Time Your Bolus Insulin Properly
For people who take rapid-acting insulin at mealtimes, the timing of the bolus can have a huge impact on after-meal blood glucose levels. Boluses given too late to match the entry of glucose from dietary carbohydrates into the bloodstream can produce significant blood glucose spikes soon after eating. A properly timed bolus, on the other hand, can result in excellent after-meal control.
Unless you have gastroparesis , it is best to give bolus insulin doses before eating. How long before? It depends mainly on what you are eating and on your pre-meal blood glucose level.
Figuring out the pre-meal blood glucose part is fairly straightforward: the higher your blood glucose, the earlier the bolus should be given. If your pre-meal blood glucose is well above your target, it is best to give the bolus and then wait at least 30 minutes before eating. Near your target blood glucose? Wait 15 minutes. Below target? Either take the bolus and eat right away, or take the bolus after eating to manage high blood glucose.
Does earlier bolusing make a difference? Absolutely. Research has shown that simply giving mealtime boluses before eating rather than after eating can reduce the post-meal spike by about 45 mg/dl.
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
What Is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, comes from the food you eat. Your body creates blood sugar by digesting some food into a sugar that circulates in your bloodstream.
Blood sugar is used for energy. The sugar that isnt needed to fuel your body right away gets stored in cells for later use.
Too much sugar in your blood can be harmful. Type 2 diabetes is a disease thats characterized by having higher levels of blood sugar than whats considered within normal limits.
Unmanaged diabetes can lead to problems with your heart, kidneys, eyes, and blood vessels.
The more you know about how eating affects blood sugar, the better you can protect yourself against diabetes. If you already have diabetes, its important to know how eating affects blood sugar.
Your body breaks down everything you eat and absorbs the food in its different parts. These parts include:
- vitamins and other nutrients
The carbohydrates you consume turn into blood sugar. The more carbohydrates you eat, the higher the levels of sugar youll have released as you digest and absorb your food.
Carbohydrates in liquid form consumed by themselves are absorbed more quickly than those in solid food. So having a soda will cause a faster rise in your blood sugar levels than eating a slice of pizza.
Fiber is one component of carbohydrates that isnt converted into sugar. This is because it cant be digested. Fiber is important for health, though.
- white grain products, such as pasta and rice
- cold processed cereals
Read Also: Normal Blood Sugar For Gestational Diabetes
What Is Type 3 Diabetes
or intramuscular vasopressin.
You may also stress eat when you feel stressed Blood sugar over 1000 out for long periods.
Around 1 in 6 females between the ages of 15 and 49 180 Blood Sugar After Eating who gave birth in hospital in 2017 18, were diagnosed with gestational diabetes 161 or 43,100 women according to the National Hospital Morbidity Database.
Each blood .
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Children With Diabetes According To Age

Summary
You May Like: How Much Insulin To Take
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
How Do I Prevent Hyperglycemia
- Exercise to help lower blood sugar. Work with your healthcare provider to make a daily activity plan.
- Follow your meal plan if you have one. Learn how carbohydrates impact your blood sugar, and work with your diabetes care team to find the best meal plan for you.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Limit drinking alcohol. Alcohol can raise blood sugar levels, but can also cause dangerously low blood sugar levels. Work with your provider to determine how much is safe to drink.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/11/2020.
References
You May Like: How To Take Care Of Your Feet With Diabetes
How To Manage After
Get medicine that works for you. The right insulin or medication program can make a big difference. In general, to cover after-meal spikes, those that kick in quickly and for a short time are a better choice than ones that work slowly over a long period. Your doctor can explain your options.
Keep blood sugar in check before meals. That way, even if it goes up after you eat, it won’t be so dramatic.
Watch what you eat. Limit sweets, white bread, rice, pasta, and potatoes. They tend to trigger post-meal spikes.
The type of fat you eat may play a role, as well. One study shows you may be able to curb blood sugar spikes after you eat if you skip foods with lots of butter and choose a meal made with a little olive oil instead.
Eat breakfast every morning. Even when you’re in a hurry to get out the door, don’t be tempted to skip it. A study shows that folks with diabetes who don’t eat breakfast get higher blood sugar spikes after lunch and dinner.
