What Is Normal Fasting Blood Sugar And What Is A Diabetes Blood Sugar Level
The results of the fasting blood sugar test will come back as a number:
- 99 mg/dL or lower: This is a normal fasting blood sugar level.
- 100125 mg/dL: Fasting blood sugar in this range typically indicates prediabetes. This means your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
- 126 mg/dL or above: This indicates high blood sugar, the main sign of diabetes.
If you have a high fasting blood sugar level, your healthcare provider may repeat the test to make sure. If the test reveals that you have prediabetes, your healthcare provider will recommend you repeat the fasting blood sugar test every year or two. The results will help you know whether you are progressing to Type 2 diabetes.
What Are The Preparations Needed For Gtt
GTT is an elaborate blood test, that requires frequent testing and as the special requirements need for GTT are as follows
- Have a normal diet like any other day.
- Inform the doctor about the varied prescription drugs you are taking, as certain drugs like corticosteroids, diuretics and anti- depressants can cause false results.
- Fasting is required for 8 to 10 hours prior to the test and only water is allowed during this period.
- You might want to avoid using the washroom prior to testing as urine samples might be needed
- On the morning of the test do not smoke or have coffee or caffeine based product.
- The GTT is not to be done on a sick person
Also Check: How To Treat Diabetes Insipidus
Glucose Tolerance Test Results
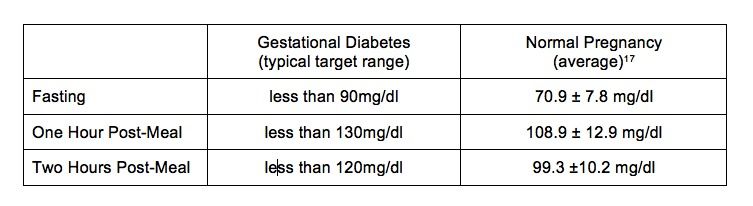
Itâs worth knowing that approximately 66 percent of pregnant women who take the glucose tolerance test end up not being diagnosed with gestational diabetes. So, just because your provider has ordered a glucose tolerance test during your pregnancy doesnât automatically mean you have gestational diabetes.So, what do the results of the glucose tolerance test indicate? Four blood samples are drawn during a glucose tolerance test. If just one of the four results is higher than normal, your provider may recommend that you make subtle changes to your current pregnancy diet. The provider may have you take another glucose tolerance test after youâve made those changes to check if the results have improved.If more than one of the results is higher than normal, your provider may determine that you have gestational diabetes. The following figures indicate higher than normal blood sugar levels:
-
Fasting blood sample: Higher than 95 mg/dL
-
1-hour blood sample: Higher than 180 mg/dL
-
2-hour blood sample: Higher than 155 mg/dL
-
3-hour blood sample: Higher than 140 mg/dL .
If itâs determined that you have gestational diabetes, your healthcare provider can help guide you in making changes to help manage it. Eating a healthy diet, exercising during your pregnancy, and taking medication prescribed by your provider have been shown to help control blood sugar and to help keep you and your baby healthy.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Diabetes
Are There Any Risks
While the test itself does not come with any real risk, there are certain risk factors for developing gestational diabetesincluding being over the age of 25, having a family history of diabetes, and/or being obese. That said, half of those who develop gestational diabetes have no known risk factors, making testing is so important.
What Can You Do If Youre At Risk For Gestational Diabetes
If youre at risk for gestational diabetes, there are a few things you can do to help lower your chances of developing the condition:
-Get regular exercise. Exercise can help your body use insulin more effectively.
-Eat a healthy diet. Eating lots of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help your body control blood sugar levels.
-Maintain a healthy weight. If youre overweight, losing just 5 to 10% of your body weight can help lower your risk of gestational diabetes.
It is important to consider these things even before pregnancy, so Im glad youre thinking about it.
Recommended Reading: What Causes High Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
What Is A Glucose Test In Pregnancy
There are two glucose tests that are typically offered during pregnancy as part of your prenatal care. Both the glucose challenge test and the glucose tolerance test measure how your body responds to glucose and help determine if you have gestational diabetes, which may develop during your pregnancy.These glucose tests are routinely done during pregnancy and are recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists for all pregnant women.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
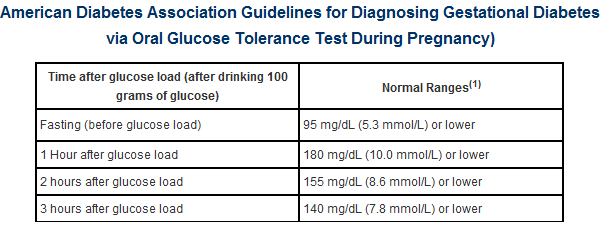
As women ages 35 and above the chances of getting affected with gestational diabetes are high and so it is important to know the ideal count of sugar to be present while carrying. If your test result is below 7.8 mmol/L after consumption of 50g glucose and lapse of 60 minutes then the sugar count is normal. There is also another way to know normal blood range by following the oral glucose tolerance test , with a sugared liquid having 75 g glucose and 3 blood tests. In the below 3 tests if minimum 1 out of the 3 blood tests values is greater than or equal to the mentioned readings then your blood count is not normal.
