Idiopathic Type 1 Diabetes
Some forms of type 1 diabetes have no known etiologies. These patients have permanent insulinopenia and are prone to DKA but have no evidence of -cell autoimmunity. However, only a minority of patients with type 1 diabetes fall into this category. Individuals with autoantibody-negative type 1 diabetes of African or Asian ancestry may suffer from episodic DKA and exhibit varying degrees of insulin deficiency between episodes . This form of diabetes is strongly inherited and is not HLA associated. An absolute requirement for insulin replacement therapy in affected patients may be intermittent. Future research is needed to determine the cause of -cell destruction in this rare clinical scenario.
Diagnostic Tests For Diabetes
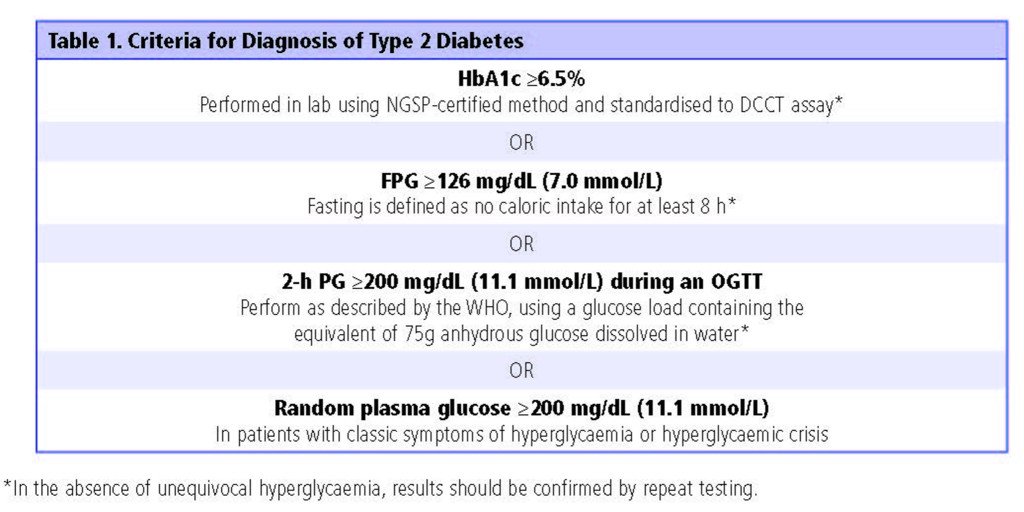
Diabetes may be diagnosed based on plasma glucose criteria, either the fasting plasma glucose value or the 2-h plasma glucose value during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test , or A1C criteria .
Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes
| FPG 126 mg/dL . Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 h. |
| OR |
| 2-h PG 200 mg/dL during OGTT. The test should be performed as described by WHO, using a glucose load containing the equivalent of 75 g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water. |
| OR |
| A1C 6.5% . The test should be performed in a laboratory using a method that is NGSP certified and standardized to the DCCT assay. |
| OR |
| In a patient with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, a random plasma glucose 200 mg/dL . |
| FPG 126 mg/dL . Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 h. |
| OR |
| 2-h PG 200 mg/dL during OGTT. The test should be performed as described by WHO, using a glucose load containing the equivalent of 75 g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water. |
| OR |
| A1C 6.5% . The test should be performed in a laboratory using a method that is NGSP certified and standardized to the DCCT assay. |
| OR |
| In a patient with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, a random plasma glucose 200 mg/dL . |
DCCT, Diabetes Control and Complications Trial FPG, fasting plasma glucose OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test WHO, World Health Organization 2-h PG, 2-h plasma glucose.
