Children And Adolescents: Standards Of Medical Care In Diabetes2020
American Diabetes Association 13. Children and Adolescents: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes2020. Diabetes Care 1 January 2020 43 : S163S182.
The American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes includes the ADAs current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide the components of diabetes care, general treatment goals and guidelines, and tools to evaluate quality of care. Members of the ADA Professional Practice Committee, a multidisciplinary expert committee , are responsible for updating the Standards of Care annually, or more frequently as warranted. For a detailed description of ADA standards, statements, and reports, as well as the evidence-grading system for ADAs clinical practice recommendations, please refer to the Standards of Care Introduction . Readers who wish to comment on the Standards of Care are invited to do so at professional.diabetes.org/SOC.
Cvd And Risk Management
This section has received endorsement from the American College of Cardiology.
ASCVDdefined as coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, or peripheral arterial disease presumed to be of atherosclerotic originis the leading cause of morbidity and mortality for individuals with diabetes. HF is another major cause of morbidity and mortality from CVD. For prevention and management of both ASCVD and HF, CV risk factors should be systematically assessed at least annually in all patients with diabetes. These risk factors include obesity/overweight, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, a family history of premature coronary disease, chronic kidney disease , and the presence of albuminuria.
Cgm Recommended For All Adults Who Take Insulin Including Basal
Last years ADA guidelines recommended that people who take rapid-acting insulin should use a CGM. This year, the ADA expanded this recommendation to include people who take only long-acting insulin . Research on CGM use in people with type 2 diabetes indicates that the devices can help those on basal-only insulin improve their day-to-day glucose management. The 2022 guidelines also recommend CGM for all children with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who use rapid-acting insulin.
Studies over the last year have made clear that if individuals are on insulin, no matter who or what age, they can benefit from CGM use, said Gabbay. Some evidence even suggests that CGM could help people who are not on insulin, but this evidence base will need some strengthening going forward.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Level Range
Aace Guidelines For Use Of Advanced Technology
In May 2021, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology released guidelines on the use of advanced technologies in diabetes management. The following recommendations are among those published.
The percentage of time in range and below range should serve as a starting point for the evaluation of the quality of glycemic control and form the basis for therapy adjustment.
For all persons with diabetes who are undergoing intensive insulin therapy , continuous glucose monitoring is strongly recommended. For individuals on insulin therapy for whom success with CGM has been limited , structured self-monitoring of blood glucose is recommended. CGM is recommended for all individuals with problematic hypoglycemia , for children/adolescents with type 1 diabetes for pregnant women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes treated with intensive insulin therapy, and for women with gestational diabetes mellitus on insulin therapy. CGM may be recommended for women with GDM who are not undergoing insulin treatment and for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are undergoing less intensive insulin therapy.
For persons with diabetes who have problematic hypoglycemia and need predictive alarms/alerts, real-time CGM should be recommended over intermittently scanned CGM . Consideration should also be given, however, to a patients lifestyle and to other factors.