- 5.1 mmol/L fasting
- 10 mmol/L 1 hour after drinking the sugary drinks or the sugary liquid
- 8.5 mmol/L 2 hours after drinking the sugary liquid
Usually when blood sugar level is higher than 200 mg/dl is seen a second evaluation i.e., an oral glucose tolerance test is recommended.
You May Like: What Is High Glucose Levels
Who Is At Risk
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- having had gestational diabetes in an earlier pregnancy
- a family history of diabetes
- having obesity or other diabetes-related conditions
- being physically inactive
If a person gains more weight than is usual during pregnancy, this may be a sign of gestational diabetes, according to the
- attending more frequent screening and seeking medical help if glucose levels go up
- insulin use, in some cases
The healthcare provider will advise on each persons needs and treatment plan, as diabetes affects everyone differently.
What Does The Glucose Tolerance Test Measure
The classic oral glucose tolerance test measures blood glucose levels five times over a period of three hours. Some physicians simply take a baseline blood sample followed by a sample two hours after drinking the glucose solution. In a person without diabetes, the glucose levels rise and then fall quickly. In someone with diabetes, glucose levels rise higher than normal and fail to come back down as fast.
People with glucose levels between normal and diabetic levels have so-called impaired glucose tolerance . People with impaired glucose tolerance do not have diabetes.
Each year, 5% to 10% of people whose test results show impaired glucose tolerance actually develop diabetes. Weight loss and exercise may help people with impaired glucose tolerance return their glucose levels to normal. In addition, some physicians advocate the use of medications, such as metformin , to help prevent/delay the onset of overt diabetes. Studies have shown that impaired glucose tolerance itself may be a risk factor for the development of heart disease, and whether impaired glucose tolerance turns out to be an entity that deserves treatment itself is something that physicians are currently debating.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Is Caused By
Who’s At Risk Of Gestational Diabetes
Any woman can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, but you’re at an increased risk if:
- your body mass index is above 30 use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI
- you previously had a baby who weighed 4.5kg or more at birth
- you had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- 1 of your parents or siblings has diabetes
- you are of south Asian, Black, African-Caribbean or Middle Eastern origin
If any of these apply to you, you should be offered screening for gestational diabetes during your pregnancy.
Assessment And Management Of Complications
Retinopathy. Women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes should ideally have ophthalmological assessments before conception, during the first trimester, as needed during pregnancy, and within the first year postpartum . The risk of progression of retinopathy is increased with poor glycemic control during pregnancy, and progression may occur for up to 1 year postpartum . Additional risk factors for retinopathy progression include: chronic and pregnancy-induced hypertension, preeclampsia, more severe pre-existing diabetic retinopathy , and a greater decrease in A1C between the first and third trimester of pregnancy . Closer retinal surveillance is recommended for women with more severe pre-existing retinopathy, those with poor glycemic control or women with greater reductions in A1C during pregnancy . Laser photocoagulation for severe nonproliferative or proliferative retinopathy prior to pregnancy reduces the risk of visual impairment in pregnancy if not performed prior to pregnancy, it is still considered safe to receive during pregnancy.
Although there are no intervention trials for ASA prophylaxis for the prevention of preeclampsia specific to women with pre-existing diabetes, ASA prophylaxis started between 12 to 16 weeks of gestation is likely to be beneficial, given the evidence of benefit in other high-risk populations, .
Read Also: Can You Eat After Taking Insulin
How To Lower Your Blood Glucose Levels
Even if you have a normal glucose screening and never test positive for glucose in your urine, its still important to follow a healthy diet during pregnancy, which can help stabilize your blood sugar levels.
Here are some tips on what to eat to keep blood sugar spikes at bay, plus other smart strategies:
Risk Factors For Developing Diabetes During Pregnancy
There is an increased risk of diabetes during pregnancy if:
- The woman is overweight
- The woman is a smoker or around smokers more than average
- The woman is older
- There is a family history of diabetes
- The woman is from an ethnic minority
- There is previous history of the birth of a large baby
There is a routine antenatal test used to measure glucose levels in urine however it has been noted it is relatively unreliable for diagnosing diabetes.
Therefore blood sugar levels are checked between 26 and 30 weeks of gestation. This is done of two separate occasions using one of two tests, either the fasting glucose test or the random glucose test. In addition to this if there are any abnormal results of these tests or there is a family history of diabetes, or a woman is regarded as obese she will be offered a glucose tolerance test.
