How Diabetes Can Affect Your Eyes
There are several different ways that diabetes can cause eye complications. All of the following diseases can cause severe vision loss and even blindness.
Your vision is just one reason that regular blood tests should be performed and blood sugar levels need to be checked. Its also vital that annual eye appointments be made to track vision for any complications.
How Diabetes Affects The Body And Eyes
Diabetes occurs when the body doesnt convert sugar into energy the way it should. This in turn leads to high blood sugar levels. If your sugar levels stay high, it can damage organs throughout the body, including the eyes. Over time, the effects of diabetes begin to cause inflammation in the tissues around the eyes.
When this happens, blood flows more slowly than it should through the blood vessels in the eyes, especially the vessels that lead to the retina. Because the retina plays a central role in producing the electrical signals your brain uses to create the images you see, restricted blood flow to the retina can compromise your vision. These developments cause a condition known as diabetic retinopathy.
Treatment Options For Diabetic Eye Disease
Your provider will work with you to develop an optimal treatment plan. Two of the most common strategies to manage diabetic eye disease include controlling your diabetes and medical management.
Control your diabetes
We typically recommend three key steps to control your diabetes:
Eye medication
During regular office visits, your ophthalmologist can administer medications directly into the eye. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy is a commonly used medication treatment to reduce retinal swelling and inhibit blood vessel growth in the retina.
Another option is corticosteroid medication, which can reduce inflammation caused by diabetic retinopathy.
Eye surgery
To find out whether you or a loved one might benefit from a check-up with an ophthalmologist, call or request an appointment online.
You May Like: What Diet Plan Is Best For Type 2 Diabetes
How Diabetes Affects Your Eyes
Diabetes affects more than 34 million people in the United States, and prediabetes impacts an additional 88 million Americans. While diabetic complications are commonly thought of as associated with heart, kidney, or nerve damage, diabetes also puts you at risk for vision loss and other eye health problems. In fact, diabetes is the leading cause of vision loss in people ages 18 to 64 years old, according to the American Diabetes Association .
To help promote eye health, we are examining the ways in which diabetes can impact your eyes, eye complications you may experience, and how you can treat these diabetes-related eye conditions.
Ways Diabetes Can Affect Your Vision And Eyes
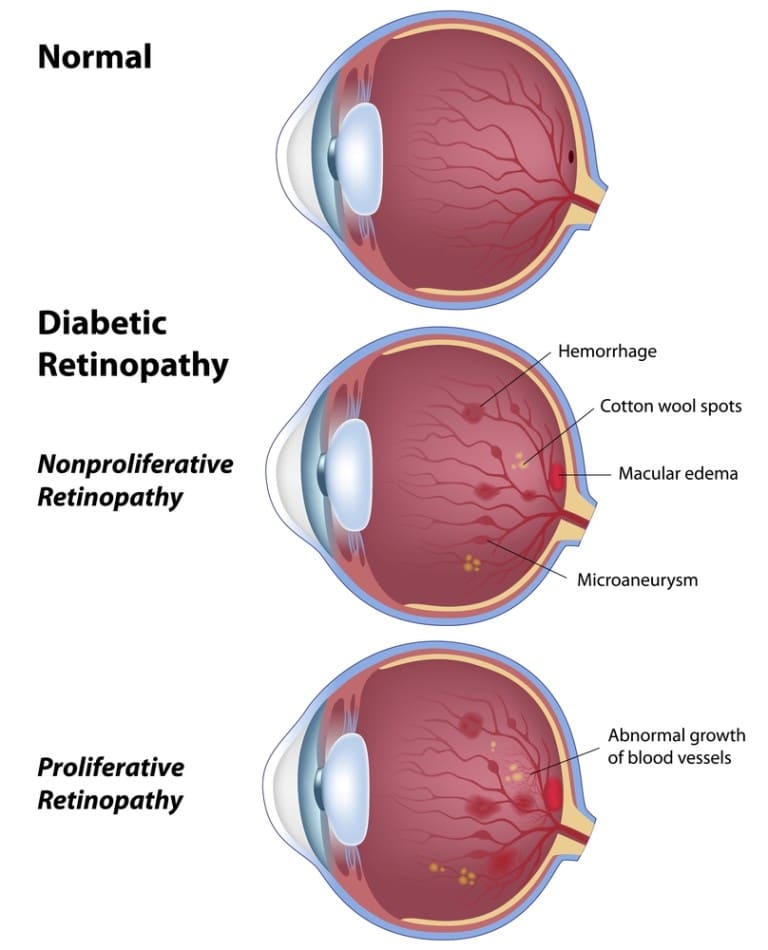
Did you know that people with diabetes are 20 times more likely to get eye diseases than those without it? There are three major eye conditions that diabetics are at risk for developing: cataracts, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy. To prevent these sight-threatening diseases, it’s important to control your blood sugar level and have your eyes checked at least once a year by an eye doctor.
