Different Types Of Diabetes
Diabetes is characterised by the bodys inability to use glucose. There are different types of diabetes including:
- Type I diabetes due to a lack of insulin
- Type 2 diabetes due to a complex mix of insulin not working properly and insufficient insulin
- Gestational diabetes a form of diabetes that some women develop during their pregnancy. Pregnancy blocks the action of insulin and can bring out a tendency to diabetes. Mothers with gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing diabetes in subsequent pregnancies and in later life.
How Can I Prevent Or Reverse Insulin Resistance And Prediabetes
Physical activity and losing weight if you need to may help your body respond better to insulin. Taking small steps, such as eating healthier foods and moving more to lose weight, can help reverse insulin resistance and prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with prediabetes.
The National Institutes of Health-funded research study, the Diabetes Prevention Program , showed that for people at high risk of developing diabetes, losing 5 to 7 percent of their starting weight helped reduce their chance of developing the disease.3 Thats 10 to 14 pounds for someone who weighs 200 pounds. People in the study lost weight by changing their diet and being more physically active.
The DPP also showed that taking metformin, a medicine used to treat diabetes, could delay diabetes. Metformin worked best for women with a history of gestational diabetes, younger adults, and people with obesity. Ask your doctor if metformin might be right for you.
Making a plan, tracking your progress, and getting support from your health care professional, family, and friends can help you make lifestyle changes that may prevent or reverse insulin resistance and prediabetes. You may be able to take part in a lifestyle change program as part of the National Diabetes Prevention Program.
Cost Of The Assay: Savings Or No Savings
One of the major concerns raised by critics of the use of A1C for diagnosing diabetes is the higher cost of the assay when compared with FPG. There is no doubt that from an analytical point of view , FPG is cheaper than A1C. However, other considerations about cost should be made. FPG assessment requires overnight fasting, whereas A1C can be assessed any time. This means that a person could go or could be driven by a relative/friend to the laboratory, even during lunch or in the late afternoon, avoiding loss of work hours. It is also possible to collect blood for A1C assessment in the evening and hand it to the laboratory in the following days. Yet, in subjects with FPG 7 mmol/L , A1C assessment would be needed the next few days as a second step in a newly diagnosed diabetes workup. On the contrary, when A1C assessment yields a value 6.5%, the second step required to initiate diabetes monitoring after diagnosis would be completed, with a substantial savings of both analytical and nonanalytical costs. On the other hand, when using FPG to screen for diabetes and finding a value in the range of 5.66.9 mmol/L , an OGTT is frequently prescribed to establish glucose tolerance. This test requires hours in the laboratory, with additional analytical and nonanalytical costs. In such cases, which represent a sizable portion of the general population, A1C rather than FPG would provide an immediate diabetes diagnosis or a valuable risk stratification without supplementary testing.
Recommended Reading: Air Force Type 1 Diabetes
How Is It Treated
If you have diabetes and notice any of the early signs of high blood sugar, test your blood sugar and call the doctor. They may ask you for the results of several readings. They could recommend the following changes:
Drink more water. Water helps remove excess sugar from your blood through urine, and it helps you avoid dehydration.
Exercise more. Working out can help lower your blood sugar. But under certain conditions, it can make blood sugar go even higher. Ask your doctor what kind of exercise is right for you.
Caution: If you have type 1 diabetes and your blood sugar is high, you need to check your urine for ketones. When you have ketones, do NOT exercise. If you have type 2 diabetes and your blood sugar is high, you must also be sure that you have no ketones in your urine and that you are well-hydrated. Then your doctor might give you the OK to exercise with caution as long as you feel up to it.
Change your eating habits. You may need to meet with a dietitian to change the amount and types of foods you eat.
Switch medications. Your doctor may change the amount, timing, or type of diabetes medications you take. Donât make changes without talking to them first.
If you have type 1 diabetes and your blood sugar is more than 250 mg/dL, your doctor may want you to test your urine or blood for ketones.
