Complications Of High Blood Sugar
Diabetes is one of the main causes of high blood sugar levels, but there are other causes that can impact your blood glucose and your risk for hyperglycemia.
Hyperglycemia is the medical term for high blood sugar levels. You can have temporary spikes in blood sugar after eating a large meal or as a result of medication side effects. Chronically elevated blood sugar levels are dangerous and common in those with diabetes. Without treatment, you run the risk of a diabetic coma.
Ketoacidosis is a condition that develops when elevated blood glucose levels go untreated. Without glucose to use for fuel, your body begins to burn fat instead and produces ketones. When there are too many ketones in the blood, it will turn acidic, which can very quickly lead to ketoacidosis, a diabetic coma, and even death.
People without diabetes can develop a similar condition known as ketosis, but they can tolerate a certain level of ketones because inulin is still effectively working.
Diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome is another serious complication of high blood sugar. This is more common among individuals with type 2 diabetes and is triggered by an infection or illness.
As a result of the high blood sugar, your body tries to push out the excess glucose by passing it through your urine. Without treatment, this can result in life-threatening dehydration so prompt medical attention would be necessary.
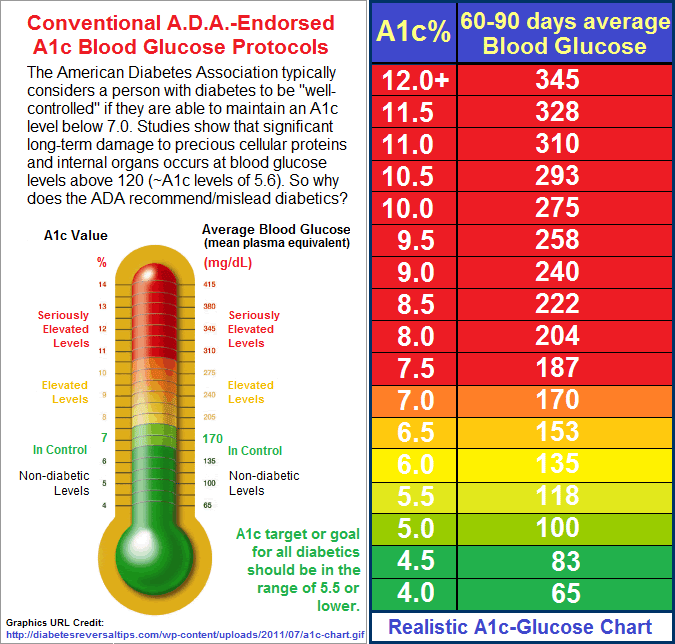
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
Target Blood Sugar Levels In Children With Diabetes
Children younger than 6 years old Blood sugar in mg/dL Bedtime 110-200
Children under 6 years of age should have blood glucose levels that range from about 80 to 200 mg/dL each day. This range is considered healthy, and the amount of glucose in a childs body will fluctuate from the time they wake up to after theyve eaten meals and again before bedtime. For this reason, kids with diabetes or hypoglycemic episodes may have to have their blood sugar levels tested in the middle of the night by their parents. Many children with type 1 diabetes wear a continuous glucose monitor , which displays glucose levels all the time and mostly eliminates the need for finger sticks.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Chances Of Getting Diabetes
Other Tips For Checking:
- With some meters, you can also use your forearm, thigh, or fleshy part of your hand.
- There are spring-loaded lancing devices that make sticking yourself less painful.
- If you use your fingertip, stick the side of your fingertip by your fingernail to avoid having sore spots on the frequently used part of your finger.
What Blood Sugar Level Is Dangerous
There is no such thing as a dangerously high blood sugar level. However, if you random blood sugar test that reads higher than 200 mg/dL and you should consult a doctor and seek advice on how to proceed with managing the same.
Please dont wait for your blood sugar level to go beyond the cut-off of 200 mg/dL. There are many blogs out there that suggest that reading above 300 mg/dL is considered dangerous.
But we have cross-checked this information with our in-house diabetologists to make sure you have the right information.
Here are a few signs and symptoms that can help you understand if your blood sugar levels are going higher than they should:
- You feel tired and weak all the time, even while doing the same activities you do on other days, but now feel more tired
- You have a dry sensation in your mouth
- You will start feeling thirsty, more than you usually do, even if you have water or fluids
- You get a feeling of nausea or vomiting
- You need to go to the toilet to urinate more often than you usually do
- Your vision feels blurry or you have trouble seeing
- You feel hungrier than you usually do
- You may feel dizzy when you stand up
Please keep in mind that the target healthy blood sugar ranges mentioned in this article are for a general overview, and in some cases, it is possible that the target healthy ranges will vary from person to person.
No more stress while managing diabetes
Dont struggle alone & get the expert care you deserve
Read Also: Glucose Numbers For Type 2 Diabetes
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose level, is the level of sugar/glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a simple version of sugar which comes from the food we eat. Therefore, the more food you consume with high sugar levels over a period of time, will typically increase your blood sugar level.
Glucose comes from the foods we eat and its sugar content. When a person consumes a food with high sugar content, that is turned into glucose. The glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream with the support of insulin. This is then distributed between the bodys cells and used as energy.
