Random Or Casual Plasma Glucose Test
A plasma glucose test is a measure of how much sugar/glucose you have circulating in your blood. Random or Casual simply means that you have blood drawn at a laboratory at any time. Whether you have fasted or recently eaten will not affect the test. A plasma glucose test measurement equal to or greater than 200 milligrams per deciliter indicates that you may have diabetes. To be sure, you will need to have the test results confirmed on another day through another random test, or by taking a fasting plasma glucose test or an oral glucose tolerance test.
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- In women: Dry and itchy skin, and frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
- In men: Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle strength.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly over a few weeks or months. Symptoms begin when youre young as a child, teen or young adult. Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting or stomach pains and yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes symptoms: You may not have any symptoms at all or may not notice them since they develop slowly over several years. Symptoms usually begin to develop when youre an adult, but prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes is on the rise in all age groups.
Gestational diabetes: You typically will not notice symptoms. Your obstetrician will test you for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of your pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: Contour Next Blood Glucose Test Strips 100 Count
Fasting Blood Glucose In Diagnosis Of Diabetes
Last reviewed 11/2021
Diabetes is diagnosed on the basis of history PLUS
- a random venous plasma glucose concentration > = 11.1 mmol/l
- OR a fasting plasma glucose concentration > = 7.0 mmol/l
- OR 2 hour plasma glucose concentration > = 11.1 mmol/l 2 hours after 75g anhydrous glucose in an oral glucose tolerance test
With no symptoms diagnosis should not be based on a single glucose determination but requires confirmatory plasma venous determination. At least one additional glucose test result on another day with a value in the diabetic range is essential, either fasting, from a random sample or from the two hour post glucose load . If the fasting or random values are not diagnostic the 2-hour value should be used.
These diagnostic criteria for diagnosing and classifying diabetes were applied to the management of diabetes in the UK from June 1st 2000 . The new criteria included lowering the threshold for diagnosing diabetes from a fasting glucose level of 7.8 mmol/l to 7.0 mmol/l.
It should be noted that children usually present with severe symptoms and diagnosis should then be based on a single raised blood glucose result, as above. Immediate referral to a Paediatric Diabetes Team should not be delayed.
A diagnosis should never be made on the basis of glycosuria or a stick reading of a finger prick blood glucose alone, although such tests may be useful for screening purposes.
HbA1c in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
Reference:
When Should I Call My Doctor

If you havent been diagnosed with diabetes, you should see your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of diabetes. If you already have been diagnosed with diabetes, you should contact your provider if your blood glucose levels are outside of your target range, if current symptoms worsen or if you develop any new symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Consequences Of High Blood Sugar
Definition And Description Of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes is associated with long-term damage, dysfunction, and failure of differentorgans, especially the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels.
Several pathogenic processes are involved in the development of diabetes. These range from autoimmune destruction of the -cells of the pancreas with consequent insulin deficiency to abnormalities that result in resistance to insulin action. The basis of the abnormalities in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism in diabetes is deficient action of insulin on target tissues. Deficient insulin action results from inadequate insulin secretion and/or diminished tissue responses to insulin at one or more points in the complex pathways of hormone action. Impairment of insulin secretion and defects in insulin action frequently coexist in the same patient, and it is often unclear which abnormality, if either alone, is the primary cause of the hyperglycemia.
Symptoms of marked hyperglycemia include polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, sometimes with polyphagia, and blurred vision. Impairment of growth and susceptibility to certain infections may also accompany chronic hyperglycemia. Acute, life-threatening consequences of uncontrolled diabetes are hyperglycemia with ketoacidosis or the nonketotic hyperosmolar syndrome.