How Is Hyperglycemia Diagnosed
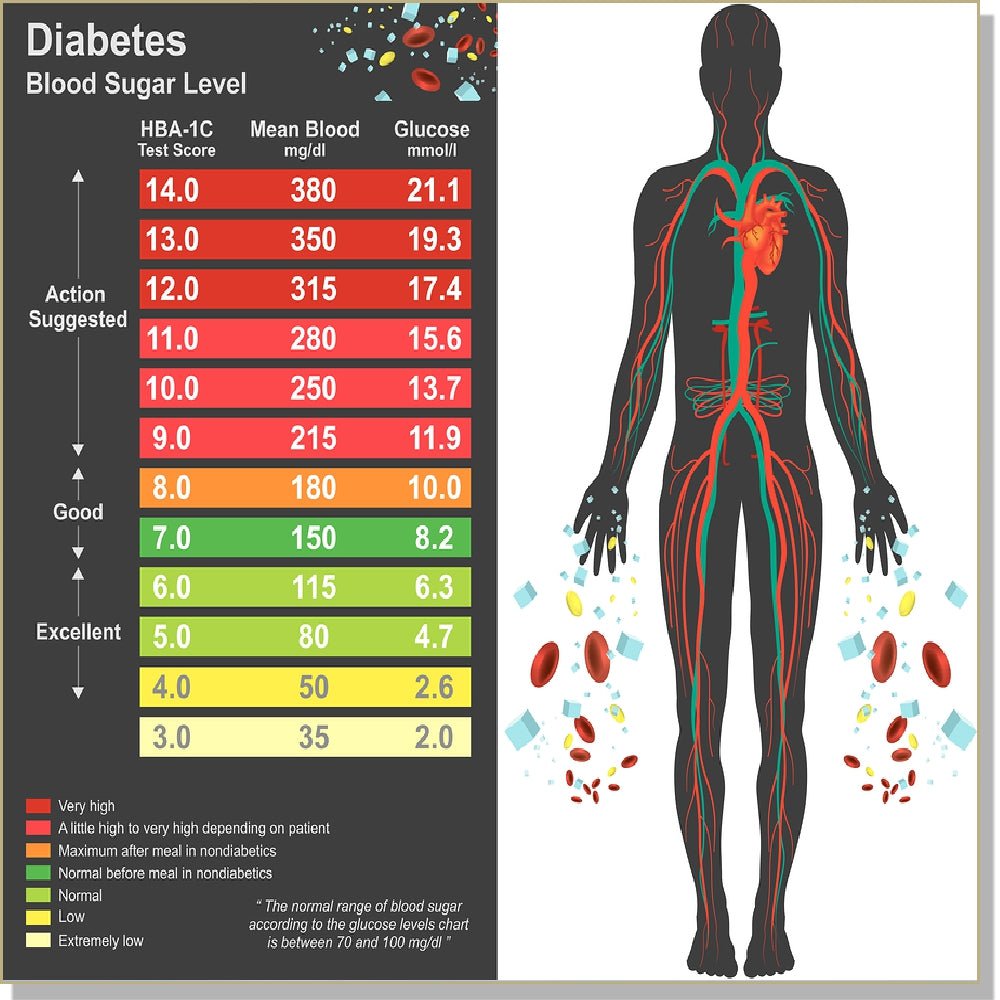
If you have diabetes and notice a sudden change in your blood sugar levels during your home monitoring, you should alert your doctor of your symptoms. The increase in blood sugar may affect your treatment plan.
Regardless of whether you have diabetes, if you begin experiencing any symptoms of hyperglycemia, you should speak to your doctor. Before going to your appointment, you should note what symptoms youre experiencing. You should also consider these questions:
- Has your diet changed?
- Have you had enough water to drink?
- Are you under a lot of stress?
- Were you just in the hospital for surgery?
- Were you involved in an accident?
Once at your doctors appointment, your doctor will discuss all of your concerns. Theyll perform a brief physical exam and discuss your family history. Your doctor will also discuss your target blood sugar level.
