How Your Body Regulates Glucose
Lets first review some basics about. The glucose in your blood serves as a primary source of energy for all the cells in your body. There are other molecules your body can make for fuel if needed, like ketones, but well keep the focus on glucose here for simplicity.
Your body has sensors throughout it to determine if you are at the correct blood glucose level. In people without, this level is typically between 70 and 120 mg/dL . There are multiple hormones that either activate or go quiet as needed to protect this glucose level. If the, your body might release catecholamine hormones to trigger an increase in the level of glucose in the blood. If, your body will release and other hormones to correct the level back down to an appropriate range.
People with diabetes dont lose the ability to raise or lower their blood sugar levels rather, the hormones that serve to keep blood glucose in the correct range dont function correctly, and the sensors that assess the glucose level are also often impaired.
Type 1 Diabetes Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Type 1 diabetes in an autoimmune disease where a persons pancreas doesnt produce insulina hormone needed to convert food into energy. It affects children and adults, comes on suddenly, and it cannot be prevented or cured. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a common and dangerous occurance with type 1 diabetes. If your blood sugar gets too low it may lead to insulin shock, which is life-threatening if not cared for. Low blood sugar can happen when your body has too little foodor glucoseor when it produces too much insulin. Type 1 diabetes hypoglycemia symptoms So what are the low blood sugar symptoms you should look out for? Its important to realize that the signs of low blood sugar will vary depending on the person. However, people with type 1 diabeteswhether its been diagnosed or notmay experience one or more of the following: -Sweating and shaking -Blurry vision -Poor coordination -Dizziness or feeling lightheaded -Difficulty concentrating -Feeling anxious or irritable -Hunger or nausea -Erratic changes in behavior What to do if you experience low blood glucose symptoms Severely low blood-sugar levels can lead to hypoglycemic seizures, unconsciousness, coma, and death if left untreated. Thats why its important to see a doctor if you think you have low blood sugar so he or she can check your blood-glucose levelslook into whether type 1 diabetes may be a causeand provide the necessary treatment. Your support is more critical than everContinue reading > >
What If Im Experiencing Hypoglycemic Episodes Even Though My Doctor Has Confirmed That Im Not Diabetic Or Prediabetic
If you have low blood sugar and dont have diabetes or prediabetes, it can be a sign of another serious health issue such as a tumor, hormone deficiency, kidney disorder, anorexia, or other eating disorder, all of which can cause dangerously low blood sugar.
Anorexia has the highest mortality of any psychiatric disorder, and the cause of death can be hypoglycemia, so take your illness seriously and seek help if you suspect your eating disorder may be progressing to the point where it is causing you to faint or experience other signs and symptoms of dangerously low blood sugar. The National Eating Disorders Association has resources on how to identify the signs that you may have an eating disorder, a hotline for help, as well as easily accessible information on everything from how to know when you need help to how to find quality treatment options in your zip code.
People who are not diabetic dont spontaneously have hypoglycemia for no reason, explains Dr. Christofides. Its often an indication of another underlying issue, such as a hormone deficiency or eating disorder, so its important to schedule an appointment with your doctor to determine the cause in order to prevent complications.
