Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Kris, a 9-year old, loves dancing. She is a famous dancer at school, and a good one too. In between classes and dance lessons is her love for juices and carbonated drinks. She love it so much that even when everyones asleep she would sneak a pack of powdered juice and mix it inside her bedroom, and drank the whole pitcher by herself. You see, diabetes mellitus runs in Kris family, and it did not take long enough for her parents to found out that she has one too.
Nursing Management For Diabetes Mellitus
Creating A Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes
When creating a nursing care plan for diabetes youll need to include the following:
- Expected Outcomes
A good nursing care plan is a written version of the nursing process. For each nursing diagnosis, you might have multiple interventions and outcomes. Youll evaluate each, instead of the diagnosis as a whole. Think of this as the problem, the proposed solution, what you think will happen, and then what actually happened. When you work on the floor you might create your nursing care plan for diabetes in your head, but if youre in nursing school youll like have to write it down by hand or use a digital template.
If you struggle with writing good nursing care plans, Nursing.com has many different nursing care plan examples and even a course.
Read Also: How Do Diabetics Get Energy
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose
May be related to lack of adherence to diabetes management inadequate blood glucose monitoring practices fluctuating physical activity level
blood glucose levels below or above normal levels
Desired Outcome identifies factors that may lead to unstable blood glucose levels verbalizes understanding of balancing body and energy needs verbalizes plan in modifying identified risk factors to prevent shifts in glucose level maintains blood glucose levels within the normal range
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Following is the nursing care plan for diabetic foot ulcers:
- Take care of the skin integrity which is generally caused because of immobilization.
- Take care of the pain which can either be associated with any infection or with any surgery.
- Keep an eye on the prevalent infection risks in your patients.
- Encourage your patients to seek proper treatment on time.
Sometimes patients also suffer from depression and stress.
Addressing these issues is important because it can impact the blood glucose levels in a very bad way.
You May Like: Are Protein Shakes Good For Diabetics
What Is The Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes
As you probably know, diabetes is one of the most common diseases. Maybe a part of the patients you saw today are diabetic.
According to the research studies more than 34 million US residents are diabetic.
This data shows that diabetes is very much prevalent and because of this reason, nurses need to have the proper knowledge about the disease and the skills to take care of their patients.
And at this point, a well-framed nursing care plan for diabetes comes into play.
So, before moving to the nursing care plans, first discuss diabetes and its types.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes or diabetes mellitus is a health problem where the levels of blood glucose are high. The most common symptoms of diabetes include:
Generally, there are three types of diabetes and the treatment and nursing care plan for diabetes depends upon these types.
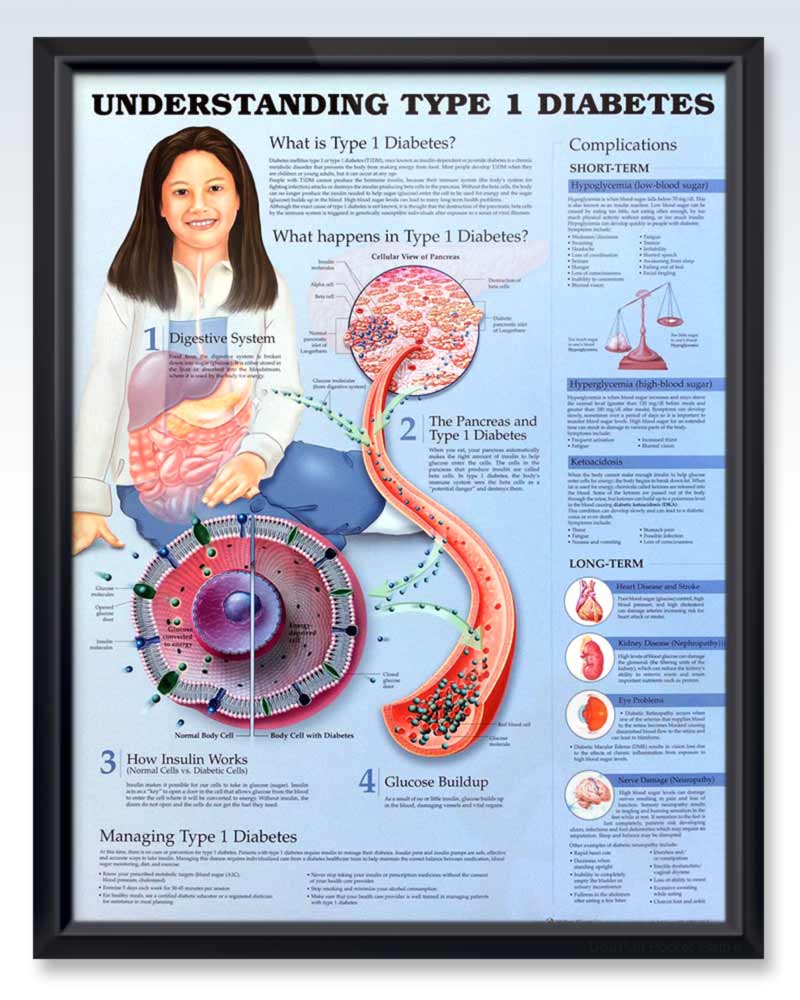
TYPE 1 DIABETES
Type 1 diabetes is also known as juvenile-onset and insulin-dependent diabetes. This type is very common in children.