Tests To Diagnose Diabetes
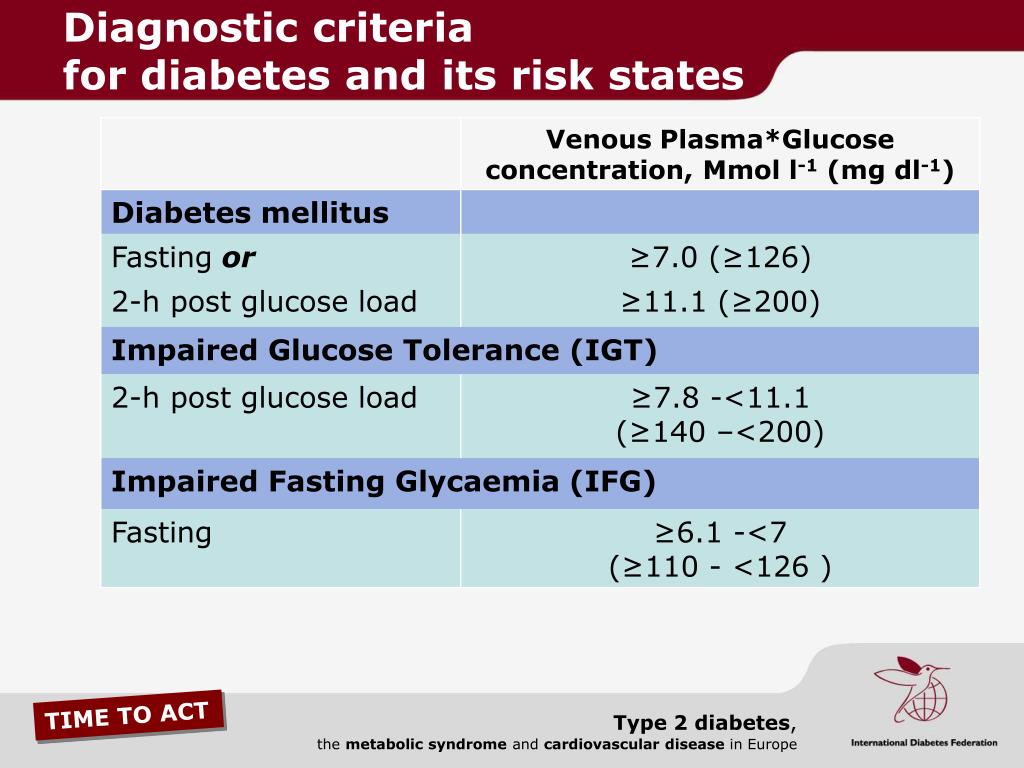
Blood Glucose Measurements. The diagnosis of diabetes is based on one of three methods of blood glucose measurement .1 Diabetes can be diagnosed if the patient has a fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg per dL or greater on two separate occasions. The limitations of this test include the need for an eight-hour fast before the blood draw, a 12 to 15 percent day-to-day variance in fasting blood glucose values, and a slightly lower sensitivity for predicting microvascular complications.15,16
Diagnostic Criteria for Diabetes Mellitus
Categories of increased risk
| Diabetes type | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Fasting glucose test: 100 to 125 mg per dL |
||
|
Two-hour OGTT : 140 to 199 mg per dL |
||
|
A1C measurement: 5.7 to 6.4 percent |
||
|
Type 1, type 2, LADA, MODY |
Fasting glucose test: 126 mg per dL |
Type 1 diabetes: decreased C peptide, presence of GADA and ICA
LADA: increased C peptide, presence of GADA and ICA, tyrosine phosphatase antibody , anti-insulin antibody |
|
Two-hour OGTT : 200 mg per dL |
||
|
Random glucose test: 200 mg per dL with symptoms |
||
|
A1C measurement: 6.5 percent |
||
|
Fasting, 95 mg per dL
One hour, 180 mg per dL |
One-hour Glucola OGTT : 140 mg per dL , confirm diagnosis with 75- or 100-g OGTT |
|
|
OGTT : Fasting, 95 mg per dL
One hour, 180 mg per dL |
Information from reference 1.
Diagnostic Criteria for Diabetes Mellitus
Categories of increased risk
Information from reference 1.
You May Like: How Much Is Lantus Insulin
How To Manage Type 2 Diabetes
The same dietary and lifestyle strategies that can help you prevent type 2 diabetes can also help you manage and reverse insulin resistance, return to normal blood glucose levels, and reverse type 2 diabetes.