Don’t Miss: 1 Hour Pregnancy Glucose Test
Diabetes And Your Eyes: 4 Things To Know
Why an ophthalmologist says its crucial to keep up with your eye exams.
When you think of diabetes, you probably think of glucose. Insulin. High blood pressure. Your pancreas.
But what about your eyes?
Although they may not be the first thing you think of when it comes to diabetes, your vision can be heavily impacted, and permanently damaged by it, with one in three people aged 40 or older with diabetes showing signs of diabetic retinopathy, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease.
Your eyes are an important window into the health of the rest of your body, said , an ophthalmologist at the Kellogg Eye Center who specializes in diseases of the retina and vitreous. Below, Rosenthal shares essential information about the disease and eye health.
Know Your Blood Sugar Blood Pressure And Cholesterol Levels
It can be easier to keep your blood sugar levels, blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control if you know what level they are and monitor them regularly.
The lower you can keep them, the lower your chances of developing retinopathy are. Your diabetes care team can let you know what your target levels should be.
Read Also: Different Types Of Insulin Pumps
How Diabetic Retinopathy Is Diagnosed
During your eye exam, your eye doctor will check how well you see the details of letters or symbols from a distance. Your doctor will also look at the retina and inside of your eyes and may use a dye to reveal leaky blood vessels. If it turns out you have diabetic retinopathy, your eye doctor may want to check your vision more often than once a year.
You should be checked for diabetic retinopathy immediately if youre diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. If you have type 1 diabetes, you should be checked within 5 years of your diagnosis and then regularly thereafter, typically every year. The sooner youre treated for diabetic retinopathy, the better that treatment will work.
- Difficulty reading or doing detail work
How Does Diabetes Develop
Researchers arent sure about the exact cause of type 1 diabetes. However, type 2 diabetes is much more well known. Insulin is a hormone that the body produces which allows the sugar in your blood to access the cells in your body. Sugar is necessary for your cells to create energy, and insulin resistance usually occurs after a specific cycle develops.
First, a person is, for whatever reason, unable to make enough insulin to cover all the glucose that they eat. The body tries to make extra insulin to make up for the shortfall. The pancreas is unable to keep up with the increased need for insulin, and excess sugar floats throughout the blood doing damage instead of being absorbed by cells to create energy.
Eventually, insulin becomes less effective at helping glucose enter the cells and blood sugar levels rise ever higher. This effect is known as insulin resistance, and in type 2 diabetes it takes place gradually. Due to the gradual nature of insulin resistance, doctors recommend certain lifestyle changes to either slow the advance of the disease or halt its progress altogether.
Don’t Miss: Best Weight Loss Plan For Type 2 Diabetes
How To Tell If Diabetes Is Affecting Your Eyes
by Matossian Eye Associates | Nov 6, 2020
It goes without saying that individuals with diabetes must give the highest priority to getting blood sugar stabilized. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a whole host of complications and body damage that theres simply not space to explore here. So, well stick to what we know best: vision care.
