Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
How Well Did The Device Work
For the study, the researchers recruited 26 patients from the Wolfson Diabetes and Endocrine Clinic at Addenbrookes Hospital in Cambridge and a local group of general practitioners.
Patients were randomly assigned to two groups. The first group tried the artificial pancreas for eight weeks and then switched to the standard therapy of multiple daily insulin injections. Meanwhile, the second group began on standard therapy and then switched to the artificial pancreas after eight weeks.
The team used several measures to assess the effectiveness of the artificial pancreas. The first was the proportion of time that patients spent with their glucose levels within a target range of between 3.9 and 10 millimoles per liter, the standard measure of glucose levels in blood.
Patients using the artificial pancreas spent two-thirds of their time with their glucose levels within the target range, double that of the control group . In contrast, patients taking the standard therapy spent 67 percent of their time with high glucose levels, which halved to 33 percent when they used the artificial pancreas.
Average glucose levels fell from 12.6 millimoles per liter when taking the control therapy to 9.2 millimoles per liter when they used the artificial pancreas. The app also reduced levels of a molecule known as glycated hemoglobin in patients.
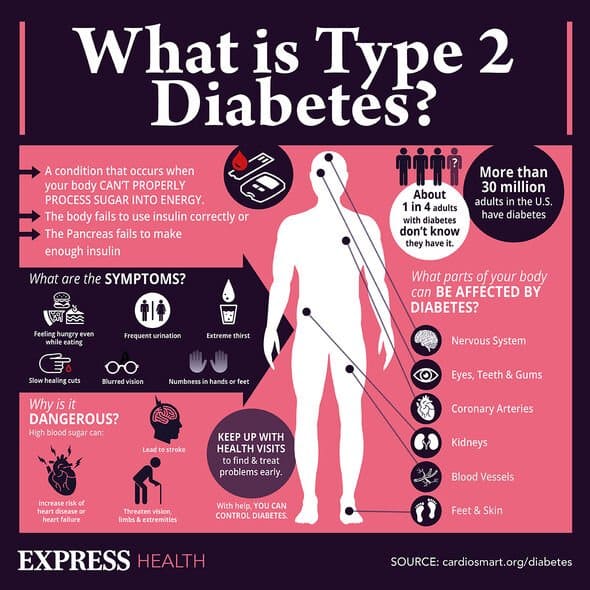
Warning Signs Of Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia can cause both short- and long-term complications. Know the signs so that you can treat the condition as soon as youre aware of it.
As a person living with diabetes, you know how important it is to reduce blood sugar when it is too high, a phenomenon called hyperglycemia. But blood sugar that is too low, or hypoglycemia, is equally critical to avoid.
Hypoglycemia happens when the amount of blood glucose drops to a level thats too low to sustain normal functioning, says Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDCES, who is based in Sparta, New Jersey. In most people, this is defined as a blood sugar level at or below 70 milligrams per deciliter .
Hypoglycemia is common among people with type 2 diabetes, according to a review published in June 2015 in the journal PLoS One. Individuals with the condition had an average of 19 mild or moderate episodes of hypoglycemia per year and nearly one severe episode per year on average, according to the researchers. Low blood sugar was particularly common among those taking insulin.
RELATED: What to Know Before You Use OTC Insulin
This decrease in blood sugar levels can cause both short-term complications, like confusion and dizziness, as well as more serious issues, including seizures, coma, and, rarely, death, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Hypoglycemia is usually the result of a too-high dose of insulin or a change in diet or exercise habits, according to Harvard Health Publishing.
Read Also: How Does Anemia Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Your Blood Sugar Isnt Just Because Of What You Eat
Mainstream media would have you believe that your blood sugar levels are impacted only by what you eat and how much you exercise, but people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who test their blood sugars frequently could tell you otherwise.
Its especially important to keep this in mind when looking at your own blood sugars and your goals because there are certain variables and challenges that impact blood sugar levels that you cant always control.