Overweight Or Obesity Therapy Recommendations Now Include Wegovy Emphasize Importance Of Food Quality Over Quantity
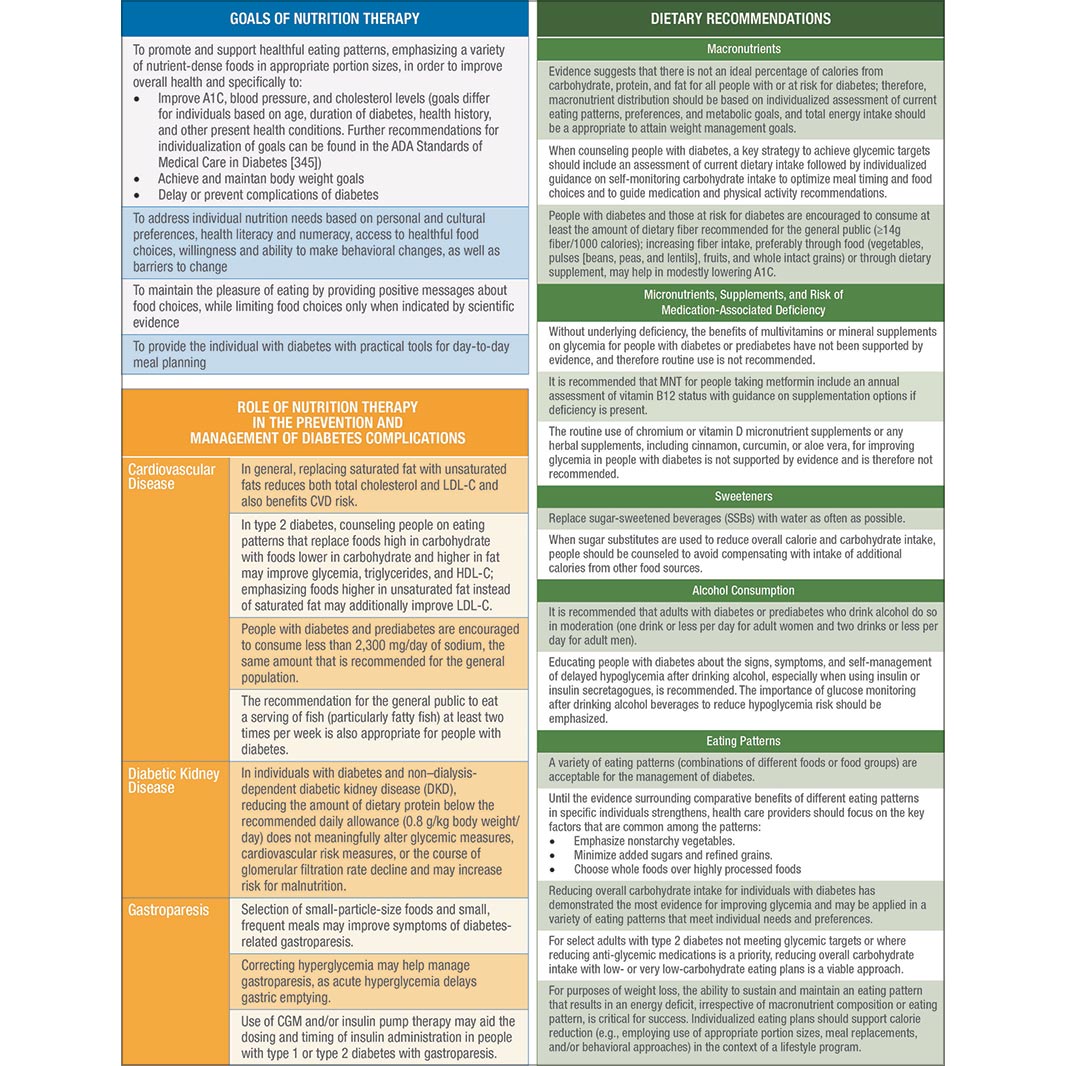
The new guidelines also now recommend Wegovy as an effective therapy for weight management for people with type 2 diabetes. For those with type 2 who take insulin, however, using Wegovy at the same time may increase the risk for hypoglycemia. The drug can still be an effective method to achieve some weight loss, but people should get educated on the signs, symptoms, and risk of hypoglycemia before starting this medication.
The guidelines also recommend managing glucose through more than just carbohydrate-counting. Regardless of the amount of carbohydrate in the meal plan, people should focus on eating high-quality and nutrient-dense carbohydrate sources that are high in fiber. Both children and adults should limit the amount of refined or processed carbs they eat that include added sugars, fat, and salt and instead focus on getting their carbs from vegetables, legumes, fruits, dairy , and whole grains.
These updates are posted in Chapter 8 of the 2022 ADA diabetes care guidelines.