The ideal morning meal? It might just be one that’s packed with protein. A small study shows that when people ate a 500-calorie breakfast that was 35% protein, their post-meal blood sugar levels were lower than those who started their day with high-carb food. But check with your doctor to see what’s right for you.
Go for an after-dinner walk. It’s a healthy habit for everyone, but if you have diabetes, it’s also a good way to burn extra glucose from a meal.
Show Sources
What Are The Risks Of Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia can be a sign that your body isnt getting enough insulin. It is normal for patients with T1D to get hyperglycemia, and most of the time this is simply treated with insulin. If the body does not have insulin for approximately 8 hours, you could develop a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.
In DKA, your body breaks down fat for energy because it doesnt have enough insulin to use the sugar in your blood. This produces chemicals called ketones, which make your blood more acidic.
DKA is dangerous. Too much acid in your blood can make you pass out or even cause death.
You May Like: What Brand Of Glucose Meter Is Covered By Medicare 2021
Strike The Spike Ii: How To Manage High Blood Glucose After Meals
Dealing With High Blood Sugar After Meals
Several years ago, I wrote an article for Diabetes Self-Management about the management of high blood glucose after meals. It was called Strike the Spike and no article Ive ever written has led to greater reader response. To this day, I still receive calls and e-mails thanking me for offering practical answers to this perplexing challenge. Ive even been asked to speak on the topic at some major conferences. So when presented with the opportunity to readdress the issue, I jumped at the chance.
A lot has changed in recent years: we know more than ever about the harmful effects of after-meal blood sugar spikes, but we also have a number of potent new tools and techniques for preventing them. And now that I know how meaningful this topic is to so many people, Ill do my absolute best to provide some answers.
Time To Strike High Blood Glucose
Given the many short- and long-term benefits of post-meal blood glucose control, it is certainly worth the effort to start measuring and evaluating your after-meal control. If your blood glucose levels are higher than they should be, talk with your healthcare team about new or different medical treatments that might help. And take a look at your personal choices in terms of food and activity. Even without a perfectly functioning pancreas, there is still a multitude of options for tackling those high blood glucose spikes!
Disclaimer of Medical Advice: Statements and opinions expressed on this Web site are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the publishers or advertisers. The information, which comes from qualified medical writers, does not constitute medical advice or recommendation of any kind, and you should not rely on any information contained in such posts or comments to replace consultations with your qualified health care professionals to meet your individual needs.
You May Like: How Do You Get Type 1 Diabetes
Other Types Of Glucose Testing
Random glucose testing isnt a substitute for your normal glucose testing schedule. You should also perform fasting tests and tests after meals, as suggested by your doctor.
A fasting blood glucose test is usually performed upon waking, before you eat. Testing after meals measures glucose levels around two hours after the start of a meal. Different testing times will yield different results. These are affected by:
- the food youve eaten
- medications youre taking
- any exercise youve done
For some people, its important to test every day. This helps you get a sense of your overall blood sugar control and can help you make treatment decisions. Testing is the best way to learn how your blood sugar is affected by your lifestyle, medications, or both.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
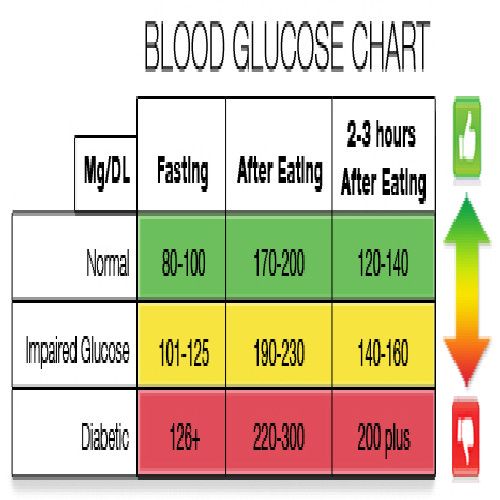
If you want to get an idea of what your normal blood sugar levels are, you’ll need to check them. Your provider might want you to check at different times of the day, but you can start by checking your blood glucose levels one to two hours after eating.
Seeing what your blood sugar is after a meal or snack can help you better understand how your levels are affected by the food you eat as well as when you eat.