For example:
- Menstrual cycles: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Adrenaline rushes from competitive sports, heated arguments, or rollercoaster rides: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- The common cold and other illnesses: usually raise blood sugar and insulin needs
- Hormonal changes due to puberty and healthy growth in young adults: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- An injury that raises overall inflammation levels: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Glucogenesis during anaerobic exercise: raises blood sugar
While you cant necessarily prevent these factors that affect your blood sugar from occurring, you can work with your diabetes healthcare team to adjust your insulin, other diabetes medications, nutrition and activity levels to help compensate for them when they do occur.
For example, when engaging in anaerobic exercise like weightlifting many people with type 1 diabetes find it necessary to take a small bolus of insulin prior to or during their workout because anaerobic exercise can actually raise blood sugar.
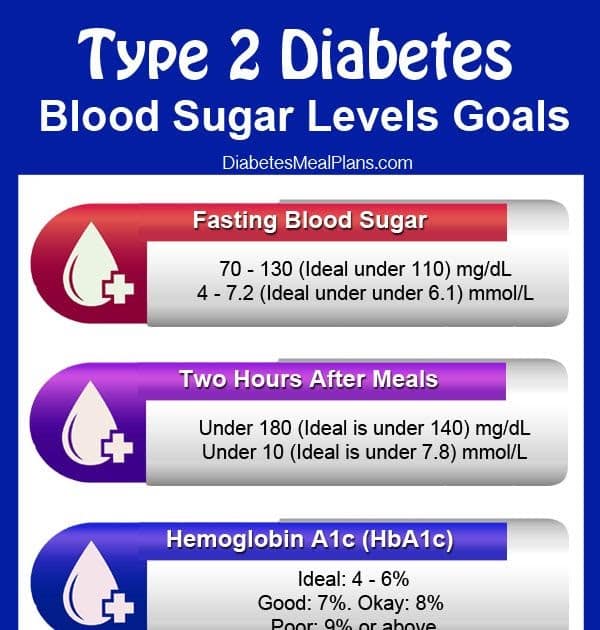
Fasting Vs Nonfasting Blood Sugar
Fasting blood sugar is a test that measures blood sugar and is used to determine if an individual has diabetes. When a person takes this test, they are not to eat or drink for at least eight hours prior to the test. The results determine whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic.
The results are measured in milligrams per deciliter or mg/dL. The following results indicate whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
To test nonfasting blood sugar, an A1C test is administered to determine the average blood sugar level of an individual over a period of two to three months. There is no need to fast prior to taking this test. The following results indicate whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
Dont Miss: What Happens When Your Blood Sugar Level Gets Too Low
Read Also: Is Freshpet Good For Diabetic Dogs
How Do I Prepare For A Blood Glucose Test
If your healthcare provider has ordered a fasting blood glucose test, youll need to not eat or drink anything except water for eight to 10 hours before the test.
If your blood glucose test is part of a basic or comprehensive metabolic panel, you may also need to fast for several hours before your blood draw. In any case, your healthcare provider will let you know if you need to follow any special instructions.
When Is The Best Time To Check Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes: how often to test blood sugar? The best time to check your blood measurements is in the early morning before breakfast. This way, the figures will be correct. After that, you can try checking on your results 2 hours after meal. Although it is less precise, this approach is the sole option for individuals who require many diagnostic sessions each day.
You May Like: Vitamin C For Diabetes Type 2
Why Do Some People Get Type 2 Diabetes
No one knows for sure why some people get type 2 diabetes, but its likely a combination of genes and the environment. Many teens who get it have someone in their family who has it too.
Type 2 diabetes happens more often in people:
- who are overweight. When a person has extra weight, sugar in the blood doesnt get into the cells as well as it should. But people dont have to be overweight to get type 2 diabetes.
- during puberty. Many kids and teens are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes around puberty. As growth hormone levels normally rise during puberty, insulin does not work as well.
- with polycystic ovary syndrome . Girls and women with PCOS have insulin resistance and are more likely to get type 2 diabetes.