The ADA expanded recommendations for continuous glucose monitor and Time in Range use in adults and for CGM and automated insulin delivery use in children. The guidelines also include using diabetes technology in hospital settings.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar Level Type 2 Diabetes
Standards Of Medical Care In Diabetes2020 Abridged For Primary Care Providers
American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes2020 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin Diabetes 1 January 2020 38 : 1038.
The American Diabetes Associations Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes is updated and published annually in a supplement to the January issue of Diabetes Care. The Standards are developed by the ADAs multidisciplinary Professional Practice Committee, which comprises physicians, diabetes educators, and other expert diabetes health care professionals. The Standards include the most current evidence-based recommendations for diagnosing and treating adults and children with all forms of diabetes. ADAs grading system uses A, B, C, or E to show the evidence level that supports each recommendation.
-
AClear evidence from well-conducted, generalizable randomized controlled trials that are adequately powered
-
BSupportive evidence from well-conducted cohort studies
-
CSupportive evidence from poorly controlled or uncontrolled studies
-
EExpert consensus or clinical experience
Screening And Diagnostic Tests For Prediabetes And Type 2 Diabetes
The diagnostic criteria for diabetes and prediabetes are shown in .
Recommendations
-
2.6 Screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes with an informal assessment of risk factors or validated tools should be considered in asymptomatic adults. B
-
2.7 Testing for prediabetes and/or type 2 diabetes in asymptomatic people should be considered in adults of any age with overweight or obesity and who have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes . B
-
2.8 Testing for prediabetes and/or type 2 diabetes should be considered in women planning pregnancy with overweight or obesity and/or who have one or more additional risk factor for diabetes . C
-
2.9 For all people, testing should begin at age 45 years. B
-
2.10 If tests are normal, repeat testing carried out at a minimum of 3-year intervals is reasonable. C
-
2.12 In patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, identify and treat other CVD risk factors. B
-
2.13 Risk-based screening for prediabetes and/or type 2 diabetes should be considered after the onset of puberty or after 10 years of age, whichever occurs earlier, in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity and who have additional risk factors for diabetes.
Criteria for testing for diabetes or prediabetes in asymptomatic adults
| 1. Testing should be considered in adults with overweight or obesity who have one or more of the following risk factors: |
| First-degree relative with diabetes |
You May Like: Diabetes And Metabolism Patient Portal
Breaking Down The 2020
In this Practical Updates for Primary Care 2020 Virtual Series session, the complex 2020-2021 diabetes guidelines were broken down to make it easier for health care providers to understand.
This topic of discussion was presented by Daniel Einhorn, MD, who is an endocrinologist and medical director at Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute in San Diego, California.
He discussed the 2020 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes by the American Diabetes Association. The latest updates to the guidelines included the official definition of prediabetes, pharmacologic interventions for prediabetes, and goals of care for a patients comorbidities.
Prediabetes
The American Diabetes Association now acknowledges prediabetes as a medical condition. It can be established using the following parameters:
- Fasting plasma glucose of 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL 5.6 mmol/L to 6.9 mmol/L OR
- 2-hour plasma glucose during 75-gram oral glucose tolerance test of 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL 7.8 mmol/L to 11.0 mol/L OR
- A1C of 5.7% to 6.4% .
When we started off with prediabetes, we got a lot of pushback, Dr Einhorn said. Again, too many people, everybody would have a diagnosis. We cant treat so many people. But its a real thing, and prediabetes fills in that gap between normal and diabetes.
Patient-Centered Decision-Making
Figure 1.
Pharmacologic Interventions
School And Child Care
As a large portion of a childs day is spent in school, close communication with and the cooperation of school or day care personnel are essential for optimal diabetes management, safety, and maximal academic opportunities. Refer to the ADA position statements Diabetes Care in the School Setting and Care of Young Children With Diabetes in the Child Care Setting for additional details.