In general, it is an autoimmune problem in which the body starts attacking the pancreas which in turn impacts insulin production.
TYPE 2 DIABETES
Type 2 diabetes is more prevalent than type 1.
In this health condition, the pancreas can not produce enough insulin required by the body.
In simple words, the body becomes resistant to insulin.
This type of diabetes can be easily controlled by making some changes in the lifestyle and regular intake of oral hypoglycemic agents.
GESTATIONAL DIABETES
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes 5
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Fluid Volume Deficit due to osmotic diuresis
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate adequate hydration and balanced fluid volume
| Nursing Interventions for Diabetes | Rationales |
| Assess vital signs and signs of dehydration. | Hyperglycemia may cause Kussmauls respirations and/or acetone breath. Hypotension and tachycardia may result from hypovolemia, or low levels of intravascular volume. |
| Commence a fluid balance chart, monitoring the input and output of the patient. | To monitor patients fluid volume accurately and effectiveness of actions to monitor signs of dehydration. |
| Start intravenous therapy as prescribed. Encourage oral fluid intake of at least 2500 mL per day if not contraindicated. | To replenish the fluids lost from polyuria and to promote better blood circulation around the body. |
| Educate the patient on how to fill out a fluid balance chart at bedside. | To help the patient or the guardian take ownership of the patients care, encouraging them to drink more fluids as needed, or report any changes to the nursing team. |
| Monitor patients serum electrolytes and recommend electrolyte replacement therapy to the physician as needed. | Sodium is one of the important electrolytes that are lost when a person is passing urine. Hyponatremia or low serum sodium level may cause brain swelling. |
Recommended Reading: Tooth Removal For Diabetic Patient
The Initial Causes Nursing Teaching Plan For Diabetes Type 1
Type 2 diabetes is a common condition in many people. This type is caused by a lack of insulin and is a result of an unhealthy lifestyle. The bodys inability to process glucose from the blood can damage many parts of the body, including the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Fortunately, there are some things you can do to avoid diabetes. Here are five tips to help you lower your risk: Eat more vegetables and fruits, get regular exercise, and avoid smoking.
High levels of triglycerides in the blood are another factor that can cause diabetes. These triglycerides are caused by a buildup of cholesterol in the blood. A high triglyceride level causes the body to misrepresent insulin as a molecule, which causes glucose to build up in the blood. A simple blood glucose test can confirm your diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. By following these tips, you can begin living a healthy life and avoid the complications of diabetes.
A person with type 2 diabetes must consume less sugar. Glucose causes thirst and dehydration because the body releases energy stores into the bloodstream instead of using insulin. If untreated, diabetes can lead to weight loss and diabetic ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition whereby the cells are deprived of energy. To prevent the condition, you must make sure that your diet is low in glycemic load and that you exercise regularly.
What You Need To Know About Diabetes Nursing Teaching Plan For Diabetes Type 1
One of the most common signs of diabetes is excessive thirst. You may also feel more hungry and pee more than usual. Its important to check your blood sugar as soon as you start to notice these symptoms. If your blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, you should immediately eat 15 grams of carbohydrates. Then, check it again fifteen minutes later. If you cant eat that much carbohydrate at once, you can try oral glucose.