These strategies are:
- Eating a low-fat, plant-based, whole-food diet specifically designed to reverse insulin resistance permanently
- Integrating intermittent fasting into your dietary schedule
- Adding daily movement to your routine
Well go into each of these areas in detail below.
S And Criteria For Diagnosing Diabetes
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
Screening And Testing For Prediabetes And Type 2 Diabetes In Children And Adolescents
In the last decade, the incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents has increased dramatically, especially in racial and ethnic minority populations . See for recommendations on risk-based screening for type 2 diabetes or prediabetes in asymptomatic children and adolescents in a clinical setting . See and for the criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes, respectively, which apply to children, adolescents, and adults. See Section 13 Children and Adolescents for additional information on type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents.
Some studies question the validity of A1C in the pediatric population, especially among certain ethnicities, and suggest OGTT or FPG as more suitable diagnostic tests . However, many of these studies do not recognize that diabetes diagnostic criteria are based on long-term health outcomes, and validations are not currently available in the pediatric population . The ADA acknowledges the limited data supporting A1C for diagnosing type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Although A1C is not recommended for diagnosis of diabetes in children with cystic fibrosis or symptoms suggestive of acute onset of type 1 diabetes and only A1C assays without interference are appropriate for children with hemoglobinopathies, the ADA continues to recommend A1C for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in this cohort to decrease barriers to screening .
Type 2 Diabetes Ada Diagnosis Criteria
Diagnostic criteria by the American Diabetes Association include the following:
-
A fasting plasma glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher, or
-
A 2-hour plasma glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test , or
-
A random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dL or higher in a patient with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, or
-
A hemoglobin A1c level of 6.5% or higher
Also Check: Diabetic Fasting Blood Sugar Goal
Choose Your Diagnosis To Learn More
Diabetes Canada is your place to find everything you need to gain a deeper understanding of how to live a healthier life. Being newly diagnosed can be an intimidating experience but just know we have the tools and resources you need to succeed. Take action to live your best life. There are several types of diabetes. This section will help you understand your diagnosis and learn more about how to manage it.
Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes
If left unmanaged, type 2 diabetes drastically increases your risk for other diseases, with one report finding that people with type 2 diabetes spent up to 3 times more on medical complications.
In addition, type 2 diabetes can cause a number of direct and indirect health problems. Direct complications from diabetes include:
- Heart disease
- Failure or restriction of blood vessels
- Retinopathy
The underlying problem of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes can also lead to indirect complications in your arteries, liver and muscles, kidneys, and ovaries, along with various neurological and brain disorders.
These diabetes complications include, but arent limited to:
- Coronary artery disease
- And various other chronic conditions
Recommended Reading: When Is Insulin Needed For Type 2 Diabetes
World Health Organisation Recommendations
Diabetes UK supports the diagnostic criteria published by the WHO in 2006: “definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycaemia“. Diabetes UK also welcomes the 2011 decision by the WHO to accept the use of HbA1c testing in diagnosing diabetes: “use of glycated haemoglobin in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus“.
Information on the diagnostic criteria for diabetes is below. For further information and an explanation of terms and classifications please refer to the full WHO guidelines.
Classification And Diagnosis Of Diabetes: Standards Of Medical Care In Diabetes2021
American Diabetes Association 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes2021. Diabetes Care 1 January 2021 44 : S15S33.
The American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes includes the ADA’s current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide the components of diabetes care, general treatment goals and guidelines, and tools to evaluate quality of care. Members of the ADA Professional Practice Committee, a multidisciplinary expert committee , are responsible for updating the Standards of Care annually, or more frequently as warranted. For a detailed description of ADA standards, statements, and reports, as well as the evidence-grading system for ADA’s clinical practice recommendations, please refer to the Standards of Care Introduction . Readers who wish to comment on the Standards of Care are invited to do so at professional.diabetes.org/SOC.
Recommended Reading: What Is Diabetic Retinopathy With Macular Edema
Transitioning Away From Medications
Remember, treating the symptoms of type 2 diabetes with medication will not treat the underlying causes.