You May Like: What Is Early Onset Diabetes
Diabetes Care In The Hospital
Among hospitalized patients, both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are associated with adverse outcomes, including death. Therefore, careful management of inpatients with diabetes has direct and immediate benefits. When caring for hospitalized patients with diabetes, consult with a specialized diabetes or glucose management team when possible.
Management Of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Hypertension Screening
Recommendations
-
13.31 Blood pressure should be measured at each routine visit. Children found to have elevated blood pressure or hypertension should have elevated blood pressure confirmed on three separate days. B
Hypertension Treatment
Recommendations
-
13.32 Initial treatment of elevated blood pressure includes dietary modification and increased exercise, if appropriate, aimed at weight control. If target blood pressure is not reached within 36 months of initiating lifestyle intervention, pharmacologic treatment should be considered. E
-
13.33 In addition to lifestyle modification, pharmacologic treatment of hypertension should be considered as soon as hypertension is confirmed. E
-
13.34 ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers should be considered for the initial pharmacologic treatment of hypertension E in children and adolescents, following reproductive counseling due to the potential teratogenic effects of both drug classes. E
-
13.35 The goal of treatment is blood pressure consistently < 90th percentile for age, sex, and height or < 120/< 80 mmHg in children 13 years. E
Blood pressure measurements should be performed using the appropriate size cuff with the child seated and relaxed. Hypertension should be confirmed on at least three separate days. Evaluation should proceed as clinically indicated . Treatment is generally initiated with an ACE inhibitor, but an angiotensin receptor blocker can be used if the ACE inhibitor is not tolerated .
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes Can It Be Reversed
Prevention And Management Of Diabetes Complications
Nephropathy
Recommendations
Neuropathy
Recommendations
-
13.84 Youth with type 2 diabetes should be screened for the presence of neuropathy by foot examination at diagnosis and annually. The examination should include inspection, assessment of foot pulses, pinprick and 10-g monofilament sensation tests, testing of vibration sensation using a 128-Hz tuning fork, and ankle reflex tests. C
-
13.85 Prevention should focus on achieving glycemic targets. C
Retinopathy
Recommendations
-
13.86 Screening for retinopathy should be performed by dilated fundoscopy or retinal photography at or soon after diagnosis and annually thereafter. C
-
13.87 Optimizing glycemia is recommended to decrease the risk or slow the progression of retinopathy. B
-
13.88 Less frequent examination may be considered if there is adequate glycemic control and a normal eye exam. C
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Recommendations
-
13.89 Evaluation for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease should be done at diagnosis and annually thereafter. B
-
13.90 Referral to gastroenterology should be considered for persistently elevated or worsening transaminases. B
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Recommendation
-
13.91 Screening for symptoms of sleep apnea should be done at each visit, and referral to a pediatric sleep specialist for evaluation and a polysomnogram, if indicated, is recommended. Obstructive sleep apnea should be treated when documented. B
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Recommendations
Cardiovascular Disease
Recommendation
Dyslipidemia
Combination Therapy May Be Considered For People With Established Heart Or Kidney Disease

A combination of medications using two or more different types of drugs, has been effective in helping people manage their diabetes. The ADA now recommends that people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin combine insulin with a GLP-1 receptor agonist if additional glucose lowering is needed, as opposed to only increasing insulin dosing.
Past ADA guidelines recommended using an SGLT-2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 receptor agonist for heart or kidney disease. This year, however, recommendations suggest that a combination of the two should be considered to lower risk even more. In addition, instead of adding the drugs one by one, it may be best to start with a combination of the two depending on the individuals situation.
These updates are posted in Chapter 10 of the 2022 ADA diabetes care guidelines.
Read Also: Best Way For A Type 1 Diabetes To Lose Weight
Finerenone Can Be Used To Treat Ckd When Sglt
The updated guidelines now suggest that certain individuals who have stage 4 CKD to take SGLT-2 inhibitors to preserve kidney function. In the past, ADA recommended that after progressing to stage 4 kidney disease, people should stop using SGLT-2s, as the risk for additional kidney damage actually increased at advanced stages. The updated guidelines changed this threshold, suggesting that more people in advanced stages of CKD can now safely use an SLGT-2 inhibitor.
