When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Two hours after a meal.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
Also Check: Freestyle Lite Blood Glucose Test Strips
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels For People Without Diabetes
Normal blood glucose ranges for people without diabetes are:
- Fasting: 70-99 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after a meal: less than 140 mg/dL
< p class=pro-tip> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=/blog/blood-sugar-spikes-exercise> how exercise can affect blood sugar levels< /a> < /p>
Most blood sugar charts show recommended levels as a range, allowing for differences between individuals. Some people may find they have much lower blood sugar while others hover a bit higher, but the ranges above are considered diagnostic cut-offs by medical professionals.
Note: The Signos app uses a slightly different range to support weight loss, as youâll learn about more below.
Read Also: Is Truvia Sugar Good For Diabetics
A High Sugar Level After A Meal
Related Articles
It’s normal for your blood sugar level to rise after you eat, especially if you eat a meal high in refined carbohydrates. But if your blood sugar rises more than most people’s, you might have diabetes or pre-diabetes, a condition that indicates a strong risk for developing diabetes in the future. If you already have diabetes, you doctor will recommend keeping your blood sugar within a prescribed range. A glucose tolerance test, done one to three hours after you eat a high-carbohydrate meal, can check your blood sugar levels.
Does A Blood Sugar Spike Mean You Have Diabetes

Occasional high spikes donât mean you have diabetes. Itâs normal for your blood sugar to go up after eating a meal high in carbohydrates or even due to lifestyle habits and events. Besides food, your blood sugar can be affected by stress, lack of sleep, age, menstrual cycle, physical activity, and even being sick.
What affects one person’s blood sugar may also affect yours differently. We can all have different responses to food, so monitoring the overall trend of your blood sugar gives you the most insight into your overall health.
However, while infrequent spikes aren’t a problem, if they happen more regularly, it’s time to take a closer look at what’s contributing.
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/mitigate-high-glucose-spikes”> how to mitigate glucose spikes to avoid fat storage< /a> < /p>
Don’t Miss: Can I Buy A Diabetes Test Kit
How Long After Eating Does Blood Sugar Return To Normal
Everyone is different.
If youre diabetic you should know how long it takes you to return to a normal level after a meal. Factoring in:
- Your beginning blood glucose
- How early you take supplements, medication or insulin before a meal
- How many supplements, medication or insulin do you take
- How many and the type of carbs you eat.
Knowing comes from your experience. Join our community and share your experience with us.
Dont Miss: What Does It Mean When You Have Diabetes
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Recommended Reading: Is Glaucoma Related To Diabetes
Whats Considered A Normal Glucose Level
Your doctor will likely test your blood glucose levels as a screening test for diabetes during a standard yearly check-up. Additionally, many people track their glucose at home with an over-the-counter finger-prick test. When you check blood glucose , either at a doctors office or with a home finger stick glucose monitor, the results are in milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood.
One of the most common glucose measurements is fasting plasma glucose or fasting blood glucose , and its found by checking blood glucose levels after not having any calories at least eight hours before the test. According to the American Diabetes Association , people can be classified into three categories depending on their fasting plasma glucose levels: normal, prediabetes, and diabetes. To be considered normal, fasting glucose must be under 100 mg/dl.
Of note, CGM devices measure interstitial glucose levels compared to blood/plasma glucose levels measured in the FPG tests. While interstitial glucose and blood/plasma glucose levels correlate highly, they are not precisely the same, and diagnoses are not made from interstitial measurements.
Below is a summary overview of data about 24-hour glucose trends in nondiabetic individuals wearing CGM to gain a better understanding of whats normal.
Blood Sugar Level Chart By Age
Blood sugar levels tend to rise with age due to an increase in insulin resistance and decrease in insulin sensitivity. In one study by the National Health Institute , each extra decade of age was linked to a 2.7 mg/dl increase in fasting glucose, and a 4.5 mg/dl increase in 2-hour post-prandial glucose levels.
Read Also: Sure Comfort Insulin Syringes 30 Gauge
How To Do A Finger
Your healthcare team will show you how to do it the first time, but these are the key steps:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water. Dont use wet wipes as the glycerine in them can affect the test result. Make sure your hands are warm so its easier to get blood and wont hurt as much.
- Take a test strip and slot it into the meter to turn it on. Some meters will have tests strips built in.
- Remove the cap from your finger prick device and put in a new lancet. Then put the cap back on and set the device by pulling or clicking the plunger.
- Choose which finger to prick but avoid your thumb or index finger . And dont prick the middle, or too close to a nail. Place the device against the side of your finger and press the plunger. Use a different finger each time and a different area.
- Take your meter with the test strip and hold it against the drop of blood. Itll tell you if the test strip is filled, usually by beeping.
- Before you look at your reading, check your finger. Use a tissue to stop bleeding, then use it to take out the lancet and throw it away in your sharps bin.
- You can use the same tissue to take out the test strip and throw that away too. Taking out the strip will usually turn the meter off.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: When To Check And Why
Managing diabetes is one part investigation and two parts action. Unlike some other diseases that rely primarily on professional medical treatment, diabetes treatment requires active participation by the person who has it. Monitoring your blood sugar level on a regular basis and analyzing the results is believed by many to be a crucial part of the treatment equation.
When someone is first diagnosedwith diabetes, he is usually given a blood sugar meter and told how and when to use it, as well as what numbers to shoot for. However, the advice a person receives on when to monitor and what the results should be generally depend on his type of diabetes, age and state of overall health. It can also depend on a health-care providers philosophy of care and which set of diabetes care guidelines he follows. At least three major health organizations have published slightly different recommendations regarding goals for blood sugar levels.
