Evidence From A Systematic Review And Meta
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Laboratory of Diabetes and Islet Transplantation Research, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
Background: The American Diabetes Association 2003 diagnostic criteria divide impaired glucose tolerance into isolated impaired glucose tolerance with normal fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance combined with impaired fasting glucose , while the World Health Organization 1999 criteria do not. The aim of this meta-analysis was to evaluate whether IGT should be divided into I-IGT or IGT+IFG according to their risk of progression to type 2 diabetes.
Methods: The MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched to identify prospective cohort studies published in English prior to April 18, 2020. Review Manager 5.3 was used to calculate the pooled risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals as summary statistics for each included study.
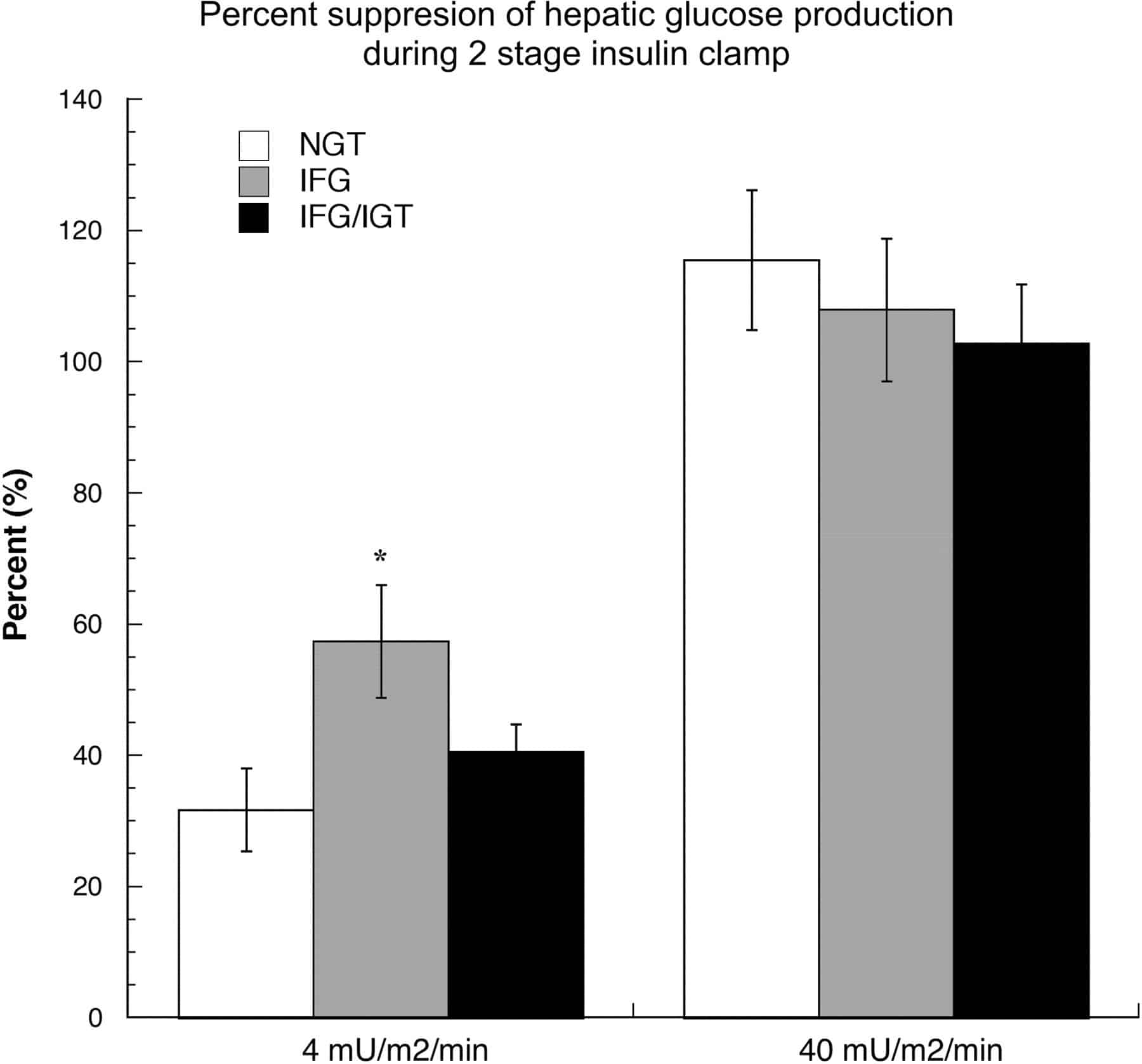
Results: Sixteen eligible studies were included in the analysis. The subsequent incidence of type 2 diabetes was lower in the I-IGT group than in the IGT+IFG group . It was higher in the I-IFG, I-IGT , and IGT+IFG groups than in the normoglycemic group . In general, the incidence of diabetes in the IGT+IFG group was the highest in the prediabetic population.
Prediabetes Causes And Risk Factors
Youâre more likely to get prediabetes if you:
- Are older, especially over age 45
- Have a waist larger than 40 inches around if youâre a man and 35 inches around if youâre a woman.
- Eat a lot of red and processed meat, drink sugary beverages, and donât eat much fruit, veggies, nuts, whole grains, or olive oil
- Are Black, Native American, Latino, or Pacific Islander
- Are overweight or obese, especially if you have extra pounds around your middle
- Have a sleep problem, like sleep apnea, or work changing shifts or night shifts
Get tested for prediabetes if those things apply to you and if you:
- Have had an unusual blood sugar reading
- Show signs of insulin resistance, which means your body makes insulin but doesn’t respond to it the way it should. These include darkened areas of skin, trouble concentrating, and more fatigue or hunger than usual.