The only way to effectively reverse type 2 diabetes is to reverse the underlying insulin resistance, which will reduce, and ultimately reduce your biological need for medication.
Pharmaceutical medications can have many benefits. They may help to control your blood glucose, improve insulin secretion, reduce your blood pressure, reduce your cholesterol, and reduce pain in the short term.
But the intensive treatment of blood glucose with medications can have an extensive list of side effects, and a number of negative long-term effects, which include increased risk for heart failure, liver failure, kidney failure, stroke, and even death.
Thats why we recommend a dedicated, concerted effort through lifestyle and dietary changes. These changes are safe, increase your energy and overall health, and are a sustainable long-term solution.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Through Intermittent Fasting
Another powerful strategy to reverse type 2 diabetes involves intermittent fasting.
Intermittent fasting is a dietary strategy where periods of food consumption alternate with fasting periods .
Regular intermittent fasting has been shown to be a powerful tool for weight loss, reduced insulin resistance, better cardiovascular health, improved neurological activity, and improved liver health.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Get An Insulin Pump
Pancreatic Diabetes Or Diabetes In The Context Of Disease Of The Exocrine Pancreas
Pancreatic diabetes includes both structural and functional loss of glucose-normalizing insulin secretion in the context of exocrine pancreatic dysfunction and is commonly misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Hyperglycemia due to general pancreatic dysfunction has been called type 3c diabetes and, more recently, diabetes in the context of disease of the exocrine pancreas has been termed pancreoprivic diabetes . The diverse set of etiologies includes pancreatitis , trauma or pancreatectomy, neoplasia, cystic fibrosis , hemochromatosis, fibrocalculous pancreatopathy, rare genetic disorders , and idiopathic forms , which is the preferred terminology. A distinguishing feature is concurrent pancreatic exocrine insufficiency , pathological pancreatic imaging , and absence of type 1 diabetesassociated autoimmunity . There is loss of both insulin and glucagon secretion and often higher-than-expected insulin requirements. Risk for microvascular complications is similar to other forms of diabetes. In the context of pancreatectomy, islet autotransplantation can be done to retain insulin secretion . In some cases, autotransplant can lead to insulin independence. In others, it may decrease insulin requirements .
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
In type 1 diabetes, insulin deficiency initially occurs as a result of an autoimmune condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks the beta cells in your pancreas.
As a result, the population of beta cells in your pancreas is significantly compromised, resulting in insulin insufficiency and high blood glucose.
In non-insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes, the beta cells in your pancreas can produce enough insulin, but the insulin they produce is not powerful enough to overcome the amount of insulin resistance in your muscle and liver.
In the case of insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes, beta cells that have been overproducing insulin for months to years begin dying, resulting in a reduced population and insufficient insulin production.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Your Child Has Type 1 Diabetes
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, is a chronic condition characterized by high blood glucose and a wide range of ensuing side effects.
Type 2 diabetes, sometimes referred to as adult-onset diabetes, affects more than 31 million people in the U.S. alone, and is one of the fastest-growing chronic conditions in the world today.
Type 2 diabetes specifically manifests as a result of a condition called insulin resistance, which is caused by the accumulation of excess fat in cells that are not designed to store large quantities of fat.
In its early stages, type 2 diabetes is referred to as non-insulin-dependent, which is characterized by the following sequence of events:
- Step 1: Insulin resistance in your muscle and liver dramatically increase your insulin requirements
- Step 2: Insulin resistance in your muscle and liver increases over time, resulting in an increased demand for insulin production
- Step 3: The beta cells in your pancreas increase their insulin output, resulting in hyperinsulinemia
- Step 4: When beta cells can’t make enough insulin to overcome insulin resistance in your muscle and liver, your blood glucose becomes elevated, causing hyperglycemia
In later stages, type 2 diabetes can become classified as insulin-dependent, resulting in the following events:
Fortunately, type 2 diabetes is reversible in the majority of cases via strategic diet and lifestyle changes that increase insulin sensitivity.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Through Diet
The most effective way to manage and reverse type 2 diabetes involves your diet.
