry too much about. Once diagnosed, this condition can be treated fairly easily, meaning you can rest assured that your child will grow up strong, healthy, and capable of leading a perfectly normal and even exceptional! life.
BabyCenter’s editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you’re seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
UpToDate. Management and Outcome of Neonatal Hypoglycemia
National Institutes of Health. Low blood sugar newborns.
Read Also: What Is A Good Score For Diabetes
Information About Your Child
We collect and use your childs information to provide your child with care and treatment. As part of your childs care, information about your child will be shared between members of a healthcare team, some of whom you may not meet. Your childs information may also be used to help train staff, to check the quality of our care, to manage and plan the health service, and to help with research. Wherever possible we use anonymous data.
We may pass on relevant information to other health organisations that provide your child with care. All information is treated as strictly confidential and is not given to anyone who does not need it. If you have any concerns please ask your childs doctor, or the person caring for your child.
Under the General Data Protection Regulation and the Data Protection Act 2018 we are responsible for maintaining the confidentiality of any information we hold about your child. For further information visit the following page: Confidential Information about You.
If you need information about your childs health and wellbeing and their care and treatment in a different format, such as large print, braille or audio, due to disability, impairment or sensory loss, please advise a member of staff and this can be arranged.
How We Care For Hypoglycemia
At Boston Childrens Hospital, we treat hypoglycemia in our General Endocrinology Program, a multi-disciplinary program dedicated to the treatment of a wide range of endocrinological disorders. Caring for more than 7,000 patients each year, our division is one of the largest pediatric endocrinology practices in the country. We provide state-of-the-art diagnosis, treatment, and clinical management for children with hypoglycemia and related disorders.
Read Also: When To Go To Er For High Blood Sugar
What Treatment May Be Needed
-
If your baby’s blood sugar level is a little bit low we recommend extra feeds.
-
If your baby’s blood sugar is very low or if the extra feeds don’t improve the level, a glucose solution is given intravenously to bring the baby’s blood sugar level up to normal. Your baby would need to be admitted to NICU to have this.
If you have concerns or want more information about your baby, ask the doctor or nurse providing your baby’s care.
Low Blood Sugars In Babies
We have recommended your baby be closely monitored because he or she is at risk of, or has had a low blood sugar level. Babies with a low blood sugar level may need to be admitted to the Newborn Intensive Care Unit for treatment until their blood sugar level reaches and is maintained within a normal range. However, many babies at risk of low blood sugars are able to be with their mother on the ward. A baby who has had a low blood sugar level with no complications does not need special checks after leaving hospital.
Recommended Reading: How Does Anemia Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Who Is Affected By Hypoglycemia In The Newborn
Approximately two out of 1,000 newborn babies have hypoglycemia. Babies who are more likely to develop hypoglycemia include:
- Babies born to diabetic mothers are at a risk for developing hypoglycemia after delivery because the source of glucose is gone and the baby’s high insulin level tends to metabolize the existing glucose faster.
- Small for gestational age, prematurity, low brith weight or growth-restricted babies may have limited glycogen stores in the liver or have immature liver function that results in hypoglycemia.
What To Do If An Infant Has Hypoglycemia
It is common for infants to temporarily have hypoglycemia immediately after birth. If this happens, a doctor will monitor their blood glucose to see if it returns to normal. If it does, treatment may not be necessary.
However, if an infant is showing signs of hypoglycemia in the days, weeks, or months after birth, call a doctor right away.
The doctor may advise giving breast milk, formula, or a mixture of glucose and water, if a person has any, to try to raise the infants blood sugar levels. They may also recommend visiting a health center to get a blood glucose test.
The symptoms of hypoglycemia in newborns are similar to those of many other conditions, so it is important to get help from a healthcare professional.
Prompt feeding at birth and ongoing, on-demand feeding can reduce the risk of hypoglycemia by ensuring that an infant gets adequate nutrition. If someone is nursing, frequent feeding also
There are several reasons that a newborn might develop hypoglycemia. These include the following.
Read Also: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
What Are The Treatment Options For Hypoglycemia
Children with hypoglycemia have different symptoms, and these vary from one child to another. But no matter what your childs symptoms, the overriding goal is the same to bring the blood sugar back up to normal as rapidly as possible and return your child to good health.
Most often, your childs blood sugar can be brought back up to normal by eating or drinking something that has sugar in it, such as fruit juice, regular soda, table sugar, maple syrup, candy, glucose tablets, glucose gel, or cake frosting. Consider encouraging your child to:
- eat regular meals throughout the day
- eat frequent snacks
For children with diabetes, the goal is to consistently maintain a blood sugar level that is in a healthy range. This involves testing blood sugar often, learning to recognize the earliest symptoms of low blood sugar, and treating the condition quickly, based on instructions given by your child’s healthcare providers.
If your child has recurrent or severe hypoglycemia, the first thing is to determine the cause, because different causes have different treatments. While the cause is determined, some children will receive glucose intravenously in the hospital to make sure their blood-sugar level stays normal.
Some causes of hypoglycemia can be treated with changes in your childs diet or medication. For some rare cases of severe hypoglycemia that dont respond to medical treatment, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove most of the pancreas.
What Happens When A Baby Has Neonatal Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is defined as low glucose levels. The body produces insulin, a hormone that regulates glucose levels. If more glucose is produced than the body needs, or if there isnt enough glucose consumed, levels will drop. When blood sugar levels get too low, there may not be enough glucose reaching the brain . That may impair growth and cause brain cells to begin dying.
Neonatal hypoglycemia happens when a newborn baby has very low blood sugar levels. When a baby is born and no longer receives glucose from their mother through the umbilical cord, they need to get glucose from feeding. Babies who dont get enough from feeding or have problems feeding may have to be given medication to provide glucose. Its normal for a babys glucose levels to fall right after birth. However, levels typically return to a normal level after feeding.
Recommended Reading: Inulin And Diabetes Type 2
What Do I Do If My Baby Has Low Blood Glucose Levels
Your baby will be checked for signs of illness. He will need extra feedings if his levels dont rise on their own. The extra feeds can be given:
- from the breast,
- as expressed breast milk, or
If the extra feedings dont raise the blood glucose level, glucose gel can be provided with a feed to raise the blood sugar. This can be repeated once, but if your babys blood sugar remains low or if your baby is not able to feed well, they will need intravenous treatment . Preterm babies or babies with low birth weight often have an intravenous started when they are born.
Treatment Of Neonatal Hypoglycemia
-
Enteral feeding
-
Sometimes IM glucagon
Most high-risk neonates are treated preventively. For example, infants of diabetic women who have been using insulin are often started at birth on a 10% D/W infusion IV or given oral glucose, as are those who are sick, are extremely premature, or have respiratory distress. Other at-risk neonates who are not sick should be started on early, frequent formula feedings to provide carbohydrates.
Any neonate whose glucose falls to 50 mg/dL should begin prompt treatment with enteral feeding or with an IV infusion of up to 12.5% D/W, 2 mL/kg over 10 minutes higher concentrations of dextrose can be infused if necessary through a central catheter. The infusion should then continue at a rate that provides 4 to 8 mg/kg/minute of glucose . Serum glucose levels must be monitored to guide adjustments in the infusion rate. Once the neonates condition has improved, enteral feedings can gradually replace the IV infusion while the glucose concentration continues to be monitored. IV dextrose infusion should always be tapered, because sudden discontinuation can cause hypoglycemia.
Read Also: Can Diabetics Eat Ramen Noodles