There is some common ground when it comes to blood sugar monitoring practices. For example, most people take a fasting reading before breakfast every morning. Some people also monitor before lunch, dinner and bedtime some monitor after each meal and some monitor both before and after all meals. However, when monitoring after meals, some people do it two hours after the first bite of the meal, while others prefer to check one hour after the start of a meal.
Also Check: Cheapest Insulin In The World
Why Is It Important To Reduce The Size And Duration Of These Spikes
Reducing these spikes may help you to increase the amount of time you spend in your target blood sugar range , which will have a positive impact on your future health. You should consult your healthcare team to understand the best target range for you, as this will differ from person to person. However, the International Society for Paediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommends a target of 5.0-10.0 mmol/L .
Symptoms of a high blood sugar level also vary in individuals, but they may cause you to feel thirsty, tired, stressed and need to go to the toilet a lot. In the short term, by avoiding prolonged high blood sugar readings after eating, you should also reduce the occurrence of these symptoms and improve your energy, cognitive and athletic ability and overall mood.
Read Also: What Does Impaired Fasting Glucose Mean
Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their health care provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
Read Also: Does White Vinegar Lower Blood Sugar
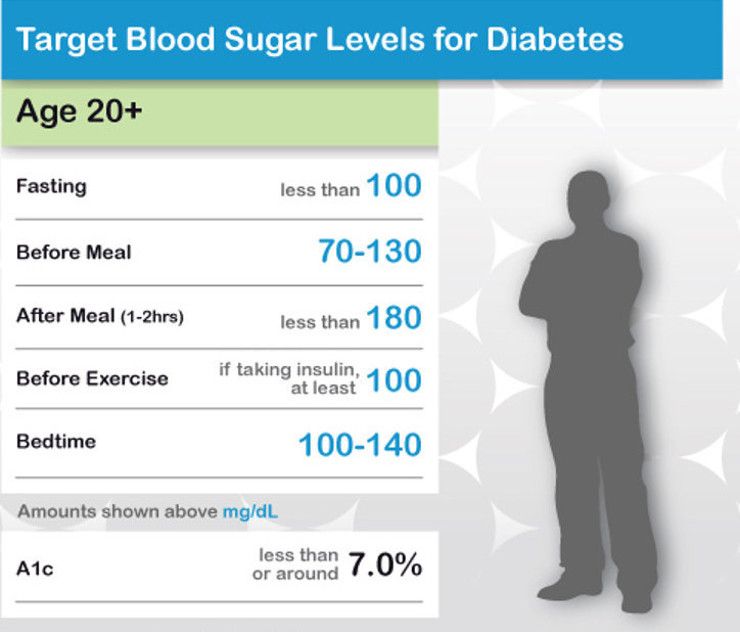
What Should My Blood Sugar Level Be When I Wake Up
These are goal levels, according to The Joslin Diabetes Center:
- Under 100 mg/dl if you do not have diabetes.
- 70 to 130 mg/dl if you have diabetes.
The dawn effect can often lead to a high morning measurement in diabetes. This is your body’s tendency to get ready for the day by raising blood sugar by increasing levels of counter-regulatory hormones ââ¬â the ones that counteract insulin as in normal blood sugar. For people with diabetes, you do not have the capacity to counterbalance this rise in blood sugar, so levels can be dangerously high.
Ways to lower your morning blood sugar value include:
- Eating dinner earlier
- Checking your medications ââ¬â making sure you are taking them properly and asking your doctor if they are correct
- Going for a walk after dinner
- Including protein with your dinner
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
Read Also: Finger Stick Glucose Test Normal Range
How Soon After Waking Up Should I Test My Blood Sugar
Blood sugar testing at home
In most cases, doctors ask people to measure fasting blood sugar immediately upon waking and before they have anything to eat or drink. It may also be appropriate to test blood sugar before eating or 2 hours after a meal, which is when blood sugar returns to normal levels.
How To Prevent Post
Taking fast-acting prandial, or mealtime, insulin 2030 minutes before eating a meal can reduce blood sugar spikes because the insulin will begin to work when glucose from food starts to enter the bloodstream. Additionally, a portioned diet rich in foods like vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and fruit can cause a slower rise in blood sugar and help prevent post-meal spikes. Your healthcare provider can help you determine what strategy is best for you.
Also Check: Vital Nutrients Blood Sugar Support
When Things Go Awry
When we eat food, the pancreas goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue, and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose . If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis . Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, its all about the blood glucose.
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
You May Like: What Happens If Your Blood Sugar Is Too Low
Determining The Right A1c Goal For You
Just because a normal blood sugar range of 70 to 130 mg/dL is considered the healthiest doesnt necessarily mean thats the appropriate goal range for you especially if you have type 1 diabetes, or take insulin as a person with type 2 diabetes.
The reason this may not be the right goal for you is that extremely tight blood sugar management in people taking insulin can potentially lead to frequent low blood sugars which can be dangerous.
Achieving extremely tight blood sugar management, like a range of 70 to 130 mg/dL, also often requires a strict nutrition plan, more frequent than usual blood sugar monitoring, precise medication management, and most importantly, years of experience studying your blood sugar levels.
What Should Your Blood Sugar Be 3 Hours After Eating
1-hour post-meal glucose values average 121-123 mg/dl for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. 3-hour post-meal glucose values were around 97-114 mg/dl. Peak post-meal values appeared to be around 60 minutes after eating.
Is blood sugar higher 1 hour or 2 hours after eating?
A: The highest peak blood sugar levels generally occur 1 hour after a meal if carbohydrates were eaten. At 2 hours after a meal, protein begins to break down into blood sugar which could again increase blood sugar.
Don’t Miss: Nursing Teaching Plan For Diabetes Type 1