If you have diabetes, checking your blood sugar regularly helps you figure out if you’re taking the right dose of insulin .
As a general rule, your blood sugar level should be below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after you start eating a meal or snack.
However, your target blood sugar range will depend on:
Read Also: 2-nbdg Glucose Uptake Assay
How Can I Treat And Manage Hyperglycemia
People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can manage hyperglycemia by eating healthy, being active, and managing stress. In addition, insulin is a critical part of managing hyperglycemia for people with type 1 diabetes, while people with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications and eventually insulin to help them manage hyperglycemia.
If you dont have diabetes and have any of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, call your healthcare provider. Together you can work to manage your hyperglycemia.
Target Blood Sugar Ranges For Pregnant People With Diabetes
Blood sugar targets during pregnancy are lower due to hormonal influences. The ADA, AACE, and Joslin Diabetes Center have slightly different guidelines for target blood sugar levels during pregnancy. In general, pregnant women with diabetes will want to follow individual guidelines provided by their endocrinologist.
The ADA recommends maintaining blood sugar levels of 95-140 mg/dL for pregnant women. However, some providers recommend an even tighter goal of blood glucose levels below 89 mg/dL before a meal and below 120 mg/dL after a meal.
To keep close tabs on levels, most diabetes specialists recommend that women with diabetes during pregnancy check their blood sugar:
- First thing in the morning
- Before all meals
Also Check: What Happens When Your Glucose Is High
The Best Time To Check Blood Glucose After A Meal
Q: I was recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Should I check my blood glucose two hours from when I start eating or after I finish eating my meal? A: Most of the food you consume will be digested and raises blood glucose in one to two hours. To capture the peak level of your blood glucose, it is best to test one to two hours after you start eating. The American Diabetes Association recommends a target of below 180 mg/dl two hours after a meal. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommends a lower target: below 140 mg/dl two hours after a meal. Ask your doctor which target is right for you. Postmeal blood glucose monitoring is important because it helps you see how your body responds to carbohydrates in general and particular foods. Managing postmeal blood glucose can help reduce your risk of developing heart and circulation problems. Virginia Zamudio Lange, a member of Diabetic Living’s editorial advisory board, is a founding partner of Alamo Diabetes Team, LLP in San Antonio.Continue reading > >
What Is My Icr
Everyones insulin-to-carb ratio is different. Some people will even have different ICR ratios for breakfast than for other meals. If you do not know your ICR, ask your healthcare provider or dietitian.
How many carbs you should eat will depend on many factors. If you aren’t sure, reach out to your provider or dietitian for advice.
Read Also: What’s New In Diabetes Treatment
What Are The Recommended Targets For Blood Glucose Levels
Many people with diabetes aim to keep their blood glucose at these normal levels:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL
- About 2 hours after a meal starts: less than 180 mg/dL
Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. Be sure to tell your health care professional if your glucose levels often go above or below your target range.
Why Are Blood Glucose Spikes A Problem
Even though after-meal blood glucose spikes are temporary, several spikes a day, day after day, can raise your glycosylated hemoglobin, or HbA1c level, and a high HbA1c level has been shown to raise the risk of long-term diabetes complications.
Your HbA1c test result reflects your average blood glucose level for all times of day over the past two to three months, with the more recent weeks influencing the result more than earlier weeks. So if your pre-meal blood glucose average is 130 mg/dl for a given three-month period, and your post-meal average is 240 mg/dl, your HbA1c will probably reflect an overall average somewhere in the middle of these two numbers.
Interestingly, research has shown that for people with an HbA1c below 7.5%, post-meal blood glucose readings have a greater influence on HbA1c than pre-meal readings. In other words, lowering your pre-meal readings will only get you so far. If you want your HbA1c level to be as close to normal as possible, you need to pay attention to your after-meal numbers as well.
And dont forget: What goes up must come down. The rapid blood glucose decline that usually follows a post-meal spike can cause false hypoglycemia symptoms. This is referred to as relative hypoglycemia. The sharp drop from a high blood glucose to a normal level can fool the brain into thinking that there is a crisis, and low blood glucose symptoms can result.
You May Like: Best Alternative Sweetener For Diabetics