If youre age 59 or younger, a safe blood sugar range is generally between 80 and 120 milligrams per deciliter . This is also the projected range for people who dont have any underlying medical conditions.
People who are age 60 or older and those who have other medical conditions or concerns may have levels between 100 and 140 mg/dL.
Your doctor may conduct an A1C test to determine what your average blood sugar level has been in recent months. This is done by measuring the amount of blood sugar attached to the oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin in your red blood cells.
Read Also: Free Diabetic Meter And Test Strips
If You Regularly Have High Blood Sugar Levels
Having high blood sugar levels regularly is not something you should live with. This is because in the long-term it can increase your risk of developing diabetes complications, such as neuropathy and retinopathy.
If you notice that your blood sugar levels are often high, you should contact your diabetes healthcare team. They will review your treatment and provide you with advice on how to get your blood sugar levels back within your target range. This advice may include increasing your medication.
In the video below, Lynsey talks to Khalida about feeling anxious after getting a high blood sugar level reading. If youre finding it hard to deal with similar feelings, weve got information on emotional health that you may find helpful.
High Hba1c May Increase Mortality
Higher HbA1c levels were associated with increased mortality from all causes among nondiabetics, in a meta-analysis of 11 studies with over 113k people .
A study of over 2.1k people who had a stroke reported that the risk for all-cause mortality was significantly increased when HbA1c level was > 5.5% compared to HbA1c < 5.5%, and it further dramatically increased 2 3 times in the highest HbA1c group 7.2% .
The American Diabetes Association estimated that the risk of diabetes-related mortality increased by 25% for each 1% increase in HbA1c. It has also been estimated that each percentage point increase in HbA1c corresponds to a 35% increase in the risk of heart disease and an 18% increase in the risk of heart attack .
Why does elevated HbA1c relate to mortality? Ample evidence shows that elevated glucose can increase oxidative stress. Oxidative stress then damages blood vessels, contributing to heart disease. Oxidative stress can also damage DNA, potentially resulting in gene mutation and cancer development .
Don’t Miss: Low Carb Meal Plan For Diabetics Type 2
Whats Considered High Glucose In A Blood Test
If your doctor asked you to avoid eating and drinking for several hours before your blood test, you likely had what’s called a fasting blood sugar test. According to Mayo, a fasting blood glucose test result of less than 100 milligrams per deciliter is considered normal. If your result was between 100 and 125, your doctor may evaluate you for prediabetes, and if your result was 126 or higher, your doctor likely will evaluate you for diabetes.
What Does High Glucose Mean
First of all, high glucose means that you need to take action – either prevent prediabetes / diabetes type 2 or diabetes complications – depending on the ranges your blood sugar levels fall within. If your blood sugar levels are still within pre-diabetes ranges you may reverse the condition by normalizing your diet and increasing physical activities. Read more what high glucose means.
High blood sugar means that your are on your way to diabetes or may already have it. However, the condition can be reversed. The earlier you take action the greater the chance to get back to healthy blood sugar levels.
Also Check: How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
What If It Goes Untreated
Hyperglycemia can be a serious problem if you don’t treat it, so it’s important to treat as soon as you detect it. If you fail to treat hyperglycemia, a condition called ketoacidosis could occur. Ketoacidosis develops when your body doesn’t have enough insulin. Without insulin, your body can’t use glucose for fuel, so your body breaks down fats to use for energy.
When your body breaks down fats, waste products called ketones are produced. Your body cannot tolerate large amounts of ketones and will try to get rid of them through the urine. Unfortunately, the body cannot release all the ketones and they build up in your blood, which can lead to ketoacidosis.
Ketoacidosis is life-threatening and needs immediate treatment. Symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
Talk to your doctor about how to handle this condition.
What Does A High Glucose Level Mean
High blood sugar means that your are on your way to diabetes or may already have it. However, the condition can be reversed. The earlier you take action the greater the chance to get back to healthy blood sugar levels.