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being Black, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Having overweight/obesity.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Having overweight/obesity before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Diabetes 1 And 2
Predictive Performance In Subjects With Different Risk Of Developing Diabetes
Although factors such as age, sex, race, ethnicity, BMI, smoking, SBP and non-HDL cholesterol increased the likelihood of developing diabetes, the predictive performance of RPG was similar in those at higher and lower risk the ROC AUC ranged from 0.840.88 for each subgroup, as shown in Table 4. However, the risk for incident diabetes was much higher with even modest elevation in RPGodds ratio 5.4 for RPG 110119 mg/dl, and OR 45.3 for RPG 130139 .
Testing For Type 1 Diabetes Risk
The incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes is increasing . Patients with type 1 diabetes often present with acute symptoms of diabetes and markedly elevated blood glucose levels, and approximately one-third are diagnosed with life-threatening DKA . Several studies indicate that measuring islet autoantibodies in relatives of those with type 1 diabetes may identify individuals who are at risk for developing type 1 diabetes . Such testing, coupled with education about diabetes symptoms and close follow-up, may enable earlier identification of type 1 diabetes onset. A study reported the risk of progression to type 1 diabetes from the time of seroconversion to autoantibody positivity in three pediatric cohorts from Finland, Germany, and the U.S. Of the 585 children who developed more than two autoantibodies, nearly 70% developed type 1 diabetes within 10 years and 84% within 15 years . These findings are highly significant because while the German group was recruited from offspring of parents with type 1 diabetes, the Finnish and American groups were recruited from the general population. Remarkably, the findings in all three groups were the same, suggesting that the same sequence of events led to clinical disease in both sporadic and familial cases of type 1 diabetes. Indeed, the risk of type 1 diabetes increases as the number of relevant autoantibodies detected increases .
Don’t Miss: Normal Range For Fasting Glucose
Diagnostic Criteria And Testing
The 1997 ADA consensus guidelines lowered the blood glucose thresholds for the diagnosis of diabetes.5 This increased the number of patients diagnosed at an earlier stage, although no studies have demonstrated a reduction in long-term complications. Data suggest that as many as 5.7 million persons in the United States have undiagnosed diabetes.6Table 1 compares specific diagnostic tests for diabetes.1114
| Test |
|---|
|
Diabetes can also be diagnosed with a random blood glucose level of 200 mg per dL or greater if classic symptoms of diabetes are present. Lower random blood glucose values have a fairly high specificity of 92 to 98 percent therefore, patients with these values should undergo more definitive testing. A low sensitivity of 39 to 55 percent limits the use of random blood glucose testing.15
The oral glucose tolerance test is considered a first-line diagnostic test. Limitations include poor reproducibility and patient compliance because an eight-hour fast is needed before the 75-g glucose load, which is followed two hours later by a blood draw.17 The criterion for diabetes is a serum blood glucose level of greater than 199 mg per dL .
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Work to achieve a healthy weight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
You May Like: Daily Sugar Intake For Diabetics
Random Plasma Glucose Test
A random blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or more, plus presence of the following symptoms, can mean that you have diabetes:
- Increased urination
- Increased thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
Other symptoms include fatigue, blurred vision, increased hunger, and sores that do not heal. Your doctor will check your blood glucose level on another day using the FPG or the OGTT to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
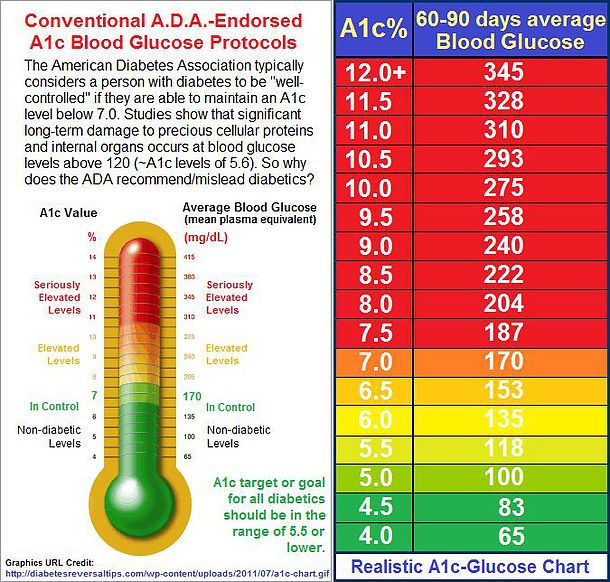
Newer guidelines use hemoglobin A1c as a screening tool or diagnostic test for prediabetes or diabetes . An HbA1c of 5.7% to 6.4% is consistent with prediabetes and marks a time when it can be reversed by lifestyle changes. An HbA1c of 6.5% or higher is consistent with diabetes.
