What Do Insulin Pumps Cost
This can be a tricky question, because when it comes to diabetes technology the cost often varies based on ones insurance coverage.
Generally, you can spend thousands of dollars on the initial purchase because youre buying a new device along with that first set of supplies to use it. The starting cost can be anywhere from $3,000 to $8,000 depending on the device, and monthly supplies can also add up quickly. Most companies do offer payment plans, too.
Keep in mind, this is just the first-time buy and doesnt include the needed pump supplies including infusion sets, tubing, cartridges or reservoirs for insulin, as well as adhesives wipes for site prep. Of course, youd also need to purchase the insulin to fill the pump and any separate CGM supplies that you might use alongside this pump.
Even with insurance, it can cost hundreds of dollars per month to afford an insulin pump.
Most private insurance companies cover insulin pumps under the durable medical equipment portion of the policy. Youll need to work with a doctor to get a prescription and Letter of Medical Necessity confirming your diagnosis and medical need.
The paperwork can be somewhat daunting, so most insulin pump companies offer help in the form of dedicated insurance service teams that work with patients to apply for coverage.
The terms of coverage vary, and your choice of covered device may be limited because some insurance companies have preferred deals with certain pump makers.
Why Choose Pump Or Pen Therapy
Our motto in advising our patients is that the form of insulin delivery should suit you, but increasingly we will advise you to use diabetes technology to achieve your desired goals. We know by now, that the more you use technology, the better your diabetes goals and guidelines can be achieved, such as an HbA1c of 7%. Before starting insulin pump therapy, we, as practitioners, impose some conditions on your knowledge of diabetes control, such as carbohydrate counting, uploading your blood glucose values to us at least every four weeks and, not unimportantly, keeping in touch with your diabetes team.
Also Check: Cheapest Insulin In The World
Diabetes Specialist Nurses/educators Keep It Human
Hall says he concurs with the late eminent UK diabetes specialist Robert Tattersalls observation on what he considers one of the most important advances in the management and treatment of type 1 diabetes: the human touch.
Referring to Tattersalls book, Diabetes: A Biography, Hall quoted: If asked what innovation had made the most difference to their lives in the 1980s, patients with type 1 diabetes in England would unhesitatingly have chosen not human insulin, but the spread of diabetes specialist nurses these people did more in the last two decades of the 20th century to improve the standard of diabetes care than any other innovation or drug.
In the United States, DSNs were diabetes educators until recently, when the name changed to certified diabetes care and education specialist .
Above all, they have humanized the service and given the patient a say in the otherwise unequal relationship with all-powerful doctors, concludes Hall, again quoting Tattersall.
For more diabetes and endocrinology news, follow us on and
Follow Medscape on , , , and .
Dont Miss: Non Insulin Injections For Type 2 Diabetes
Also Check: Diabetes How To Control Blood Sugar
Who Should Use A Pump
Insulin pumps have been used successfully across the age spectrum. Whether or not to use a pump is a personal decision. You can manage your diabetes equally well with pumps or multiple injections, so it really comes down to your preference.
Remember that a pump is just a toolyou can reach your blood glucose goals with a pump or injections. Choosing one method over the other is not a lifelong commitment. Some people go on and off their pumps .
Is Insulin Pump Therapy Right For Me
Choosing to start insulin pump therapy to manage type 1 diabetes for yourself or a loved one is a decision that you should make in concert with a diabetes healthcare provider. Insulin pump therapy may be a good option if you or a loved one:2,3
-
need and want a less burdensome way to deliver insulin
-
have an unpredictable schedule day to day that results in varied insulin needs as well.
-
need very small amounts of basal insulin.
-
have higher and lower basal insulin needs during the 24 hours in a day.
-
travel across time zones or do shift work.
-
participate in athletics and/or intense yet irregular exercise.
-
want to give insulin discreetly
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus
Omnipod Insulin Management System
The OmniPod and the Omnipod DASH may be the most popular pump for individuals with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes on the market today. It includes a Pod that weighs only 25 grams without insulin and is entirely self-contained. Youll control your Pod with your PDM, which makes up the other half of the OmniPod system. With the PDM, you can adjust the timing of insulin delivery, calculate boluses, check up to 90 days of data, and even test your blood sugar level with a built-in glucose monitor. It is tubeless, waterproof and wireless meaning you wont have to deal with tubing or having to lug a large device around!