Often with gestational diabetes, the woman is advised to take a number of steps to change their diet and exercise habits to ensure the best possible pregnancy.
It is reportedly advisable to increase participation in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, yoga and pilates. In addition to this it is advisable to eat regular meals watching the amount of fat being eaten, remembering it is controlling the amount of fat not cutting it out of the diet completely.
Also reducing the amount of salt in the diet and ensuring that plenty of fruit and vegetables are included in the diet.
Recommended Reading: Eye Issues Caused By Diabetes
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
A routine test can help to find out whether a woman has developed diabetes in pregnancy. This kind of diabetes, known as gestational diabetes, can then be treated early enough. But the test can also cause women to worry for no reason.
Women who have gestational diabetes temporarily have high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. This is usually not a problem and nothing to worry about. But in some women it will lead to an increased risk of particular complications during pregnancy and birth. High blood sugar levels can usually be lowered enough by changing your diet and doing more exercise. If necessary, women can also inject insulin during pregnancy.
Group B Streptococcus Test
GBS is a healthy vaginal bacterium however, not all women will test positive. GBS does not usually pass to the baby, but if it does, it can cause serious illness. A vaginal-rectal swab will be done around 35-37 weeks to identify whether you have this bacteria present. If our laboratory identifies that the bacteria is present, you will be treated with antibiotics while in labour.
Read Also: At What Blood Sugar Level Should I Take Insulin
What Are The Benefits Of This Routine Test
The benefits of this routine screening test havent yet been looked at in comparative studies. So it isnt exactly clear what advantages and disadvantages it may have. If the made it possible to treat the diabetes early enough, and that was shown to lower the risk of complications at birth, for instance, then that would be an advantage.
The research so far has shown the following:
- Treating gestational diabetes reduces the likelihood that the child will weigh more than 4,000 grams at birth.
- Treatment reduces the risk of one of the childs shoulders getting stuck in the mothers pelvis during the birth , which also reduces the risk of injury to the mother and child.
- Many women who are diagnosed with gestational diabetes dont have any related problems during pregnancy or childbirth.
Although the pros and cons of the test havent been thoroughly researched, it is thought that the advantages outweigh the disadvantages and that screening for gestational diabetes can somewhat lower the risk of complications in childbirth.
Impact Of Adoption Of Iadpsg Criteria
Since the publication of the IADPSG consensus thresholds, there have been numerous retrospective studies that have examined the impact of adoption of these criteria. It is difficult to apply the results of these studies to clinical practice due to their retrospective nature and the wide variation in the comparison groups used. In all of these studies, adoption of IADPSG criteria has led to an increase in the number of cases diagnosed while the impact on perinatal outcomes is inconsistent . Studies comparing pregnancy outcomes before and after changing from a variety of different GDM diagnostic criteria to the IADPSG criteria show differing results. LGA was lower in 1 study and caesarean delivery was lower in several studies after adoption of the IADPSG criteria. However, others did not find reductions in LGA , and 1 study found an increase in primary caesarean section rate .