Show Sources
Why The Test Is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have signs of diabetes . More than likely, the doctor will order a fasting blood sugar test.
The blood glucose test is also used to monitor people who already have diabetes.
The test may also be done if you have:
- An increase in how often you need to urinate
- Recently gained a lot of weight
SCREENING FOR DIABETES
This test may also be used to screen a person for diabetes.
High blood sugar and diabetes may not cause symptoms in the early stages. A fasting blood sugar test is almost always done to screen for diabetes.
If you are over age 45, you should be tested every 3 years.
If you’re overweight and have any of the risk factors below, ask your health care provider about getting tested at an earlier age and more often:
- High blood sugar level on a previous test
- Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher, or unhealthy cholesterol levels
- History of heart disease
- Member of a high-risk ethnic group
- Woman who has been diagnosed with gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary disease
- Close relative with diabetes
- Not physically active
Children age 10 and older who are overweight and have at least two of the risk factors listed above should be tested for type 2 diabetes every 3 years, even if they have no symptoms.
Also Check: Best App To Track Diabetes
Why Is My Blood Glucose Level High How Does This Happen
The process of digestion includes breaking down the food you eat into various different nutrient sources. When you eat carbohydrates , your body breaks this down into sugar . When glucose is in your bloodstream, it needs help a “key” to get into its final destination where it’s used, which is inside your body’s cells . This help or “key” is insulin.
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas, an organ located behind your stomach. Your pancreas releases insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin acts as the key that unlocks the cell wall door, which allows glucose to enter your bodys cells. Glucose provides the fuel or energy tissues and organs need to properly function.
If you have diabetes:
- Your pancreas doesnt make any insulin or enough insulin.
- Your pancreas makes insulin but your bodys cells dont respond to it and cant use it as it normally should.
If glucose cant get into your bodys cells, it stays in your bloodstream and your blood glucose level rises.
What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
You May Like: Why Do Diabetics Need Insulin
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
The types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. Its usually diagnosed in children and young adults . It was once better known as juvenile diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or your bodys cells dont respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it having a touch of sugar.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you’re at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Less common types of diabetes include:
Diabetes insipidus is a distinct rare condition that causes your kidneys to produce a large amount of urine.
What Test Results Tell Me If I Have Diabetes Or Prediabetes
Each test to detect diabetes and prediabetes uses a different measurement. Usually, your doctor will use a second test to confirm you have diabetes.
The table below helps you understand what your test results mean if you are not pregnant.1 If you are pregnant, some tests use different cutoffs. Ask your doctor what your test results mean.
Read Also: Freestyle Abbott Diabetes Care Instructions
What Happens During A Diabetes Test
There are several ways to screen for and diagnose diabetes. Most tests involve measuring glucose levels in the blood.
To get a blood sample, a health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
The different types of glucose blood tests include:
- Blood glucose test, also known as fasting blood glucose. Before the test, you will need to fast for eight hours before the test. This test is often used as a screening test for diabetes. It may be repeated to confirm a diagnosis.
- Oral glucose tolerance test . This test also requires fasting before the test. When you arrive for your test, a blood sample will be taken. You will then drink a sugary liquid that contains glucose. About two hours later, another blood sample will be taken.
- Random blood sugar. This test can be taken at any time. No fasting is required.
- Hemoglobin A1c . This test measures the average amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin over the past 3 months. Hemoglobin is the part of your red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. No fasting is required for this test.