What Is Insulin Pump Therapy
Insulin pump therapy is the term used to describe the use of insulin pumps in managing blood glucose levels in people with insulin-dependent diabetes.
It is also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion , which basically explains the function of an insulin pump to continually infuse insulin into the layer of fat just under the skin .
Insulin pump therapy has been recognised as being effective in helping people with diabetes, particularly people with type 1 diabetes, to achieve improved HbA1c levels and, in many cases, helping to improve quality of life.
Read Also: I Need Help With My Diabetes
How Insulin Pumps Work Who Benefits From Them And Different Types Of Pumps
As people with diabetes know, keeping blood sugar levels in a safe range is extremely important. Good blood sugar control not only makes you feel well, but also helps prevent long-term diabetes complications, such as blindness, kidney failure and heart disease.
People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin, a hormone that helps the body use sugar , a key source of energy that comes from carbohydrates. If you have type 1 diabetes you must make up for the lack of insulin with insulin therapy.
Meanwhile, people with type 2 diabetes produce insulin, but their bodies dont use insulin properly, or they dont produce enough insulin. Diet, exercise and medication can often work to control glucose levels. However, in certain cases, these measures arent enough, and insulin therapy is needed to better control blood sugar levels.
While insulin can be given by self-injection, people who take multiple daily injections of may also consider using an insulin pump.
An insulin pump provides continuous delivery of short acting insulin all day long. The insulin pump substitutes the need for long acting insulin. A pump also replaces the need for multiple daily injections with a continuous insulin infusion, and also helps to improve your blood sugar levels.
Minimed 630g Insulin Pump With Optional Cgm
The MiniMed 630G insulin pump delivers precise doses of insulin to your body. When combined with our CGM, it takes action for you with the SmartGuard Suspend on low feature providing protection that can help keep your glucose levels stable. ,3
Individuals pictured and/or quoted here were compensated for spending the day with us and allowing us to photograph them and their family. Their thoughts and opinions are their own.
Important Safety Information: MiniMed 770G System With SmartGuard TechnologyThe MiniMed 770G system is intended for continuous delivery of basal insulin and administration of insulin boluses for the management of type 1 diabetes mellitus in persons two years of age and older requiring insulin as well as for the continuous monitoring and trending of glucose levels in the fluid under the skin. The MiniMed 770G System includes SmartGuard technology, which can be programmed to automatically adjust delivery of basal insulin based on continuous glucose monitoring sensor glucose values and can suspend delivery of insulin when the SG value falls below or is predicted to fall below predefined threshold values.
The Medtronic MiniMed 770G System consists of the following devices: MiniMed 770G Insulin Pump, the Guardian Link Transmitter, the Guardian Sensor , one-press serter, the Accu-Chek® Guide Link blood glucose meter, and the AccuChek®Guide Test Strips. The system requires a prescription.
Read Also: Signs To Know If You Have Diabetes
How Is An Insulin Pump Worn
A small, soft catheter is placed using a tiny needle in the upper arm, belly, hip, buttock, or thigh. Thin tubing connects the catheter to the pump, which is worn in a pouch, pocket, or on a belt. Together, the catheter, needle, and tubing are all called an infusion set. Throughout the day and night, the pump delivers a programmed amount of insulin that passes through the tubing and catheter into the body.
When the catheter is in place, your child wont feel it. They can do their usual activities, including sleep. Some pumps can even be worn while bathing or swimming. The catheter stays in place for 23 days before you replace it.
Handling Sports And Physical Activity
While older pumps needed to be disconnected before engaging in physical activity, newer pumps have an exercise mode, and if you have one, taking the pump off is no longer recommended.
However, you’ll still need to check your glucose before, during, and after playing sports or exercising. You may also need to take a bolus of insulin and have a small snack an hour prior to activity due to the missed basal dose.
Work with your healthcare provider to come up with an effective protocol to follow.
Don’t Miss: Is Type 2 Diabetes Curable
Interoperability And Homemade Diabetes Tech
The future of insulin pumping definitely appears to be connecting these devices to CGMs for improved blood glucose control. This of course has pushed to the forefront the issue of device interoperability and do-it-yourself technology.