Foods high in glucose include most carbohydrates and a handful of proteins and fats. Most foods contain glucose as it is simply a natural sugar that occurs in most dietary forms. However, it is carbohydrates that contain the most sugar and 100% of it turns into glucose, through the process mentioned above, once consumed. The concentration of glucose present in the blood will determine your blood sugar level.
Here is a quick video explaining Blood sugar levels chart :
Your blood sugar level can either be low, normal or high. Depending on what you eat and health conditions, it will vary from person to person. Here is a breakdown of how your blood sugar works and how low or high blood sugar levels happens:
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
Recommended Reading: Does Water And Baking Soda Help Diabetes
When Should I Check My Bgls
The number of times a day you check your BGLs will depend on what type of treatment you are taking e.g. insulin. Your diabetes team can advise when and how often to monitor. In general, you can check:
- When you wake up this measures your fasting glucose level
- 2 hours after a meal
- Overnight: 2 -3am
How Do I Check My Blood Sugar
Checking your blood sugar is simple and can be done at home with the right equipment. The most traditional and effective way of doing so is with a glucose meter. You wash your hands to wash away germs, prick your finger with a needle, apply the blood from the pricked finger to a test strip and insert it into the machine. Your blood sugar level will appear on the meters display. Alternatively, there are a few modern methods that have been developed. They show results but are considered not to be as accurate as glucose meters.
Recommended Reading: How To Reverse Ed In Diabetics
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
Also Check: What Size Syringe For Insulin
Different Levels And What They Mean
The ranges of safe levels of blood glucose depend on factors such as what time of day it is and when you last ate. Safe levels of blood sugar are high enough to supply your organs with the sugar they need, but low enough to prevent symptoms of hyperglycemia or complications of diabetes which follow the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases guides. Dangerous levels of blood glucose are outside of this range.
The target levels can also vary if you have diabetes. For example, if you are diabetic and are monitoring your blood sugar, you might get a reading of 65 mg/dl. That is considered to be mild hypoglycemia, and you would be wise to eat 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and retest your blood sugar in 15 minutes.
If you were not diabetic, you probably would not know that your sugar was low because you would not test and because you would not symptoms, and you would not act.
That is fine because your body is capable, under normal circumstances, of raising your blood glucose to healthy levels when needed, even if you have not eaten. It is important to keep them in control to help prevent issues like heart disease or nerve damage.
Looking for the best prediabetes diet? Learn what foods are best to help you manage your prediabetes.
Work With Your Health Care Team
Most people with diabetes get health care from a primary care professional. Primary care professionals include internists, family physicians, and pediatricians. Sometimes physician assistants and nurses with extra training, called nurse practitioners, provide primary care. You also will need to see other care professionals from time to time. A team of health care professionals can help you improve your diabetes self-care. Remember, you are the most important member of your health care team.
Besides a primary care professional, your health care team may include
- an endocrinologist for more specialized diabetes care
- a registered dietitian, also called a nutritionist
Don’t Miss: What Problems Can Diabetes Cause
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar
Depending on the cause of your high blood sugars, the symptoms could develop quickly or gradually.