Despite the many complications of type 1 diabetes, you can still find ways to manage it. By reading about diabetes, youll be better prepared to live a healthy and happy life. You can avoid diabetes by making healthy choices. In fact, there are many treatments available for type 1 diabetes. In some cases, a patient may even experience an improvement in their overall health after the transplant. In some cases, you can even reverse your diabetes through a simple procedure.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type. Most people with type 1 diabetes have type 2 diabetes. They both require insulin to regulate their blood sugar. If youre overweight, you may have type 2 diabetes. If youre concerned about diabetes, its important to learn about it. Your doctor can provide you with more information on your condition, including tips on how to cope with it. You should never be afraid to ask questions. Just remember, youll have to answer them. Youre not alone.
Recommended Reading: Can You Donate Blood If Diabetic
What Should A Diabetes Care Plan Include
Diabetes management requires a balance of healthy eating, regular physical activity, and blood sugar monitoring.
Your diabetes care plan should include your blood sugar management goals and methods, such as insulin dosages, device settings, and medications.
The outlines a diabetes care plan based on your daily, monthly, and other regular-interval activities. The daily parts of your diabetes care plan should include:
| Points |
|---|
| Get a dilated eye examination. Get a cholesterol test. See a doctor for a complete foot check. |
At every phase of your care plan, its important to identify when you should call your healthcare team and who else will help you manage your health daily or in case of an emergency.
How Will Dsmes Help Me
DSMES can help you improve your blood sugar levels so you can prevent or delay serious diabetes complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and vision loss. This improvement can help you avoid emergency care, save money on health care costs, and improve your quality of life. People who participate in DSMES are more likely to have better overall health.
Recommended Reading: Any Breakthrough In Diabetes Treatment
Patient Centered Diabetes Education
Traditional patient education models focused on disease-oriented patient education and were physician centered. Newer models are known as health-oriented patient education and include empowerment strategies that place the patient rather than the physician at the center this strategy sees the patient as a partner in decision making. Based on adult learning theory, psychodynamic motivational theories, and the Chronic Care Model, diabetes educators now focus on strategies that help patients help themselves.
The goal of diabetes education is to help patients manage their own chronic disease with the resources of a team of healthcare professionals supporting them. The role of the diabetes educator has changed from sage on stage to guide on the side. Effective diabetes education begins with a paradigm shift to a role as health coach and often cheerleader instead of professional laying down orders for the patient to follow.
Each patient should have a partnership role in making medical decisions. That means patient education must be customized to meet the individuals needs and include the patients goals and desires. Instead of a diabetes educator simply writing a patients diet and exercise plan, an effective diabetes educator needs to assess the patients goals, abilities, barriers, interests, and resources and develop a goal plan together. Adherence improves because patients are working toward their own goals and not those dictated to them.
Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity
If your patient has developed peripheral neuropathy because of their diabetes, the risk for a wound or ulcer developing is significantly increased. Often patients with neuropathy have a lowered sensation of pain, and so they may not realize if they have received an injury to their feet or if a pressure ulcer is developing.
Recommended Reading: Blue Cross Blue Shield Diabetic Supplies
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes 4
Nursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased metabolic energy production as evidenced by overwhelming lack of energy, verbalization of tiredness, generalized weakness, blood sugar level of 210 mg/dL, and shortness of breath upon exertion
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstration active participation in necessary and desired activities and demonstrate increase in activity levels.
| Nursing Interventions for Diabetes | Rationales |
| Assess the patients activities of daily living, as well as actual and perceived limitations to physical activity. Ask for any form of exercise that he/she used to do or wants to try. | To create a baseline of activity levels and mental status related to fatigue and activity intolerance. |
| Encourage progressive activity through self-care and exercise as tolerated. Explain the need to reduce sedentary activities such as watching television and using social media in long periods. Alternate periods of physical activity with rest and sleep. | To gradually increase the patients tolerance to physical activity. |
| Teach deep breathing exercises and relaxation techniques. Provide adequate ventilation in the room. | To allow the patient to relax while at rest. To allow enough oxygenation in the room. |
| Refer the patient to physiotherapy / occupational therapy team as required. | To provide a more specialized care for the patient in terms of helping him/her build confidence in increasing daily physical activity. |
What Is A 504 Plan For Diabetes Care In School
If you or a loved one is in school and have diabetes, you are protected by section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 to create a 504 plan. This plan ensures that the school provides a medically safe environment and fair treatment. The ADA provides sample 504 plans, and the school may have examples as well.