What does high glucose level mean? The good news is that is does not necessarily mean that the person with a high glucose reading has diabetes and will have to live with this all the life long, but paying attention to this issue is absolutely necessary. You may have to lower high glucose foods consumption. The best option is switch to low glycemic diet so as to normalize you high glucose levels and prevent insulin resistance and diabetes, which may be not so far ahead.
First of all, blood glucose levels change over the day, the reading depends on when your do the test and other factors, such as as having stress, illness, hormone level changes, alcohol and exercise. When did you have your blood tests and how did you have it measured?
There are different approaches to measuring blood glucose levels and there is a lot of debate which of them are more accurate and informative. Here, we’ll dwell on A1C test, the most widely used test. A1C measures your average blood glucose levels over the last three month, regardless of what and when you’ve been eating. You’ll have to take finger pricks for at least 90 days. A1C test shows the percentage of glucose in your blood.
Read Also: How Can A Diabetic Wound Heal Faster
Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. Having prediabetes puts you at greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but participating in the program can lower your risk by as much as 58% .
Random Blood Sugar Test
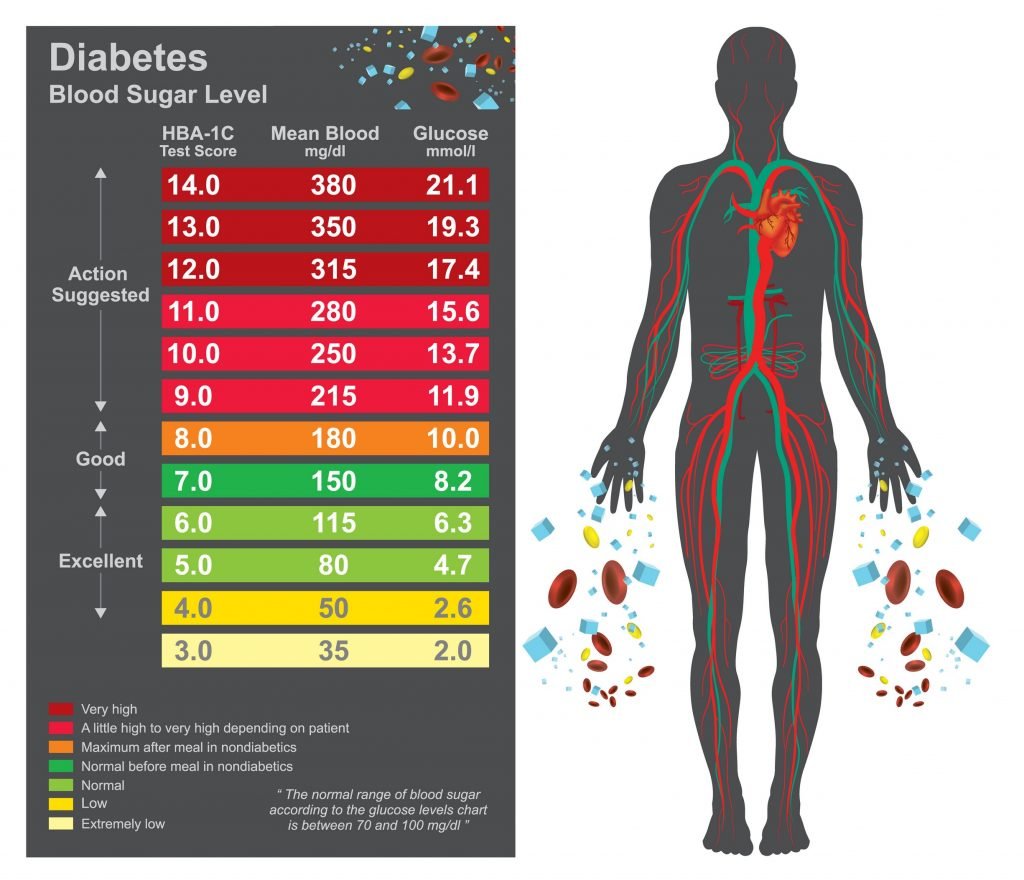
This measures your blood sugar at the time youre tested. You can take this test at any time and dont need to fast first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
| 140 mg/dL or below | N/A |
*Results for gestational diabetes can differ. Ask your health care provider what your results mean if youre being tested for gestational diabetes.Source: American Diabetes Association
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also tested for autoantibodies that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
Also Check: Pre Diabetic Diet To Lose Weight
How To Avoid And Deal With Hyperglycemia
Minimising long time exposure to high blood sugar levels is one of the key objectives of diabetes control
Testing blood sugar levels will help in managing hyperglycemia. People who take insulin may be able to take additional insulin. However, only take additional insulin if your doctor is happy for you to do so, as miscalculations could lead to dangerously low blood sugar levels.
