How Long To Fast Before Glucose Test Pregnancy
How Long To Fast Before Glucose Test Pregnancy
The length of time you should fast before a glucose test during pregnancy depends on the type of glucose test you are having. For a fasting glucose test, you should fast for at least 8 hours before the test. For a glucose tolerance test, you should fast for at least 24 hours before the test.
Your Glucose Test During Pregnancy: How To Pass It
This post may contain affiliate links where I earn a small commission your purchase at no cost to you. Feel free to check my disclosure and terms for more info! Please note the advice on this site is general advice and you should consult a provider before making choices for yourself.
If youre pregnant and expecting to have a glucose test as part of your prenatal care, you might be wondering how to prepare for the test. What can you eat and drink before the test? And what should you do on the day of the test? Keep reading for all the information you need to know about glucose tests during pregnancy.
But first, how do I know all of this?
Hi Im Hilary The Pregnancy Nurse . I have been a nurse since 1997 and I have 20 years of OB nursing experience, I am also the curly head behind Pulling Curls and The Online Prenatal Class for Couples. I even helped in a diabetes clinic during my 3rd pregnancy. I have helped LOTS of diabetic moms, and fielded lots of questions about the glucose test during pregnancy.
Possibly, similarly important, I have taken the glucose test with my three pregnancies, and I understand your desire to PASS that test.
First, lets chat a bit about what it is.
What If I Have Gestational Diabetes
GD is increasingly common, with about 7% of women having the condition. If you are found to have GD, you will work closely with your health care provider to keep your blood glucose levels in a healthy range. This involves choosing a healthy diet, gaining the recommended weight during your pregnancy, getting exercise, and if needed, taking insulin or pills to lower your blood sugar. Your babys wellbeing will be carefully monitored by regular measurements of growth and amniotic fluid volume. If you have GD you will be offered a repeat glucose tolerance test between 6 weeks and 6 months postpartum to detect prediabetes and diabetes. You may also be offered induction between 38-40 weeks of pregnancy. Finally, it is strongly recommended that women with GD breastfeed their infants.
Recommended Reading: How To Test Glucose Levels At Home
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
As women ages 35 and above the chances of getting affected with gestational diabetes are high and so it is important to know the ideal count of sugar to be present while carrying. If your test result is below 7.8 mmol/L after consumption of 50g glucose and lapse of 60 minutes then the sugar count is normal. There is also another way to know normal blood range by following the oral glucose tolerance test , with a sugared liquid having 75 g glucose and 3 blood tests. In the below 3 tests if minimum 1 out of the 3 blood tests values is greater than or equal to the mentioned readings then your blood count is not normal.
- 5.1 mmol/L fasting
- 10 mmol/L 1 hour after drinking the sugary drinks or the sugary liquid
- 8.5 mmol/L 2 hours after drinking the sugary liquid
Usually when blood sugar level is higher than 200 mg/dl is seen a second evaluation i.e., an oral glucose tolerance test is recommended.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- having had gestational diabetes in an earlier pregnancy
- a family history of diabetes
- having obesity or other diabetes-related conditions
- being physically inactive
If a person gains more weight than is usual during pregnancy, this may be a sign of gestational diabetes, according to the
- attending more frequent screening and seeking medical help if glucose levels go up
- insulin use, in some cases
The healthcare provider will advise on each persons needs and treatment plan, as diabetes affects everyone differently.
Who Is At Risk Of Gestational Diabetes
Between 3% and 8% of pregnant women develop gestational diabetes. It is usually detected around weeks 24 to 28 of pregnancy, although it can develop earlier. Being diagnosed with gestational diabetes can be both unexpected and upsetting. It is important to reach out and get support and help with managing it.
Some women are at increased risk of developing gestational diabetes. This includes women who:
- are over 40 years of age
Don’t Miss: Best Yogurt For A Diabetic
One Hour Glucose Results:
- Glucose test 1 hour after drinking glucose solution < 140
- If they take a fasting test, they likely want it to be less than about 95
Again, if your numbers are greater than this, they will likely ask you to take the 3 hour test.
I have seen people who the numbers were SO high with the 1-hour test, that they just diagnosed them with diabetes and sent them to a dietician for a consult and further testing.