Some people, however, may not respond well to treatment with an SGLT-2 inhibitor. In this case, finerenone , a recently approved non-steroidal MRA drug, can alternatively be used to improve both kidney and heart outcomes.
These updates are posted in Chapter 11 of the 2022 ADA diabetes care guidelines.
Pharmacologic Therapy For Type 1 Diabetes
Recommendations
-
9.1 Most people with type 1 diabetes should be treated with MDI of prandial and basal insulin or CSII. A
-
9.2 Most individuals with type 1 diabetes should use rapid-acting insulin analogs to reduce hypoglycemia risk. A
-
9.3 Patients with type 1 diabetes should be trained to match prandial insulin doses to carbohydrate intake, premeal blood glucose, and anticipated physical activity. C
See 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment in the complete 2020 Standards of Care for more detailed information on pharmacologic approaches to type 1 diabetes management.
You May Like: Hotels Near Joslin Diabetes Center Boston
Obesity Management For The Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
There is strong evidence that treating obesity can delay the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes. It also has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Modest and sustained weight loss has been shown to improve glycemic control and reduce the need for glucose-lowering medications. Clinical benefits can be seen with a minimum of 35% weight loss.
Limitations Of Ada Standards Of Medical Care In The Context Of Gdm
Time of pregnancy for the diagnosis of GDM ADA guidelines define GDM as diabetes diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy that was not clearly overt diabetes prior to gestation. ADA clearly states that IADPSG criteria as well as the diagnostic criteria used in the two-step approach were not derived from women enrolled in the first half of pregnancy. In light of this observation, the rationale behind extending the diagnostic criteria to the entire second trimester and selectively excluding the first trimester is not clear. World Health Organization 2013 and FIGO guidelines recommend diagnosis of GDM if the IADPSG criteria are fulfilled anytime during the pregnancy . Clearly, more consensus is needed on the applicability of a diagnosis of GDM during early pregnancy.
Use of term overt diabetes prior to gestation in the GDM definition In 2010, an IADPSG consensus panel introduced a new term, overt diabetes during pregnancy, which demarcated women with GDM from those with hyperglycemia of greater severity . This term was used to label women who were diagnosed with diabetes for the first time during the pregnancy. A similar definition was used by WHO 2013 guidelines, albeit with a different term diabetes in pregnancy . The term overt diabetes prior to gestation used in the ADA definition is not in alignment with our current understanding of GDM and should have been overt diabetes during gestation.
You May Like: How Does Blood Sugar Work
Ada Guidelines On Pharmacologic Means Of Glycemic Therapy In Type 2 Diabetes
In September 2020, the ADA published clinical guidelines on pharmacologic means of glycemic therapy in type 2 diabetes. They include the following:
- Metformin therapy is the preferred initial pharmacologic treatment for type 2 diabetes
- To extend the time to treatment failure, early combination therapy can, in some patients, be considered at treatment initiation
- If evidence of ongoing catabolism exists , if symptoms of hyperglycemia are present, or when HbA1c or blood glucose levels are very high , consider early introduction of insulin
- Employ a patient-centered approach to guide the choice of pharmacologic agents, with factors such as cardiovascular comorbid conditions, hypoglycemia risk, impact on weight, cost, risk for side effects, and patient preferences taken into account
- It is recommended that a sodium-glucose cotransporter2 inhibitor or glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonist with demonstrated cardiovascular disease benefit be administered to patients with type 2 diabetes who have established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease , indicators of high ASCVD risk, established kidney disease, or heart failure
- The use of GLP-1 RAs, when possible, is preferred over insulin therapy in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes who need greater glucose reduction than oral agents can provide
- Reevaluate the patients medication regimen and medication-taking behavior every 3 to 6 months, adjusting them as needed to incorporate specific factors that affect treatment choice