Diabetes UK advise people with type 1 diabetes to test for ketones if blood glucose levels rise above 15 mmol/l or the signs of ketoacidosis appear. Contact your health team if high levels of ketones are present.
If blood glucose levels remain high for long periods of time, contact your health team for advice.
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome : When Hyperglycemia Becomes Severe For People With Type 2 Diabetes
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome is very rare, but you should be aware of it and know how to handle it if it occurs.
HHNS is when your blood glucose level goes way too highyou become extremely hyperglycemic. HHNS affects people with type 2 diabetes.
HHNS is most likely to occur when you’re sick, and elderly people are most likely to develop it.
It starts when your blood glucose level starts to climb: when that happens, your body will try to get rid of all the excess glucose through frequent urination. That dehydrates your body, and you’ll become very thirsty.
Unfortunately, when you’re sick, it’s sometimes more difficult to rehydrate your body. For example, it might be difficult to keep fluids down.
When you don’t rehydrate your body, the blood glucose level continues to climb, and it can eventually go so high that it could send you into a coma.
To avoid hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome, you should keep close watch on your blood glucose level when you’re sick .
Talk to your health care professional about having a sick-day plan to follow that will help you avoid HHNS.
You should also be able to quickly recognize the signs and symptoms of HHNS, which include:
-
Extremely high blood glucose level
-
Dry mouth
Read Also: Eli Lilly Insulin Assistance Programs
What Are Risk Factors For Hyperglycemia
Major risk factors for hyperglycemia are:
- You have a family history of type 2 diabetes.
- You are African American, Native American, Hispanic or Asian American.
- You are overweight.
- You have high blood pressure or cholesterol.
- You have polycystic ovarian syndrome .
- You have a history of gestational diabetes.
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
Recommended Reading: How To Make French Toast With Cinnamon Sugar
Also Check: Hope For Type 1 Diabetes Cure
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
When the body doesn’t have enough insulin, glucose stays in the blood and can’t get into the body’s cells to be used for energy. This can happen, for example, when someone skips doses of insulin or when the need for insulin suddenly increases and the doses are not adjusted.
When the body can’t use glucose for fuel, it starts to use fat. When this happens, chemicals called ketones are released into the blood. Some of these ketones, like extra glucose, pass out of the body through the urine.
High levels of ketones in the blood can be a problem because they cause the blood to become acidic. Too much acid in the blood throws off the body’s chemical balance and causes the symptoms listed below. In people with diabetes, this problem is called diabetic , or DKA. DKA is a very serious condition that can lead to coma or death if it’s not treated. The good news, though, is that it’s preventable and can be treated.
DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but can sometimes also happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
Can High Levels And Dka Be Prevented
These two problems donât sound like much fun, so youâre probably wondering how to prevent them. The solution is to keep your blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible, which means following your diabetes management plan. Checking your blood sugar levels several times a day will let you and your parents know when your blood sugar level is high. Then you can treat it and help prevent DKA from happening.
What else can you do? Wear a medical identification bracelet that says you have diabetes. Then, if you are not feeling well, whoeverâs helping you even if the person doesnât know you will know to call for medical help. And the doctors will be able to get you better more quickly if they know you have diabetes. These bracelets also can include your doctorâs phone number or a parentâs phone number. The quicker you get the help you need, the sooner youâll be feeling better!
Recommended Reading: Is Bio X4 Safe For Diabetics