Behind this evolution has been pressure from the patient community rallying behind a #WeAreNotWaiting mantra pushing to get innovative technology out more quickly and allow data and device integration.
Many of the folks creating DIY connected systems are using older, discontinued insulin pumps such as the Minimed Revel and Paradigm models. Despite an FDA warning and mainstream media concern that surfaced in 2019, thousands of people are now safely and successfully using these homemade systems.
Meanwhile, FDA has published new interoperability protocols to help the established medtech industry create products that are more modular and can work together safely and seamlessly. For insulin pumps like the Tandem t:slim X2, that means gaining a marking that new pump as interoperable technology.
This is important to keep in mind when shopping for new insulin pump technology.
Benefits Of Insulin Pumps

Insulin pumps have many benefits over traditional insulin injection therapy. Research evidence shows that pumps are better at controlling blood sugar and cause fewer complications. People using insulin pumps have fewer episodes of severe hypoglycaemia and less than half the admissions for the serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis. Insulin pump advantages include:
- Better diabetes control
- The pump is small and discreet usually smaller than a pack of cards
- Delivers a steady supply of insulin 24 hours a day
- You can add a bolus of insulin at meals quickly and easily
- The insulin is introduced through a cannula, meaning fewer injections
- You only need to change the cannula every 2-3 days
- Pumps simplify your regime because you only need rapid-acting insulin
You May Like: How Do I Control My Diabetes
Taking A Break From Insulin Pump
If you have been using an insulin pump for some time, you may be getting tired of having it attached to your body. This may warrant a time to take a break from the insulin pump just to keep your sanity.
When taking a break from the insulin pump, there are some things you need to consider first to ensure your safety and health. Here are some tips to help you with taking a break from your insulin pump.
When Can A Person With Type 1 Diabetes Start Insulin Pump Therapy
A person with type 1 diabetes can successfully start insulin pump therapy at any point of their life with diabetes, including at the time of diagnosis.1 If insulin pump therapy is something that you and/or your caregivers believe would benefit your diabetes management, discuss this with your diabetes healthcare providers.
Recommended Reading: Can You Donate A Kidney If You Have Diabetes
The Different Types Of Insulin Pumps Available In 2022
Welcome to the ultimate guide to the different types of insulin pumps on the market the 2019 edition! I thought since I am on an insulin pump, and have done the research into choosing that insulin pump, that it would be useful to have a little guide on all the different types available and what is the âbest insulin pump on the marketâ.
If youâre interested in why I think an insulin pump is good for travelling, then you can check out my post here.
How Many Insulin Pumps Are Available And How Are They Tested
Today there are a handful or so of companies that manufacture insulin pumps around the globe. Prior to being made available for purchase, these insulin delivery devices are thoroughly tested by the manufacturer and reviewed by regulatory authorities, such as the Food and Drug Administration in the U.S. Once a device is given the green light to be sold, it must be prescribed to the person with type 1 diabetes by their healthcare provider. Along with the prescription the healthcare provider gives specific instructions for how the insulin pump should be set up. Next the person with type 1 and their caregivers are taught by a healthcare provider, typically a Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist , that is also a Certified Pump Trainer for the insulin pump the user has chosen. Users of insulin pump therapy learn all the ins and outs of insulin pump therapy and the specifics about the particular pump they choose to use. In addition, manufacturers provide continuous 24/7 customer support to people who use their pump management system.
Don’t Miss: Non Insulin Drugs For Diabetes
Hyperglycemia And Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Studies have also shown improved glycemic control in patients using insulin pumps compared with patients using multiple daily insulin injections. Another study showed that the incidence of DKA is equivalent for pump users and patients on MDIs. In particular, nocturnal and predawn glycemic control is improved on insulin pump therapy, as hour-by-hour preprogrammed basal rate changes facilitated by the pump help counteract prebreakfast blood glucose increases that are not easily addressed with injection therapy.
However, hyperglycemia and DKA can occur with insulin pump use, whether due to user error in programming or to device malfunction. Studies show that device problems leading to hyperglycemia include diminished insulin delivery due to a depleted or malpositioned battery, occlusion or crimping of the cannula, disruption of the infusion set , or complete pump failure. DKA in particular occurs more frequently early after starting insulin pump use, suggesting that acclimation to the device has a learning curve.