Common causes of hypoglycemia in people without diabetes include:
- Pancreatic tumor
- Medication that inhibits the proper production of insulin
- Hepatitis or kidney disorders
Recommended Reading: How Do I Get Off Sugar
Don’t Miss: Ideal Glucose Level For Type 2 Diabetes
Hypoglycemia And Low Blood Sugar
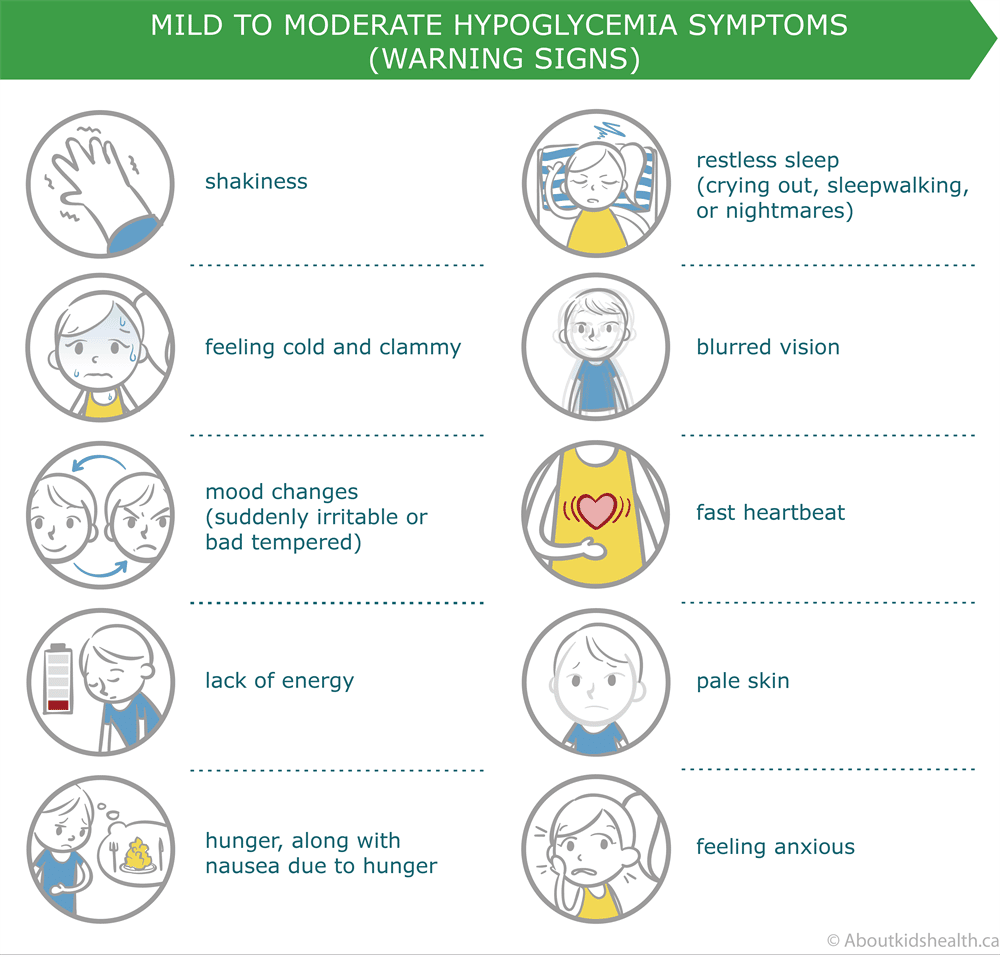
What are the symptoms of hypoglycemia? While each child may experience symptoms of hypoglycemia differently, the most common include: shakiness dizziness sweating hunger headache irritability pale skin color sudden moodiness or behavior changes, such as crying for no apparent reason clumsy or jerky movements difficulty paying attention or confusion What causes hypoglycemia? The vast majority of episodes of hypoglycemia in children and adolescents occur when a child with diabetes takes too much insulin, eats too little, or exercises strenuously or for a prolonged period of time. For young children who do not have diabetes, hypoglycemia may be caused by: Single episodes: Stomach flu, or another illness that may cause them to not eat enough fasting for a prolonged period of time prolonged strenuous exercise and lack of food Recurrent episodes: accelerated starvation, also known as ketotic hypoglycemia, a tendency for children without diabetes, or any other known cause of hypoglycemia, to experience repeated hypoglycemic episodes. medications your child may be taking a congenital error in metabolism or unusual disorder such as hypopituitarism or hyperinsulinism.Continue reading > >
Time In Range Goals Stay Out Of The Highs And The Lows
Effective diabetes management is an attempt to stay in the target glucose range. This means that you should aim to spend as much time as possible with your glucose level between 70 to 180 mg/dL The amount of time you spend in this target zone is called your Time in Range and is measured by a continuous glucose monitor , though you can also measure TIR using your blood glucose meter. When glucose level exceeds 180 mg/dL, this is referred to as Time Above Range . If your glucose level goes below 70 mg/dL, this is Time Below Range .