Below are four of the most common eye complications from diabetes, plus the single biggest thing you can do to avoid them:
Recent Posts
How Diabetes Can Affect The Eyes
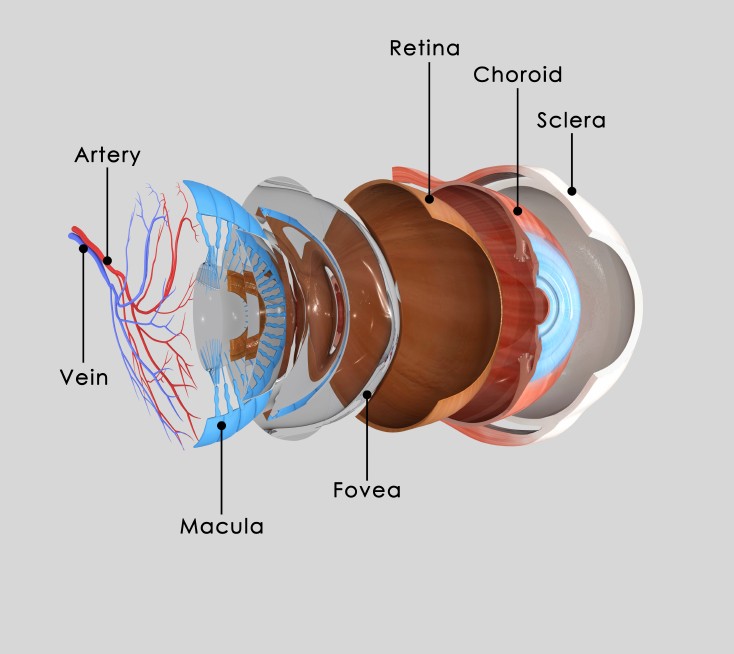
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of cells at the back of the eye that converts light into electrical signals. The signals are sent to the brain which turns them into the images you see.
The retina needs a constant supply of blood, which it receives through a network of tiny blood vessels.
Over time, a persistently high blood sugar level can damage these blood vessels in 3 main stages:
- background retinopathy tiny bulges develop in the blood vessels, which may bleed slightly but do not usually affect your vision
- pre-proliferative retinopathy more severe and widespread changes affect the blood vessels, including more significant bleeding into the eye
- proliferative retinopathy scar tissue and new blood vessels, which are weak and bleed easily, develop on the retina this can result in some loss of vision
However, if a problem with your eyes is picked up early, lifestyle changes and treatment can stop it getting worse.
- eye pain or redness
- difficulty seeing in the dark
These symptoms do not necessarily mean you have diabetic retinopathy, but it’s important to get them checked out.
Do not wait until your next screening appointment.
Don’t Miss: Low Blood Sugar Heart Rate
Risks And Side Effects
Possible risks and side effects of anti-VEGF injections include:
- eye irritation or discomfort
- floaters or a feeling of having something in your eye
- watery or dry, itchy eyes
There’s also a risk that the injections could cause blood clots to form, which could lead to a heart attack or stroke. This risk is small, but it should be discussed with you before you give your consent to treatment.
The main risk with steroid injections is increased pressure inside the eye.
Do Floaters From Diabetes Go Away
If the amount of bleeding is small, you might see only a few dark spots . In more-severe cases, blood can fill the vitreous cavity and completely block your vision. Vitreous hemorrhage by itself usually doesnt cause permanent vision loss. The blood often clears from the eye within a few weeks or months.
Recommended Reading: Does Gastric Sleeve Cure Diabetes
How Does The Eye Work
To understand the eye disorders that can be caused by diabetes, its good to know how the eye works. The eye is covered by a strong outer membrane which is clear and curved. The curved part is the cornea which focuses light and helps protect the eye.
Once light passes through the cornea, it travels through the fluid-filled anterior chamber through the pupil and then through the lens that helps with focusing. The light then passes through another fluid-filled chamber in the middle of the eyeball and hits the retina in the back of the eye.
The retina records the light images that get focused on it and converts those images to electrical signals. The electrical signals are sent to the brain via the optic nerve and the brain decodes them. The macula, part of the retina, is highly specialized for seeing detail. Blood vessels in and behind the eye supply the macula with nourishment.
Long Term Effects Of Diabetes
Over time, uncontrolled diabetes or chronic hyperglycemia can cause damage to the blood vessels throughout the body, including those in your eyes.
When the blood vessels in the retina become damaged, diabetic retinopathy, a serious eye disease, can develop.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when the retinal blood vessels leak blood and fluid into the retina, causing blurred vision and eventually leading to vision loss.
- Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of permanent vision loss among people with diabetes.
- Half of the people diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy will also be affected by permanent vision loss from diabetic macular edema.
Diabetic macular edema occurs when the fluid from the damaged blood vessels also leaks into the macula, the center of the retina, causing central vision loss and loss of vision for fine details.
Treatments to help slow down the progression of these sight-threatening diseases are aimed at preventing further vision loss. It is therefore crucial to visit your eye doctor for regular eye exams, as per your doctors recommendations.