Your diabetes care plan isnt just for an emergency. You may also need school or work contacts to know your plan if you need extra help or time. Examples could include:
- letting a cafeteria or meal plan know you need low carbohydrate foods or are counting carbohydrates
- making sure you have regular breaks to check your blood sugar and inject insulin
- identifying a refrigerator where you can store your meals or insulin safely
Employment rights can also be a big issue when it comes to diabetes care, and Americans have many different employment rights via the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990. Some of those rights under federal law might include questions relating to the following:
- What are reasonable accommodations at work?
- Do I have a right to medical leave to take care of my diabetes?
- Can my employer require me to get a medical examination because of my diabetes?
- What if my employer fires me over my diabetes management?
The ADA is a key organization that addresses employment and school rights for the Diabetes Community, and it has an entire division aimed at legal advocacy for those who might be facing these workplace or school situations.
Read Also: Glucose Tolerance Test In Pregnancy
Diabetes Classification And Pathophysiology
There are many types of diabetes, and they can be usefully classified into four groups. The condition of prediabetes will also be discussed.
Type 1 diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease caused by genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers . It is characterized by pancreatic cell destruction and lack of insulin production . The onset typically occurs during childhood or adolescence, and type 1 diabetes accounts for ~ 5-10% of all disease cases in the United States . In a very small percentage of cases of type 1 diabetes, the patients do not secrete insulin, but there is no evidence of autoimmunity these patients have what is called idiopathic type 1 diabetes .
Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and a relative lack of insulin production . Type 2 diabetes is also caused by an interplay of genetics and environment, but in this form of the disease, the environmental factors that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes have been identified, and many of them are modifiable, e.g., diet, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle .
Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes is defined as insulin resistance and abnormal glucose tolerance that occurs during pregnancy . Approximately 9% of all pregnancies are complicated by gestational diabetes7 Many women who have gestational diabetes will develop the disorder in subsequent pregnancies, and approximately 50% will eventually develop type 2 diabetes .
Risk For Deficient Or Imbalanced Fluid Volume
When blood sugars rise, the body attempts to remove that excess sugar by increasing the release of fluid through excessive urination and thirst. The increase may cause the body to become dehydrated and have electrolyte imbalances. When choosing a diagnosis, you may select either deficient or imbalanced fluid volume depending on your patients situation.
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Blood Sugar And Cholesterol
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes 10
Risk for Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management related to new-onset illness, treatment management that is not well understood, and a difficult medical management secondary to diabetes mellitus.
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate awareness of diabetic self-care techniques,
will express verbally the comprehension of the diabetes disease process and its possible complications, and the patient will be able to perform all necessary procedures accurately and give discuss reasons for the actions.
Overcoming Barriers To Effective Teaching
Many barriers prevent healthcare professionals from teaching effectively, or even at all. The first barrier is the fear of inadequate knowledge about the disease. Some dont know all the facts about diabetes and feel embarrassed to admit it in front of a patient, so they just omit the teaching. You do not have to be a certified diabetes educator to teach patients about diabetes. Healthcare professionals who teach about diabetes include lay health workers, health aids, medical assistants, nurses, pharmacists, physical therapists, social workers, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and certified diabetes educators.
Clearly knowledge is needed before you can teach, however research confirms the adage that people care more about how much you care and not just how much you know . Creating relationships of trust, non-judgment, and emotional safety are foundational for effective teaching.
Barriers to teaching also include poor communication, lack of time, low priority in acute settings, low or no reimbursement for teaching, low resources, and low interest from the patient yet making sure the information is correct and correctly understood are critical to good patient outcomes. Overcoming these barriers has been the quest of the American Association of Diabetes Educators , and the organization is a wonderful resource for content, study guides, and even lesson plans for teaching .
Clinical Scenario
Recommended Reading: One Touch Ultra Glucose Meter