For most people with diabetes, these are the recommended TIR goals :
-
At least 70% of the day in range this is almost 17 hours a day
-
Less than 4% of the day below range this is 1 hour a day
-
Less than 1% of the Time Below Range less than 54 mg/dL or 3.0 mmol/L this is 15 minutes a day
Minimize the time each day above range to less than 25% – this is 6 hours a day
Less than 5% of the Time Above Range above 250 mg/dL or 13.9 mmol/L this is 1 hour 15 minutes
These are general recommendations, however, you should strive for even more TIR and less Time Above and Below Range if possible.
Read Also: What’s The Normal Diabetes Level
What Drinks And Foods Raise Blood Sugar Fast
- 4 teaspoons of sugar
- 1/2 can of regular soda or juice
Many people like the idea of treating low blood sugar with dietary treats such as cake, cookies, and brownies. However, sugar in the form of complex carbohydrates or sugar combined with fat and protein are much too slowly absorbed to be useful in acute treatment.
Once the acute episode has been treated, a healthy, long-acting carbohydrate to maintain blood sugars in the appropriate range should be consumed. Half a sandwich is a reasonable option.
If the hypoglycemic episode has progressed to the point at which the patient cannot or will not take anything by mouth, more drastic measures will be needed. In many cases, a family member or roommate can be trained in the use of glucagon. Glucagon is a hormone that causes a rapid release of glucose stores from the liver. It is an injection given intramuscularly to an individual who cannot take glucose by mouth. A response is usually seen in minutes and lasts for about 90 minutes. Again, a long-acting source of glucose should thereafter be consumed to maintain blood sugar levels in the safe range. If glucagon is not available and the patient is not able to take anything by mouth, emergency services should be called immediately. An intravenous route of glucose administration should be established as soon as possible.
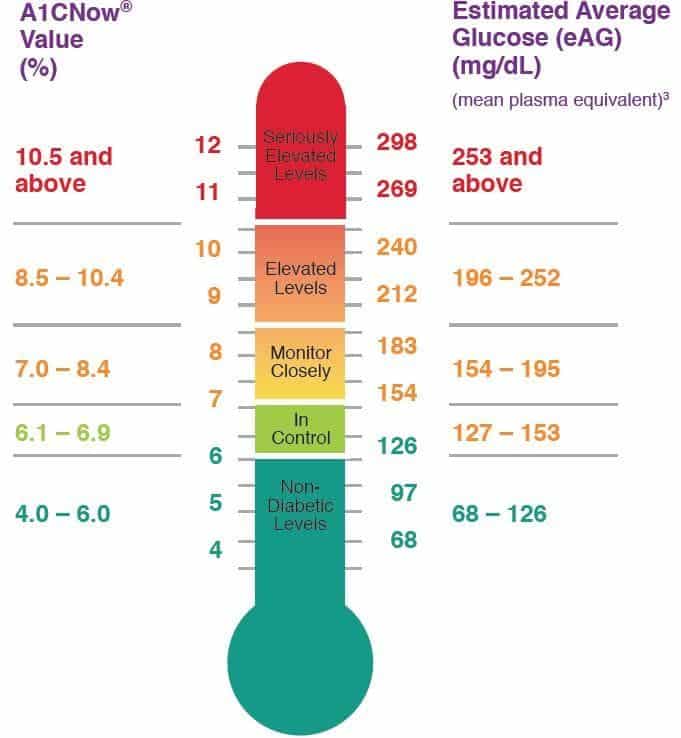
Fasting Glucose Vs A1c
Hello, I’ve never been concerned about diabetes before as my fasting blood glucose levels have always been under 100.However, my last fasting glucose test as well as my husband’s were both high .The doctor had us return for A1c tests which were in the normal range .Based on that, the doctor assumed we had eaten something before the fasting test and said, ‘see you in 3 months’.But we didn’t eat anything. I do have doubts about the fasting results because my doctor uses his own lab.While I know it must be state regulated, we have gotten strange results in the past from this lab.I told my 80-year Mother about it and she showed me several of her blood test results from years ago that showed her fasting glucose levels were as high as 123, however, her last blood test showed 97.So…why did she have such high levels in the past and now her readings are normal?She does not have diabetes.What would cause high fasting glucose other than diabetes or pre-diabetes?I’m very confused and would appreciate any insight into this.Thank you.Continue reading > >
Read Also: Ice Pack For Insulin Pen
What Causes Low Blood Glucose
- Symptoms occur when blood glucose levels fall below 70 mg/dl a condition known as hypoglycemia.