People with undiagnosed type 1 diabetes will develop nearly all of the symptoms of high blood sugar very quickly, over the course of a few weeks, because their blood sugar levels are rising rapidly while insulin production is declining rapidly.
People with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes may not notice these symptoms for months or years because gradually increasing insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction can take a long time to become severe enough to produce noticeable symptoms.
Earlier symptoms:
Also Check: What Damage Does High Blood Sugar Cause
Also Check: Is Diabetes A Metabolic Disorder
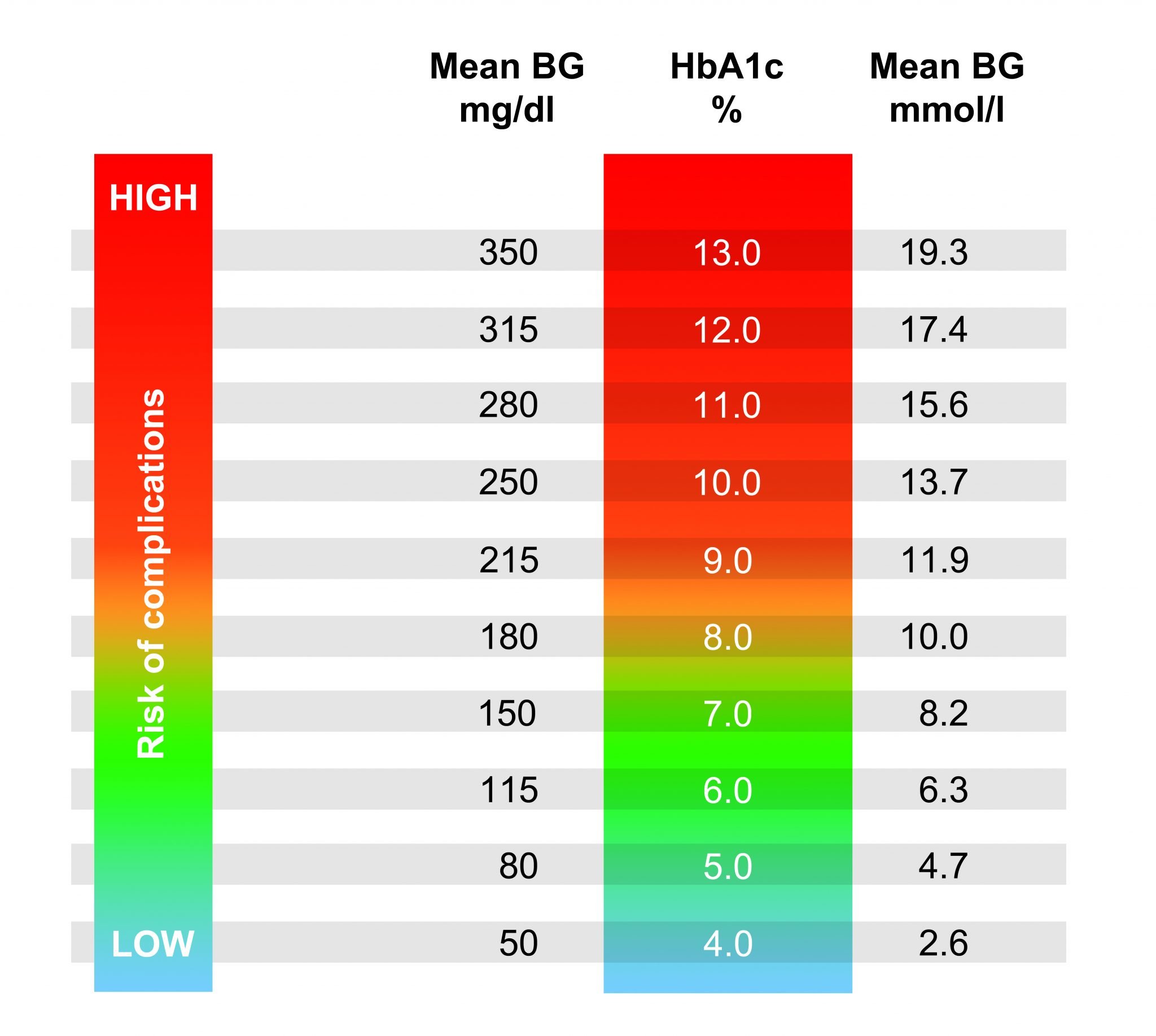
How To Calculate Your Blood Sugar Level: The Complete Guide
To get an accurate reading of your blood sugar level, the best and most effective method is using a glucose meter. This will involve a small prick in your finger so receive a blood sample. The strip is then inserted into the meter and tested.
You may be wondering what your reading should be. There is no normal reading, an ideal reading differs from person to person. Everyone will get different readings at different times of the day. However, there is a rough range to determining a low, normal and high blood sugar level. Blood sugar level is read in mmol/L, which stands for millimoles per liter. Here is a guide as to what an ideal reading is for each diabetic type and non-diabetic patients:
| Child | |
| 4 5.9 mmol/L< 7.8 mmol/L | 4 5.9 mmol/L< 7.8 mmol/L |
It is advised to check it regularly if you are concerned, show regular symptoms or have diabetes. You should check before meals, exercise, before bedtime and after driving. Everyone is different so it is best to ask your doctor if you are unsure how many times and when you should check your blood sugar levels.
Research shows that over 50% who try to estimate their blood sugar level reading are incorrect. This may be due to over underlying medical conditions that did not know they had or poor lack of judgement. Therefore, this suggests it is very important to test at home to check in on your levels regularly to avoid any unnecessary future complications.
What Is Considered High Blood Sugar Level
Chronically high blood sugar is caused by a number of abnormalities in the body, one of them being the affected vascular walls of small and large arteries in a process called atherosclerosis.
We can say that a blood sugar level is high if we measure glucose level and get the following values more than 110 mg/dL on an empty stomach or at any time more than 200 mg/dL .
High blood sugar levels affect the arteries throughout the body, especially the organs which have the richest blood circulation: heart, brain, kidney, senses, nerves and other organs.
If the high blood sugar is associated with disturbances in lipid metabolism , the abnormalities are more intense. Diabetes is among the risk factors for major non-communicable diseases: cardiovascular disease, cerebral vascular disease and peripheral vascular diseases.
Read Also: How Long Does Low Blood Sugar Last
Read Also: Is A1c The Same As Glucose
Manage Your Carb Intake
Your carb intake strongly influences your blood sugar levels .
Your body breaks carbs down into sugars, mainly glucose. Then, insulin helps your body use and store it for energy.
When you eat too many carbs or have insulin-function problems, this process fails, and blood glucose levels can rise.
Thats why the American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes manage their carb intake by counting carbs and being aware of how many they need .
Some studies find that this can help you plan your meals appropriately, further improving blood sugar management (
Foods that are high in fiber include:
The recommended daily intake of fiber is about 25 grams for women and 35 grams for men. Thats about 14 grams for every 1,000 calories .
Summary
Eating plenty of fiber can aid blood sugar management. Soluble dietary fiber appears to be more effective than insoluble fiber for this purpose.