- whose mothers had diabetes during pregnancy. Babies are exposed to more sugar in the womb when their mother has diabetes. This along with genetic factors increase the chance of getting type 2 diabetes later in life.
Carbohydrates And Blood Sugar
When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood.
- As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage.
- As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fall.
- When this happens, the pancreas start making glucagon, a hormone that signals the liver to start releasing stored sugar.
- This interplay of insulin and glucagon ensure that cells throughout the body, and especially in the brain, have a steady supply of blood sugar.
Carbohydrate metabolism is important in the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body cant make enough insulin or cant properly use the insulin it makes.
- Type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually over a number of years, beginning when muscle and other cells stop responding to insulin. This condition, known as insulin resistance, causes blood sugar and insulin levels to stay high long after eating. Over time, the heavy demands made on the insulin-making cells wears them out, and insulin production eventually stops.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Insulin At Walmart
What Are Treatments For Type 2 Diabetes
Unless its absolutely necessary, insulin should not be used to treat type 2 diabetes. Dr. Bergquist explains, Injecting insulin improves blood sugar but worsens underlying insulin resistance. Insulin is a fat-storage hormone. Higher insulin leads to more fat storage in organs where its toxic, making them more insulin resistant.
Insulin should only be used when the pancreas fails and the B cells cannot be regenerated, says Dr. Apovian. When type 2 diabetes is caught early enough, you can reverse it with lifestyle, medication, and bariatric surgery. In certain cases, when a person is severely overweight, bariatric surgery is a successful treatment for type 2 diabetes, because it effectively decreases a persons body weight set point and can reverse hormonal imbalances that underlie obesity and fuel type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, new type 2 diabetes medications have been approved by the FDA, including a class of drugs known as glucagon-like-peptides , which aid the pancreas in producing more insulin by decreasing glucose production in the liver. Researchers are also working to understand the role that inflammation and hormonal imbalances have in the development of T2D.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Diabetics
The American Diabetes Association recommends that the blood sugar 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal be less than 180 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. This is typically the peak, or highest, blood sugar level in someone with diabetes. Again, this target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: Ginger For Diabetes Type 2
Diabetes Uk Show How To Test Feet For Diabetic Feet Sensitivity
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Over a period of six years, research findings gathered in North Karelia, Finland, identified three factors that influence the risk of hyperglycaemia. Hyperglycaemia is the medical term to describe high blood sugar, the NHS clarifies. People who have type 2 diabetes may notice their blood sugar is too high when they feel extremely thirsty, they’re urinating frequently, and feel weak or tired.
To Check Or Not To Check
Ultimately, while the researchers mentioned here found that blood glucose monitoring had no effect on the A1Cs of those with type 2 who did not take insulin, they hope that their findings will inspire both adults with diabetes and providers to regularly engage in conversations about the question.
If you currently monitor, you shouldnt stop doing so without first consulting your physician.
And while its the rare person who would choose to monitor if a doctor deemed it unnecessary, its ultimately very individual. In the end, patient-centric care matters most.
Recommended Reading: How Does Diabetes Affect You Emotionally
What Are The Side
No patients experienced dangerously low blood sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia, during the study period. One patient needed hospitalization while using the artificial pancreas due to an abscess at the site of the pump needle.
Participants said they were happy to have their blood sugar managed in this way and nine out of 10 reported spending less time overall managing their condition. Users liked the fact they no longer needed to jab themselves and made them more confident in managing their blood sugar. Downsides included increased anxiety about developing hyperglycemia, which the team say may reflect greater awareness and monitoring of blood sugar levels, and practical annoyances with wearing devices.
Many people with Type 2 diabetes struggle to manage their blood sugar levels using the currently available treatments, such as insulin injections. The artificial pancreas can provide a safe and effective approach to help them, and the technology is simple to use and can be implemented safely at home, says Dr. Charlotte Boughton from the Wellcome-MRC Institute of Metabolic Science at the University of Cambridge in a media release.