Specifically, the research points to a low-fat, plant-based, whole-food diet thats high in whole carbohydrates.
This way of eating results in dramatically increased insulin sensitivity, which in turn results in:
- Better blood glucose control
- A 10-60% reduction in insulin use
- Reduced oral medication use
- Increasing your time in range
- A 2.0% reduction in A1c
- Reduced LDL cholesterol
- Increased energy levels
- Reduced risk for many chronic diseases
Compared to the Standard American Diet, these new guidelines can be quite a shift. Here are some helpful guidelines.
Also Check: Signs Of Diabetes In Toddler Girl
Is Type 2 Diabetes Curable
Yes, type 2 diabetes is curable.
The key to reversing type 2 diabetes is in reversing insulin resistance through strategic changes to your diet and activity levels.
If you are able to do that, you are able to effectively reverse type 2 diabetes .
Simply managing the symptoms of diabetes using oral medications or insulin does not reverse type 2 diabetes.
Pharmacological treatment does not dramatically increase your level of insulin sensitivity, which is required to completely reverse type 2 diabetes.
Below, well touch on the three major areas that can help you reverse type 2 diabetes permanently.
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
The core problem that all forms of diabetes have in common is hyperglycemia , which can have a wide variety of side effects.
As a result, type 2 diabetes symptoms can include:
- Thirst
- Frequent infections
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck
Its important to note that these symptoms overlap with many other forms of diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, prediabetes, gestational diabetes, and type 1.5 diabetes.
Read Also: Does Diabetes 2 Go Away
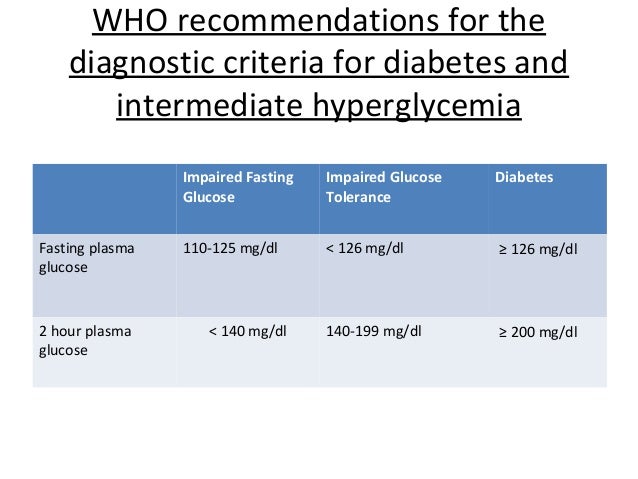
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood sugar levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink. It tells the doctor how your body processes sugar.
- Diabetes is diagnosed at 2 hour blood sugar of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl
|
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
|
| Normal | |
| 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl | |
| Diabetes | 200 mg/dl or higher |
Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis And Screening
PARITA PATEL, MD, and ALLISON MACEROLLO, MD, Department of Family Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Apr 1 81:863-870.
Based on etiology, diabetes is classified as type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 diabetes mellitus, latent autoimmune diabetes, maturity-onset diabetes of youth, and miscellaneous causes. The diagnosis is based on measurement of A1C level, fasting or random blood glucose level, or oral glucose tolerance testing. Although there are conflicting guidelines, most agree that patients with hypertension or hyperlipidemia should be screened for diabetes. Diabetes risk calculators have a high negative predictive value and help define patients who are unlikely to have diabetes. Tests that may help establish the type of diabetes or the continued need for insulin include those reflective of beta cell function, such as C peptide levels, and markers of immune-mediated beta cell destruction . Antibody testing is limited by availability, cost, and predictive value.
Prevention, timely diagnosis, and treatment are important in patients with diabetes mellitus. Many of the complications associated with diabetes, such as nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and death, can be delayed or prevented with appropriate treatment of elevated blood pressure, lipids, and blood glucose.14
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Recommended Reading: What Is A Good Diet For Type 2 Diabetes