- In most cases, low blood glucose results from overtreatment: Either taking too much diabetes medication or not eating enough food. Higher doses of medicine than the person actually requires can also lead to hypoglycemia.
- People who aim for too-low values on their A1C test tend to experience more frequent drops in blood glucose.
- Vigorous exercise doesn’t just burn calories, it also burns blood glucose! Hypoglycemia can occur unless blood glucose levels are carefully monitored during and after exercise.
- Not eating on a regular basis can deprive the body of glucose and make it difficult to prevent hypoglycemia. Eat balanced meals throughout the day and always keep a snack on hand.
When Should I Go To The Hospital For Blood Sugar
Certain symptoms of blood sugar levels signal when you should seek medical help. Typically, if you feel extremely fatigued, notice increased thirst and urination, or weight loss, you should seek help right away. These symptoms can signify an abnormal blood sugar level and/or other health conditions. A routine health check is also advised, even if you do not show any symptoms.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When A Type 2 Diabetic Eats Sugar
How Does Hypoglycemia Occur Without Diabetes
Hypoglycemia usually happens to people living with diabetes, but its possible to have low blood sugar without diabetes.
Blood sugar, or glucose, is what your body uses for energy. After eating a meal or drinking a beverage, the hormone insulin allows sugar to enter your bodys cells, where its used for energy. Insulin is a hormone produced by your pancreas.
Hypoglycemia occurs when you have too much insulin in your bloodstream. This might happen if you dont eat for several hours, such as 8 hours or more. A drop in blood sugar means there isnt enough glucose in your bloodstream to fuel your brain and body.
Low blood sugar without diabetes can also occur if you take a medication that lowers your blood sugar. These include pain relievers like:
- blood pressure medication
- some antibiotics
Other causes of low blood sugar without diabetes include binge-drinking and increased physical activity.
Plus, some medical conditions can increase the amount of insulin your pancreas produces. These include a pancreatic tumor, adrenal gland disorders, and hepatitis.
You could also experience low blood sugar if you have prediabetes, or if you eat a lot of refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and pastries.
What Are The Symptoms
While it can sometimes be easy to recognize signs and tell the difference between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, at other times it can be hard to tell them apart because of some overlap. For example, confusion and headaches can occur in both cases. Try to be aware of any symptoms you experience that can help you differentiate between the two conditions. And talk to your care team to see if getting a CGM is something that could benefit you. CGM is a great tool to help you know when you are too high or too low.
Though not everyone experiences all of these symptoms every time, and it may take time to learn to recognize these symptoms quickly, here is what can occur with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia:
|
Hyperglycemia |
Don’t Miss: How To Manage Blood Sugar
How Is Hypoglycemia Diagnosed
Your doctor will diagnose hypoglycemia based on a physical exam, your health history, your symptoms, and testing of blood glucose. A first step in diagnosis can be to document blood glucose values of less than 70 mg/dL at home when symptoms occur. This may be confirmed with a blood draw.
Timing of hypoglycemia can be important in the diagnosis. Some causes of hypoglycemia are more likely to result in low blood glucose when fasting, while other causes can induce hypoglycemia after meals.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
Beato Health Coach Madhuparna Pramanick Shares Her Expertise On Maintaining A Normal Blood Sugar Level And The Repercussions Of Low Or High Blood Sugar Levels
Republicworld
Diabetes management is not an impossible task. You can keep your blood sugar levels under control in several ways. One can avoid exacerbating the issue and lead a healthy and happy life by making the necessary lifestyle and dietary modifications. However, there are instances when no matter how hard you try to keep your blood sugar levels normal, they wind up being too high or too low. Let us try to comprehend what high and low blood sugar levels are, as well as their potential consequences and treatments.