Treatments For Gestational Diabetes
If you have gestational diabetes, the chances of having problems with your pregnancy can be reduced by controlling your blood sugar levels.
You’ll be given a blood sugar testing kit so you can monitor the effects of treatment.
Blood sugar levels may be reduced by changing your diet and exercise routine. However, if these changes don’t lower your blood sugar levels enough, you will need to take medicine as well. This may be tablets or insulin injections.
You’ll also be more closely monitored during your pregnancy and birth to check for any potential problems.
If you have gestational diabetes, it’s best to give birth before 41 weeks. Induction of labour or a caesarean section may be recommended if labour does not start naturally by this time.
Earlier delivery may be recommended if there are concerns about your or your baby’s health or if your blood sugar levels have not been well controlled.
Find out more about how gestational diabetes is treated.
Also Check: Is Type 1 Diabetes Genetic
What Happens If You Fail The 3 Hour Glucose Test
If you fail the 3-hour glucose test, you have impaired glucose tolerance and you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
A failing score is considered when you have 2 or more values in these ranges:
- Fasting > 95mg/dL
- 2 Hour > 155 mg/dL
- 3 Hour > 140 mg/dL
This is a very serious condition that requires very close monitoring of your blood sugar levels every single day.
If you dont, you are putting your own life and your babys life at risk.
You will meet with a nutritionist to learn how to improve your diet, and you will have to check your finger stick blood glucose 4 times a day for the remainder of the pregnancy.
How Is It Done
You’ll get the OGTT at your doctor’s office, a clinic, hospital, or lab. Hereâs what happens:
- A nurse or doctor will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm to test your starting blood sugar level.
- You’ll then drink a mixture of glucose dissolved in water.
- You’ll get another blood glucose test 2 hours later.
During pregnancy, the test is shorter. You’ll drink a sweet liquid. Then you’ll have a blood test about 60 minutes later.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Insulin Is Basaglar
Will The Glucose Tests Make Me Feel Sick
Some moms-to-be feel nauseated after drinking the glucose solution, and a few even throw up. It may help to eat something a few hours before the screening test. If you vomit soon after you’ve gotten the drink down, you’ll have to come back on another day and repeat the test.
It’s actually more common for women to feel sick during the three-hour glucose tolerance test, because the solution for that test is twice as sweet or contains twice as much liquid as the one for the screening test, and you have to drink it after fasting.
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes
Women who have gestational diabetes have a high chance of developing type 2 diabetes at some point later in their lives. However, type 2 diabetes can be prevented. The following steps can reduce your risk:
- maintain a healthy eating plan
- maintain a healthy weight for your height
- do regular physical activity
- have regular follow-up blood tests every one to 3 years to check your blood glucose levels, especially if you have further pregnancies.
Talk to your doctor about follow-up blood tests to check for diabetes. The frequency of the tests will depend on your risk for developing diabetes.
Also Check: Is Dark Chocolate Good For Type 2 Diabetes
Also Check: Insulin Pills For Type 1 Diabetes
Why Do I Need A Glucose Tolerance Test
In pregnancy, women who will be offered a GTT will have been identified as having one of the following:
- A raised body mass index over 30kg/m². BMI is a measurement of your weight in kilograms and your height in metres.
- A previous baby over 4.5kg .
- Confirmed gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy.
- Family origin .
- First degree relative that has diabetes .
When Does A Person Need To Have Their Blood Glucose Measured With This Test
Prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes often have no symptoms at first. A person can have the condition and not know it. Healthcare providers usually order a fasting blood sugar test:
- As part of a standard annual physical examination to monitor a persons blood glucose over time.
- For pregnant women to ensure that pregnancy hormones are not causing diabetes.
- When a person has symptoms of diabetes, a family history of diabetes or risk factors for diabetes .
- When a person has had a previous blood glucose level that was higher than normal.
Also Check: Can Diabetes Make Your Kidneys Hurt
What Are The Complications Of Gestational Diabetes
If your blood sugar levels remain high during your pregnancy, this may lead to pregnancy problems such as a large baby, miscarriage or stillbirth. Having a large baby can lead to complications and injury during the birth, and increase the chances of having intervention in labour such as a caesarean birth. But the baby will not be born with diabetes.
If you have gestational diabetes, you are at higher risk of developing high blood pressure while you are pregnant and a 50% increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. Your baby is also at greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes in later life.
To reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- keep to a healthy weight
- eat a healthy diet
- be physically active
- check your blood glucose levels
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and support.
Read Also: What Is The Earliest Sign Of Diabetes Nephropathy
What If I Fail The 1
Normal Values for the 1-hour glucose test
- Fasting: Less than 95
- 1 hour: Less than 140
If your values fall outside this they will likely have you take the 3-hour test.
However, if your 1 hour glucose is high enough they may just diagnose you with diabetes and make you an appointment with someone who can make an eating plan for you.
Also Check: What To Give A Diabetic When Blood Sugar Is Low
What Are The Usual Treatments For Diabetes
For type 2 diabetes, which is the most common type of diabetes, losing excess weight, eating a healthy diet that is high in fiber and restricted in carbohydrates, and getting regular amounts of exercise may be enough to lower your blood glucose levels. In many cases, however, medications may be necessary to achieve the desired glucose level. With type 1 diabetes , insulin injections several times a day are necessary. See the article on Diabetes for more on treatment.
Control A1c Levels For Children And Adolescents
A1C goal levels chart for children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes and average Serum glucose levels.A1c goal to be less than 7.5% .Blood glucose before meals to be 90130 mg/dL Glucose level at bedtime/overnight to be 90150 mg/dL .These goals should be modified to a lower goal in children with frequent hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia unawareness.Its helpful to individualize these goals under benefit-risk assessment to assess preprandial insulin doses in those on basal-bolus or pump regimens.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Normal Sugar Level In Fasting
Also Check: Medication For Weight Loss And Diabetes
Can Urine Samples Be Tested For Glucose
Urine samples are routinely tested for glucose as part of a urinalysis. Additional testing is usually done to identify the cause of an abnormal urine glucose result.
Glucose usually only shows up in the urine if glucose is at sufficiently high levels in the blood that some of the excess is lost in the urine, or if there is some degree of kidney damage and the glucose is leaking out into the urine.
When Should I Measure My Blood Glucose
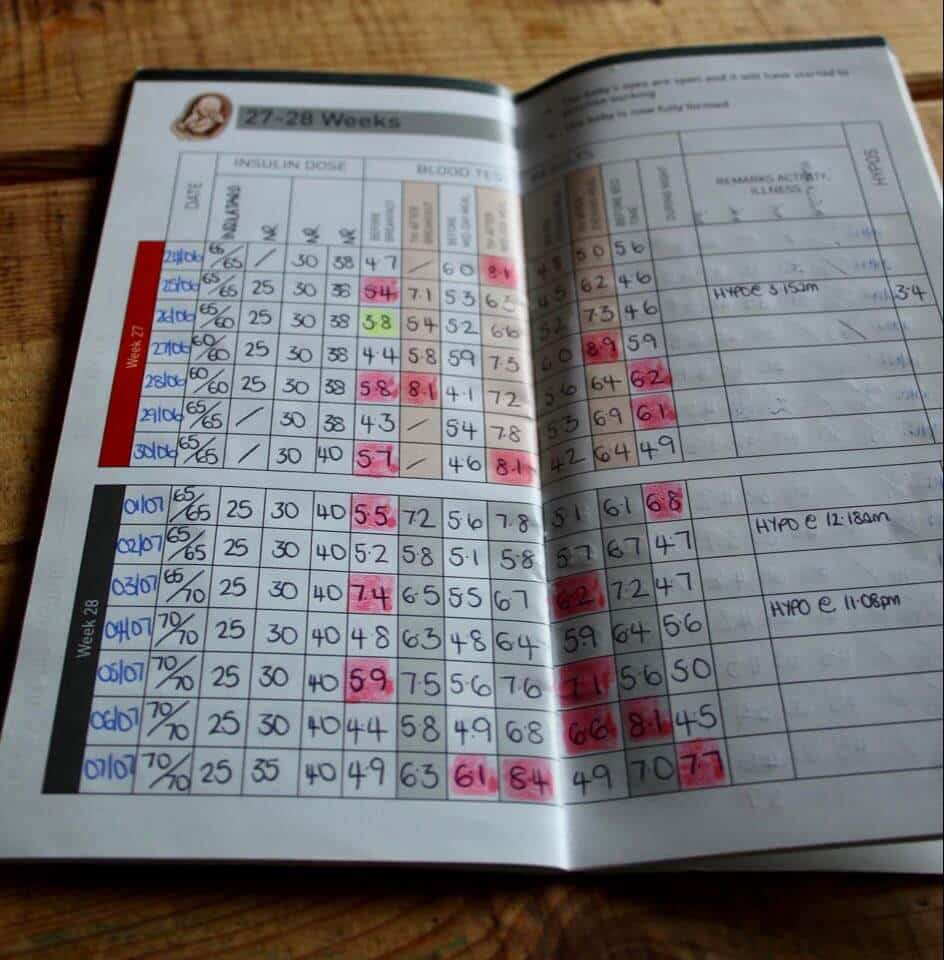
Throughout the rest of your pregnancy, you will need to measure your blood glucose levels at various points through the day, to check that they are within the limits you have been given at each of those times:
When you get up You need to measure your blood glucose levels each morning when you get up, before you have anything to eat or drink. This blood glucose level is called your fasting blood glucose level because you will have an empty stomach. You must not have eaten or drunk anything apart from water overnight, for at least eight hours.