Roller Coaster: Female Hormones
When a womans hormones change, so does their blood sugar. Keep a monthly record of your levels to get a better idea of how your menstrual cycle affects you. Hormone changes during menopause may make blood sugar even harder to control. Talk to your doctor about whether hormone replacement therapy is a good idea.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Age Range
Read Also: Why Is Smoking Bad For Diabetics
Testing Your Own Blood Glucose
Usually, blood glucose testing is done by your doctor or nurse. But some people might be able to do this at home with a continuous glucose monitor or finger prick hometesting kit. If your doctor or nurse thinks CGM or finger prick testing would be suitable for you:
-
they will give you training and support so you know what to do
-
they will assess your blood glucose testing skills and needs regularly, as part of the reviews of your diabetes care plan.
Not everyone needs to monitor their blood glucose at home. You should only do this if your doctor or nurse advises it.
Other Severe Symptoms Of Hyperglycaemia Include:
- Blood vessel damage
Mild hyperglycaemia, depending on the cause, will not typically require medical treatment. Most people with this condition can lower their blood sugar levels sufficiently through dietary and lifestyle changes.
Those with type 1 diabetes will require the administration of insulin , while those with type 2 diabetes will often use a combination of injectable and oral medications , although some may also require insulin.
You May Like: How Lower Your Blood Sugar Fast
Recommended Reading: Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every three years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every one to two years.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness Or Impaired Awareness
The goal is to help a person recognize symptoms of hypoglycemia early on so they can take action sooner. In some cases, if a person does not experience the perceived signs of hypoglycemia this can cause an unawareness. Hypoglycemia unawareness can occur in those patients with diabetes who live with chronically low blood glucose levels. on insulin are at higher risk for hypoglycemia unawareness. The brain and body of those with hypoglycemia unawareness is accustomed to long-standing hypoglycemia, so their normal physiologic response to hypoglycemia is impaired. These people may function and live normally with blood glucose values in the 70s, and only experience symptoms of hypoglycemia when the glucose values drop into the 50s or below. People with hypoglycemia unawareness are at much greater risk of experiencing severe hypoglycemia. It is important to identify those who suffer from hypoglycemia unawareness and find a medication regimen for their diabetes which is safe for them.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Measure Insulin Levels
Factors That Contribute To Blood Sugar Range
The bodys level of blood glucose is controlled by , a hormone produced in the that helps your body absorb the sugar and use it in your cells. As your level of blood glucose rises, your pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. This helps keep your average blood glucose level within a safe range.
In diabetes, the body cant produce enough insulin or cant use the insulin properly . This means that your body cant compensate well for increases in blood glucose, which prevents your pancreas from stopping sharp spikes in blood glucose and increases the average blood glucose level over time.
Blood glucose spikes happen to everyone, especially after eating and drinking, but also after skipping breakfast, when youre dehydrated, and after you get a sunburn, among other triggers. They are especially dangerous for people with diabetes because their bodies cant , or even out, the spikes.
What Is A Blood Glucose Test
A blood glucose test is a blood test that mainly screens for diabetes by measuring the level of glucose in your blood.
There are two main types of blood glucose tests:
- Capillary blood glucose test: A healthcare professional collects a drop of blood usually from a fingertip prick. These tests involve a test strip and glucose meter , which show your blood sugar level within seconds.
- Venous blood glucose test: A phlebotomist collects a sample of blood from a vein . These glucose tests are usually part of a blood panel, such as a basic metabolic panel. The provider will send the samples to a lab. There, a medical laboratory scientist will prepare your samples and perform the test on machines known as analyzers.
Venous blood glucose tests are generally more accurate than capillary blood glucose tests.
Healthcare providers often order fasting blood glucose tests to screen for diabetes. Since eating food affects blood sugar, fasting blood glucose tests show a more accurate picture of your baseline blood sugar.
Theres also at-home blood sugar testing for people who have diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes especially need to monitor their blood sugar multiple times a day to effectively manage the condition. Continuous glucose monitoring devices are another option for this.
Also Check: How Long Are Glucose Test Strips Good For