Read Also: Possible Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes
What Other Eye Diseases Are Common Among People Living With Diabetes
Cataract is the clouding of the lens in the eye, which can cause vision to become blurry and colors to become dull. Generally, cataracts are treatable with surgery that can help restore your vision. Aside from aging, diabetes is the most common risk factor for cataract.
Glaucoma, the silent thief of sight, causes damage to the optic nerve and possible loss of side vision, usually caused by an increase in fluid pressure inside the eye. Vision loss will start without any noticeable symptoms leading to tunnel vision. If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to permanent loss of vision. Once vision is lost to glaucoma, it cannot be restored. Medications and surgery can delay progression of this disease.
Risk Factors For Diabetic Retinopathy
Anyone with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes can develop diabetic retinopathy. The longer you have diabetes, the more likely you are to develop it. These factors can also increase your risk:
- Blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels that are too high.
- Race/ethnicity: African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and American Indians/Alaska Natives are at higher risk.
If you have diabetic retinopathy, low-vision aids such as magnifying glasses and special lenses can help. Ask your eye doctor to refer you to a low-vision specialist.
Read Also: How To Treat Diabetes Without Insulin
This Is How Diabetes Can Affect Your Eyes
When you think of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, its only natural to also think of high blood sugar. But do you know why prolonged high blood sugar is even a problem to begin with?
It turns out that ripple effects from diabetes-induced high blood sugar can harm so many physiological systems, including the eyes in a phenomenon known as diabetic eye disease. Heres what you need to know about it, plus how to lower the odds it will happen to you.
A key condition in this group is diabetic retinopathy, the most common cause of vision loss in people who have diabetes, according to the National Eye Institute . It happens when persistently high blood sugar damages blood vessels in the retina, the thin piece of tissue at the back of the eye that processes light.
Then theres the related condition diabetic macular edema , a repercussion of diabetic retinopathy that causes a buildup of fluid in a part of the retina called the macula, the NEI explains. The macula is responsible for the straight-ahead vision used for things like reading, driving, and seeing faces. According to the NEI, about half of people with diabetic retinopathy will go on to have DME.
Both diabetic retinopathy and DME can cause severe vision loss or even permanent blindness, the NEI says.
If youve caught diabetic retinopathy early enough, getting your blood sugar under control may be treatment enough for the time being, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Related:
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Eyes
Diabetes can lead to blurry vision in several ways.
In some cases, its a minor problem that you can resolve by stabilizing your blood sugar or taking eye drops. Other times, its a sign of something more serious thats worth discussing with your doctor.
In fact, blurred sight is often one of the first warning signs of diabetes.
Also Check: What Is Fasting Glucose Level
How The Eye Is Affected
The structure of the eye is like a camera. Light passes through the transparent front lenses, as if through the lenses of a camera, until it reaches the back wall of the eye. This wall contains a very thin piece of light-sensitive tissue: the retina.
The tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina can be damaged by diabetes. The damage can cause the blood vessels to become leaky, like a water hose with holes in it. This is called non-proliferative retinopathy. Fluid leaks out of the blood vessels and into the retinal tissue which can cause vision problems. This causes the retina to thicken, creating blurred vision. The swelling associated with diabetes in the macula, the central part of the eye responsible for staring straight ahead, called diabetic macular edema.
In another process, blood vessels damaged by hyperglycemia close, and a series of events begin. Starving retinal tissue produces growth causing new blood vessels to form on the surface of the retina. When the new blood vessels form, its called proliferative retinopathy.
These new blood vessels are weak and can easily break and bleed. This leads to scar tissue, which can build up on the back wall of the eye and stretch the retina, eventually separating it from the back of the eye. This condition is known as retinal detachment, and it can happen suddenly or slowly over time.
You can have 20/20 vision and still have diabetic retinopathy. Some of the early signs include:
Glaucoma Laser Treatments And Surgical Options
Depending on the type of glaucoma associated with diabetes, different treatment options are available. Primary open-angle glaucoma patients are treated the same as non-diabetic patients with medications, lasers, and surgery, as needed. For neovascular glaucoma, lasers and injections can be used to treat the diabetic retinopathy, but the angle-closure glaucoma usually needs to be treated with a shunt to help restore drainage. A combination of these glaucoma treatments might be required to treat steroid-induced glaucoma, which can be a side-effect of steroid injections used to treat diabetic macular edema.
Recommended Reading: Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics