What Does Postprandial Mean
When we talk about glucose in relation to food, we can break up our bodys state into three metabolic periods:
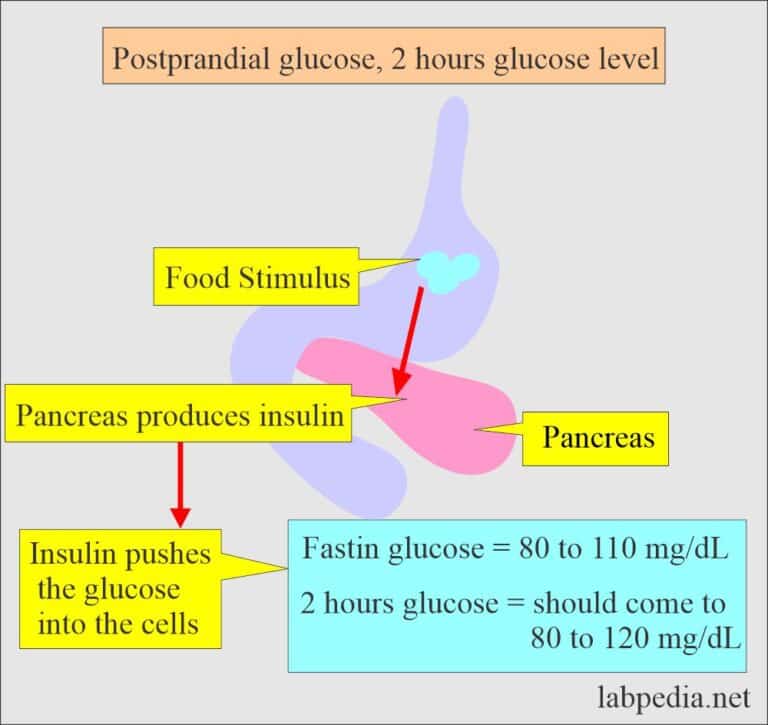
During the postprandial window, glucose concentrations rise and your body releases insulin to help regulate glucose in the body and store it in a way that can be easily accessed during the postabsorptive and fasting states. If we frequently eat high-carbohydrate meals and snacks, our body can stay in a state of elevated postprandial glucose, requiring the body to regularly release insulin, which can lead to insulin resistance.
How To Measure Your Spikes
The American Diabetes Association recommends you check your blood sugar levels right before mealtime with a blood sample from a finger stick. Then do it again 1 to 2 hours after that first bite of food.
Keep this up for a week or so. Write down the time and the blood sugar number. Make a note about anything you think might affect your levels, like medicine or exercise. And don’t forget to log exactly what you ate, along with portion sizes and the amount of carbs.What levels are too high after a meal? Experts vary on what the number should be, but the ADA says a general goal is a blood sugar level under 180 mg/dL, 1 to 2 hours after a meal. Talk to your doctor about what you should aim for, and don’t adjust your medicine without speaking to them first.
What Is Normal Post
According to the American Diabetes Association, normal postprandial blood sugar level should be under 140 mg/dL after two hours of eating. However, for a diabetic patient PPBS range under 180 mg/dL is considered to be normal. More than that can be a matter of concern and precautionary measures should be taken immediately. Results showing readings within 140-199 mg/dL shows that you do not have diabetes as of now but might be prone to diabetes in the future. Doctors usually do not prescribe medicines for patients in the prediabetic state or simply can offer dietary changes or low-dose medications. If you have readings more than 199 mg/dL, you have diabetes and should consult your doctor immediately. A 2-hour postprandial blood sugar level chart:
| Post Prandial Sugar Level |
| 140-199 mg/dL |
You May Like: Blood Sugar Test At Home
How Is The Ppbs Test Done
The PPBS test is done by drawing a blood sample from your arm. The test must be done after 2 hours starting from the time you take your meal. If the test is taken 2 hours after you finish the meal, you might get the wrong results.Patients are recommended to take their usual anti-diabetic medicines at the usual timings to get accurate results.
Why Does Blood Glucose Change All The Time
Everything in your body is changing all the time. There is fluctuation in your temperature, your blood pressure, your pH, blood sugar, etc. This is the essence of metabolism.
Like a machine that starts off with raw materials and converts them to usable energy, our bodies process nutrients, burn food for fuel, use that fuel, send signals to require more nutrients, and so on.
Think of it like this: The work of the heater or air conditioner is to maintain a comfortable temperature. So in the same way room temperature can vary a bit and is always changing in small degrees, the body is constantly trying to maintain general equilibrium.
Your blood glucose is not supposed to stay exactly the same. But it is supposed to stay within a healthy normal blood sugar range.
Read Also: Why Does My Blood Sugar Drop After Eating Protein
Who Should Check Ppg
How often you should test PPG is based on you specifically, and on your goals for controlling your blood sugar. You should work with your care team to identify your testing regimen and target goals. The ADA does recommend that certain people test PPG and blood sugar levels more frequently, including:
- People with history of high blood sugar after eating
- People who take multiple medications and are at risk for high or low blood sugar
Blood glucose levels vary at different times throughout the day over a period of weeks, Kumar says. Thus, its important to check your blood glucose at regular intervals to provide accurate information to your physician.
How Common Is Diabetes In India
Diabetes and high blood sugar are widespread chronic illnesses throughout the world. India is often called the diabetes capital of the world with diabetes being the fastest growing disease in the country. There are more than 72 million diabetics in India, which represents 49% of the global burden of the disease.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes And Sleep
What Is Postprandial Blood Sugar
Postprandial blood sugar is a measurement of the glucose concentration in your bloodstream in the period up to four hours after eating a meal. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates from foods into simple sugars, glucose and fructose, which are absorbed into the bloodstream. Glucose is the major fuel source for the body, along with fat. Every cell in your body relies on this energy source to function. In addition to ingesting glucose from food, your body can also make glucose in a process called gluconeogenesis. Your body aims to maintain a consistent level of glucose in your blood, storing or burning excess and making more if needed. High levels of glucose in your blood is known as hyperglycemia and can be problematic.
Insulin is the hormone that helps our cells take in glucose from our blood stream, bringing our blood sugar back down after a meal. While a sharp rise in glucose is an expected response to a high-carb meal, frequent spikes or glucose that stays high for a prolonged period may be signs that your body has become less efficient at removing glucose from the blood. This is called insulin resistance and its the root of metabolic dysfunction. Short of measuring insulin itself , postprandial blood sugar is the next best window into this glucose and insulin relationship in your body.
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
Don’t Miss: Does Insulin Help You Lose Weight
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Why Postprandial Blood Sugar Matters If You Dont Have Diabetes
Avoiding progression to prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes arent the only reasons to pay attention to postprandial blood glucose. Elevated postprandial blood sugar can also be a predictor of cardiovascular disease mortality and atherosclerosis in people without diabetesand its a better indicator than fasting blood sugar. In fact, in individuals at greater risk for cardiovascular events, postprandial blood sugar levels are often high even when fasting blood sugar levels are unremarkable.
There are a few reasons for this connection to cardiovascular risk. Frequent episodes of postprandial hyperglycemia leads to the production of free oxygen radicals, also known as oxidants/oxidative stress, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells, and in particular, the mitochondria. The mitochondria, the part of the cell that produces energy , cannot keep up with a high metabolic load, and generates these free oxygen radicals, which build up over time, eventually overwhelming the bodys antioxidant capabilities, and causing metabolic dysfunction.
Donât Miss: What To Do When Glucose Is High
You May Like: What To Do When Diabetic Blood Sugar Is Low
How Can I Treat Low Blood Sugar
If youve had low blood sugar without feeling or noticing symptoms , you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if its low and treat it. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Even if you dont have symptoms but think you may have low blood sugar, check it. If your blood sugar is lower than 70 mg/dL, do one of the following immediately:
- Take four glucose tablets.
- Drink four ounces of fruit juice.
- Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda.
- Eat four pieces of hard candy.
Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
How To Prepare For Post Prandial Blood Sugar Test

Postprandial blood sugar test is very simple. However, the following precautions should be taken. Eat your normal meal during the test. Include carbohydrates in your meal. This will give you accurate results. Finish your meal within 20 minutes. Rest for 2 hours after taking the meal. Do not exercise, drink, smoke, or eat anything during these 2 hours as it may affect the test results. Call your phlebotomist immediately after completion of two hours of having your meal.
Read Also: Healthy Diet For Diabetics To Lose Weight
What Is The Target Blood Sugar Level Everyone Should Achieve
| Thi gian kim tra |
| Quá cao: Tìm cách là m gim lng ng trong máu. | |
| 240 300 mg / dl | Quá cao: ây có th là du hiu ca vic qun lý lng ng huyt không hiu qu, vì vy, hãy i khám bác s. |
| 300 mg / dl tr lên | Rt cao: Cn tìm kim s chm sóc y t ngay lp tc. |
Please dialHOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and receive 20% off for consultation fee at the first appointment MyVinmec app is also available and convenient for your bookings management andTelehealth service with Vinmec doctors all in one.
XEM THÃM:
Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications like Metformin, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
You May Like: Is Diabetes Considered A Disability Under Ada
The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
An oral glucose tolerance test is one that can be performed in a doctor’s office or a lab. The person being tested starts the test in a fasting state .
An initial blood sugar is drawn and then the person is given a “glucola” bottle with a high amount of sugar in it . The person then has their blood tested again 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 3 hours after drinking the high glucose drink.
For the test to give reliable results, you must be in good health . Also, you should be normally active , and you should not be taking any medicines that could affect your blood glucose. The morning of the test, you should not smoke or drink coffee. During the test, you need to lie or sit quietly.
The oral glucose tolerance test is conducted by measuring blood glucose levels 5 times over a period of 3 hours. In a person without diabetes, the glucose levels in the blood rise following drinking the glucose drink, but then they fall quickly back to normal .
In a diabetic, glucose levels rise higher than normal after drinking the glucose drink and come down to normal levels much slower .
As with fasting or random blood glucose tests, a markedly abnormal oral glucose tolerance test is diagnostic of diabetes. However, blood glucose measurements during the oral glucose tolerance test can vary somewhat. For this reason, if the test shows that you have mildly elevated blood glucose levels, the doctor may run the test again to make sure the diagnosis is correct.
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels by Type |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Also Check: Risks Of High Blood Sugar
How Do I Get Ready For This Test
You must fast for 12 hours before the test and then eat a meal with at least 75 grams of carbohydrates. After the meal, don’t eat anything else before having the test. Plan to rest during the 2-hour waiting period, because exercise can cause blood sugar levels to rise. You may not have to fast if you’re pregnant.
Be sure your healthcare provider knows about all medicines, herbs, vitamins, and supplements you are taking. This includes medicines that don’t need a prescription and any illegal drugs you may use.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal.
Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : Less than 100 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after a meal: Less than 140 mg/dL
- 2-3 hours after eating: Less than 100 mg/dL
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar Monitoring For Type 2 Diabetes
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The oral glucose tolerance test is also known as the glucose tolerance insulin response test. The OGTT helps practitioners determine how quickly glucose is cleared from the blood, and has been used to screen for glucose dysfunction.
This test tests your fasting glucose level and then tests your level every hour after you drink a glucose beverage to observe how your blood sugar responds. The Nutrisense Nutrition Team uses and recommends the GTIR. Your dietitian can best guide you through this test and the optimal lab values for you.
Why Is Monitoring Your Postprandial Blood Sugar Important
Monitoring your postprandial blood sugar allows you to understand how well your body responds to insulin, how your glucose levels fluctuate, and to get a better overall view of your metabolic health.
While it isnât the only marker to be aware of when it comes to glucose metabolism, itâs an important one. Research has shown that postprandial blood sugar levels are strongly associated with HbA1c levels, meaning they are better indicators of glycemic control.
Postprandial hyperglycemia can indicate a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease. This refers to blood sugar levels that consistently rise above 140 mg/dL in the hours after eating. Detecting abnormal postprandial levels can also help you implement new dietary or lifestyle changes that can help lower your risk of developing these conditions.
Read Also: Can Diabetics Eat Pig Feet