Your team should have discussed this with you and agreed the ideal morning blood glucose level for you to aim for.
Before or after every meal You will probably be asked to measure your blood glucose level around the time of a meal. Some services measure before eating while others measure one or two hours after a meal .
Again, you will have discussed and agreed an ideal blood glucose level after meals with your diabetes team. These levels will be higher than your fasting blood glucose levels, as you will just have eaten.
If you are taking insulin to help to control your blood glucose levels, you may need to do a separate test before you go to bed, or even during the night, although this is unusual.
âWhen we did go out for a special meal or two, and Iâd have a little bit of cheesecake or something, it really affected my sugar levels. But that wouldâve been just twice in the whole pregnancy.âGemma, mum of one
Don’t Miss: Continuous Glucose Monitoring For Dogs
Who’s At Risk Of Gestational Diabetes
Any woman can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, but you’re at an increased risk if:
- your body mass index is above 30 use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI
- you previously had a baby who weighed 4.5kg or more at birth
- you had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- 1 of your parents or siblings has diabetes
- you are of south Asian, Black, African-Caribbean or Middle Eastern origin
If any of these apply to you, you should be offered screening for gestational diabetes during your pregnancy.
Requirements Prior To The Test
- You are to remain on a normal, unrestricted diet for at least 3 days prior to test.
- You have had no acute significant illness for 2 weeks prior to test.
- Fasting is required for a period of 8-10 hours prior to the test. You may have sips of water if you are thirsty.
- Due to the nature of the test, testing is generally done in the morning.
- Maintain normal activity prior to the test.
- Bring a list of any current medications with you to the collection centre.
- Avoid smoking for one hour before and during test.
- Before drinking the glucose, please inform the collection staff if you have any allergies.
Read Also: Medicaid For Type 1 Diabetes
Can Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Its not possible to prevent gestational diabetes entirely. However, adopting health-promoting habits can help reduce your chances of developing the condition.
If youre pregnant and have one of the risk factors for gestational diabetes, try to eat a nutritious diet and get regular exercise. Even light activity, such as walking, may be beneficial.
If youre planning to become pregnant in the near future and youre overweight, consider preparing for your pregnancy by talking with a healthcare professional about ways to safely lose excess weight.
They can help you create a plan to reach and maintain a moderate weight. Even losing a small amount of weight can help you reduce your risk of gestational diabetes.
Furthermore, its important for pregnant people to seek prenatal care and follow all doctor-recommended visits to receive the appropriate screenings and evaluations during their pregnancies.
Is There Anything I Can Do To Help Me Pass The Glucose Tests
No. If you have gestational diabetes, the glucose tolerance test will detect it. However, there are steps you can take to reduce your chances of developing gestational diabetes, as well as to keep your blood glucose levels stable even if you do have the condition. These are:
- Healthy eating: Opt for whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which are high in fiber, and cut back on foods and drinks that are high in added sugars.
- Exercise:Moderate exercise, such as walking briskly and swimming, can help keep your blood sugar under control.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Use our pregnancy healthy weight gain calculator to estimate how much you can expect to gain and whether you are on target.
Read Also: Can You Join The Airforce With Diabetes