Finally, continuous use of the same infusion set for an extended period increases the risk of cannula occlusion and changes the physiochemical environment at the delivery site, altering the rate of insulin absorption and increasing the risk of hyperglycemia, as well as other problems described below. One study has found that there was a slow but steady increase in average daily serum glucose concentrations as patients wore an infusion set continuously beyond 3 days.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
If you have diabetes and are curious about insulin pump options, talk with a healthcare provider or a Diabetes Care and Education Specialist. There are many types of insulin pumps on the market. Ask your provider which option is right for you.
Insulin pumps can offer a flexible option for insulin delivery. The pump works by sending continuous insulin or insulin surges directly into your bloodstream. Many people with diabetes find insulin pumps to be more convenient than insulin injections. Insulin pumps arent permanent. You can change your mind and return to injections if you dont like using an insulin pump. There are many insulin pump brands on the market. Speak with your healthcare provider to figure which option is right for you.
You May Like: Best Cold And Flu Medicine For Diabetes
Whats The Difference Between A Traditional Insulin Pump And A Patch Pump
Traditional insulin pumps push insulin from a chamber within the pump through tubing to a site on the skin that is connected to a smaller flexible plastic tube . The cannula is a few millimeters long and delivers the insulin underneath your skin.
Insulin patch pumps also use a flexible plastic tube under the skin, but the insulin delivery chamber and the cannula are part of one pod that sits in the skin with an adhesive patch. You can place the patch directly on your belly or arm. There is no external tubing with a patch pump, and its controlled wirelessly with a handheld controller.
The tubing and cannula are removed and replaced every two to three days. A healthcare provider called a Diabetes Care and Education Specialist will show you how to do this.
Common insulin pump brands include:
How Do Insulin Pumps Work For Type 1 Diabetes
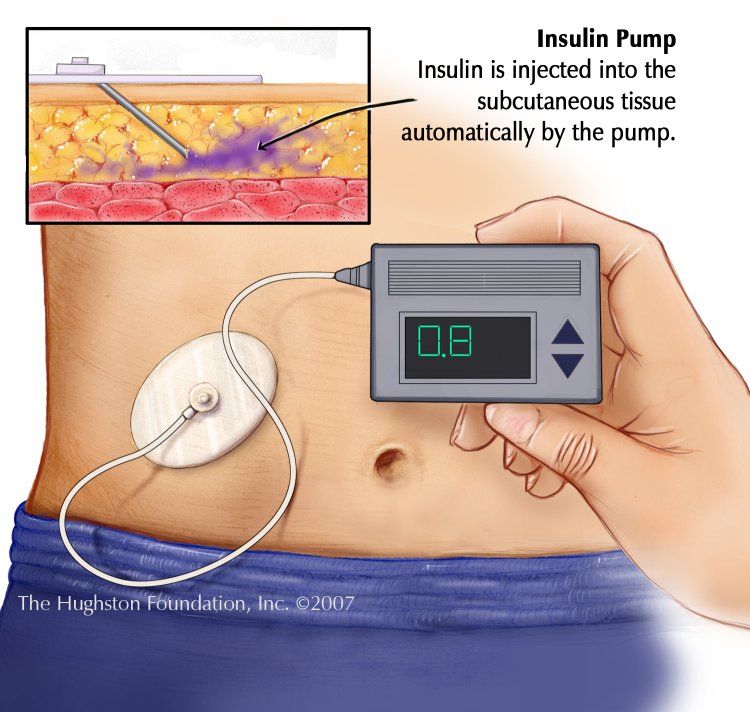
The insulin pump prevents complications when blood glucose levels go out of range.
If blood glucose levels are high, acute and chronic complications can occur, including:
-
Damaged blood vessels
-
Frequent urination from excess glucose in the blood
-
Diabetic ketoacidosis is when the body burns fat instead of glucose for energy
You may also notice dehydration, tiredness, and weight loss.
Type 1 diabetes is much less common than type 2 diabetes, which differs from type 1 in that the pancreas produces insulin but does not use it properly.
Type 1 diabetes commonly starts during childhood or adolescence thats why people often call it juvenile diabetes. However, it can affect anyone at any age. Studies² point to genetic and environmental factors causing the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic cells.
You May Like: How To Know If Your Getting Diabetes