Don’t Miss: How To Low Blood Sugar Fast
How Can I Treat And Manage Hyperglycemia
People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can manage hyperglycemia by eating healthy, being active, and managing stress. In addition, insulin is a critical part of managing hyperglycemia for people with type 1 diabetes, while people with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications and eventually insulin to help them manage hyperglycemia.
If you dont have diabetes and have any of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, call your healthcare provider. Together you can work to manage your hyperglycemia.
What Are High And Low Blood Sugar Levels
Low Blood Sugar Levels
Low blood sugar levels or hypoglycemia occur when there are low glucose levels in the blood, which makes it difficult for the body to function normally.
Low blood sugar causes primarily include diabetes-related side effects. But could also be due to:
- Eating less after taking diabetes medication
- Exercising more than normal
- Rare chances of tumor which produces extra insulin
- Endocrine disorders
Effects of low blood sugar levels include both short-term complications such as confusion, dizziness etc, and long-term complications like coma or even death.
If your blood sugar is below 70 mg/dL, you should treat yourself right away.
High Blood Sugar Levels
High blood sugar levels or hyperglycemia occur when people have high blood sugar levels in their bloodstream.
- Blood glucose levels higher than 7.0 mmol/L when fasting.
- Blood glucose levels higher than 11.0 mmol/L 2 hours after meals.
Causes of Hyperglycemia include:
- Inadequate usage of insulin or diabetes medication
- Not eating a proper diabetes diet
- Having an infection or illness
Short term effects of hyperglycemia include nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, dry mouth, among others. Long term effects of hyperglycemia include cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney damage, blindness, etc.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Diabetes Stomach Fat
Medication Used To Correct A Low Blood Sugar
This medicine is available in a kit for a low blood sugar emergency. Symptoms of a low blood sugar emergency are:
- unconsciousness
- patient is awake but unable to eat
- the patient is having a seizure
- the patients blood sugar is still less than 70 even after eating or drinking food containing sugar.
Most often, glucagon is injected into the muscle. This type of glucagon is a powder in a bottle to which sterile water is added from a pre-filled syringe. The same syringe is then used to give the injection. Do not mix the glucagon with water unless you are going to inject the glucagon.
Some glucagon can be given as a puff through the nose. Talk to your healthcare provider about which type may be best for you and your family. A family member or friend should know where you keep your glucagon kit and how to administer the medication. Read the directions that come with the kit with your friend or family member. That way you will be prepared if a low blood sugar emergency happens.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be High
Based on the ADA guidelines above, if your blood sugar is above 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it is considered above the normal range. What might cause your glucose or blood sugar to rise? Consider the following factors:
- Consuming more carbohydrates or a larger meal than usual
- Not taking enough insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Reduced physical activity
- Side effects from medications like steroids or antipsychotics
You May Like: Glucose Test 1 Hour Normal Range
What To Know About Diabetic Macular Edema
Fiber plays a preventative role, too. Studies have found that high-fiber diets can reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes by 15 to 19 percent compared to low-fiber diets, according to a March 2018 study published in the Journal of Chiropractic Medicine.
Youll find fiber in plant foods such as raspberries, peas, and whole grains, according to the Mayo Clinic. Beans are another good source of fiber. People with type 2 diabetes who ate at least a cup of legumes daily for three months had lower blood glucose levels as measured by the A1C test, according to a study published in the Archives of Internal Medicine. Beans also are an excellent source of folate, which is linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, a common diabetes complication, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Men should aim for 30 to 38 g of fiber per day, and women should eat 21 to 25 g per day, according to the Mayo Clinic.
You May Like: Over The Counter Medication For Diabetes