Given this lack of evidence, it is possible that the decision regarding the recommended screening method will be determined by the economic implications on health-care resources. Decision analysis modelling studies done in other countries have yielded a variety of results and many are of questionable applicability in the Canadian setting because of differing cost and screening and diagnostic strategies.
Read Also: Meal Replacement Shakes For Diabetics Uk
Targets Of Glycemic Control
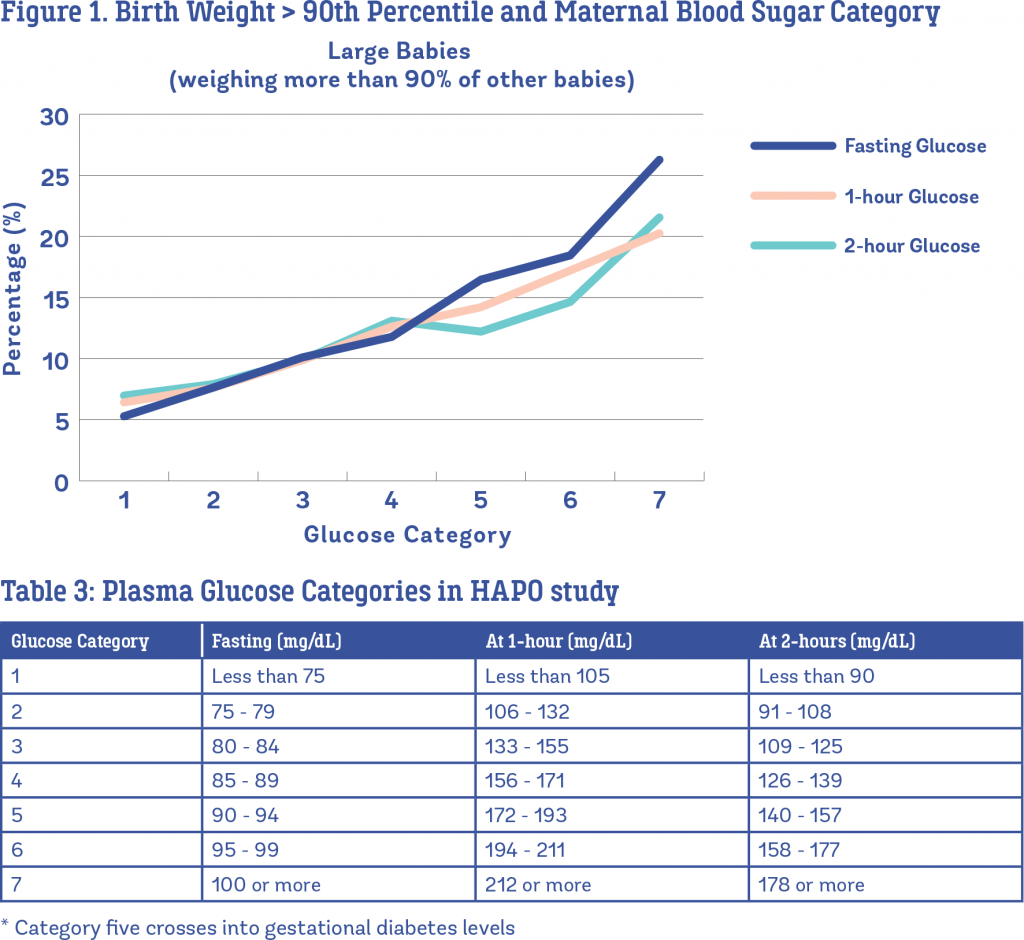
Elevated BG levels have adverse effects on the fetus throughout pregnancy. At conception and during the first trimester, hyperglycemia increases the risk of fetal malformations and intrauterine fetal demise . Later in pregnancy, it increases the risk of macrosomia, fetal and infant death as well as metabolic and obstetrical complications at birth . As a result, meticulous glycemic control throughout pregnancy is required for optimal maternal and fetal outcomes.
An important first step in achieving optimal glycemic control is to set target BG levels . However, optimal targets for fasting, preprandial and postprandial BG levels in women with pre-existing diabetes have not been examined in randomized controlled trials and a variety of BG targets are used in clinical practice. Older studies confirm that the lower the mean BG, the better the outcome, with some suggesting a target mean BG < 6.7 mmol/L and, others, a mean < 6.9 mmol/L. A fasting BG target < 5.9 mmol/L is still associated with a 29% macrosomia rate . Recent retrospective data demonstrated that a mean A1C 6.0% in pregnant women with type 2 diabetes was associated with increased risk of neonatal complications compared to women with an A1C < 6.0% . In women with type 1 diabetes and good glycemic control during pregnancy with an A1C of 4.5% to 7.0%, there is still a linear relationship between third trimester A1C and risk of macrosomia .
Monitoring Your Own Glucose Levels
Breadcrumb
HomePregnancyHubPregnancy complicationsGestational diabetes Monitoring your own glucose levels
You measure your glucose levels through a finger-prick test. You should have been shown how to do this when you were told that you had gestational diabetes. You will also have discussed the ideal blood glucose levels for you during your pregnancy.
The ideal target glucose levels are below but your team may have talked to you about your individual target level:
- fasting: 5.3 mmol/litre
- 1 hour after meals: 7.8 mmol/litre
- 2 hours after meals: 6.4 mmol/litre.
Don’t Miss: Antibiotic Cream For Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Is Low Blood Sugar Level Normal During Pregnancy
It is a known fact that the body produces more insulin for the growth of the baby but what about the sugar levels, even these change during pregnancy. When the question of the low presence of glucose in blood during pregnancy is concerned, it isnt normal however, high blood glucose level is normal.
The sugar levels come down too low in these following conditions
You are not eating enough frequently or having the wrong diet in a worry to normalize sugar level. So when this happens the baby absorbs more glucose from your body and at times may lead to low glucose in the body.
Too much exercising which leads to consumption of glucose present in the body.
At times even few medicines can drop the blood sugar quantity in the body. In such cases ask for a change of drugs so that youre saved from the low presence of sugar.
Risks And Possible Complications
There are numerous risks when gestational diabetes is not properly controlled and blood glucose levels remain high.
For the mother:
- Excess amniotic fluid, increases the risk of premature birth
- Risk of caesarean section or a more difficult vaginal birth
- Gestational hypertension or preeclampsia
- Higher risk of staying diabetic after the birth or of developing type 2 diabetes in the future .
For the baby:
Read Also: Can I Get Rid Of Diabetes
Also Check: How Do You Get Type 1 Diabetes