The Metabolic Components Including Ifg Or Igt As Risk Factors Of Hypertension
shows the results of logistic regression analysis for risk factors of hypertension during the 4 years follow-up. In the univariate model, age, BMI, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance, abdominal obesity, high serum triglyceride, low serum HDL cholesterol, and IGT were significantly related to the development of hypertension. IFG was not significantly associated with an increased risk of incident hypertension in the univariate model. Multivariate logistic analysis revealed that age, gender, and systolic blood pressure were significantly associated with the development of hypertension. In addition, among the metabolic syndrome components, abdominal obesity was the most significant risk factor, and high serum triglyceride was closely related with the development of hypertension. However, IFG and IGT were not significantly associated with new-onset hypertension in multivariate models.
Comparison of receiver operating characteristic curves for the number of metabolic components excluding IFG/IGT, and the number of metabolic components including IFG or IGT in relation to new-onset hypertension. All models are adjusted for age, gender, BMI, systolic blood pressure, and HOMA-IR. Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance IFG, impaired fasting glucose IGT, impaired glucose tolerance.
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Do I Have It
Availability Of Full Report
The full evidence report from which this summary was taken was prepared for the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality by the McMaster Evidence-based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-02-0020. Printed copies may be obtained free of charge from the AHRQ Publications Clearinghouse by calling 800-358-9295. 9295. Requesters should ask for Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 128, Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose.
The Evidence Report is also online on the National Library of Medicine Bookshelf, or can be downloaded as a PDF file.
AHRQ Publication Number No. 05-E026-1 Current as of August 2005
Internet Citation:
Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment: Number 128. AHRQ Publication Number No. 05-E026-1, August 2005. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
So How Do I Know If My Ifg Becomes Type 2 Diabetes
IFG increases type 2 diabetes risk, so go straight to your doctor or healthcare professional if you feel unnaturally thirsty, pass more urine than usual, have recurrent infections, have blurred vision, or if your wounds heal slowly.
Remember, people with IFG are 5-15 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people with normal glucose levels.
Don’t Miss: Best Hydration Drink For Diabetics
How Is Impaired Fasting Glycemia Treated
IFG doesnt require medical treatment, but lowering blood glucose levels can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes development. You can reach and maintain healthy blood sugar levels by eating a balanced diet, losing any excess weight, improving your fitness level, giving up smoking and sticking to recommended levels of alcohol
Causes Of Impaired Fasting Glycaemia
IFG develops if your body becomes unable to control glucose levels. Your body may be unable to use insulin properly or produce less insulin. There are a number of factors that may make you more likely to develop IFG. If youre black or South Asian and over 25, or if youre white and over 40, and you have one or more of the following risk factors, then you may be at risk of IFG:
- one of your parents, brother or sister has type 2 diabetes
- youre overweight or you carry extra weight around your middle rather than your hips and thighs
- you have high blood pressure or you have had a heart attack or stroke
- you have polycystic ovary syndrome and you are overweight
- you have had diabetes during pregnancy
- you have severe mental health problems
Recommended Reading: Blood Sugar 83 After Eating
My Doctor Talked About Metabolic Syndrome
AnswerMetabolic syndrome is a collection of risk factors that can increase your risk of developing diabetes and heart disease. Metabolic syndrome doesn’t always lead to diabetes. By leading a healthy lifestyle, you may be able to reduce these risk factors and prevent or delay the development of diabetes.
ExplanationMetabolic syndrome is also sometimes called syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome. If you have metabolic syndrome, it means you’re likely to develop heart disease and diabetes because you have certain risk factors. A risk factor is anything that increases your likelihood of getting a disease.There are a number of different definitions of metabolic syndrome. However, recent guidelines state that you have metabolic syndrome if you have any three of the specific risk factors outlined below.
You can reduce these risks by losing excess weight and increasing the amount of physical activity you do. Making these changes to your lifestyle can have a real impact on your health. Your GP may also suggest medicines to lower your blood pressure or to treat your cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
How Can Impaired Fasting Glucose Be Prevented
Once you are diagnosed with Impaired Fasting Glucose then it is very important to stay educated regarding the risks that it poses for you. If you have appropriate education on the condition, employ a good and healthy eating habit, stay away from smoking and alcohol, and do some type of physical activity everyday then the chances are pretty high that you could manage to get rid of impaired fasting glucose.
Also Check: What Is Considered Uncontrolled Diabetes
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A test that screens for diabetes by measuring the level of glucose in a persons blood plasma after a period of fasting . The fasting plasma glucose test is given to nonpregnant adults who are at high risk for diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, these high-risk candidates for testing include everyone age 45 or older, obese individuals , individuals with first-degree relatives with diabetes, members of high-risk ethnic groups , women whove had gestational diabetes or given birth to big babies , people with high blood pressure, people with high-density lipoprotein levels at or below 35 mg/dl or triglyceride levels at or above 250 mg/dl, and individuals who have impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance. The fasting plasma glucose test is performed after a person has fasted for at least 8 hours. A sample of blood is taken from a vein in the arm. If the blood glucose level is greater than or equal to 126 mg/dl, the person is retested and, if the results are consistent, diagnosed with diabetes. Individuals with a fasting plasma glucose level less than 126 mg/dl but greater than or equal to 100 mg/dl are classified as having impaired fasting glucose. Though they do not have diabetes, these individuals do not metabolize glucose normally, and they have an increased risk of developingContinue reading > >
Who Is Most At Risk For Developing Diabetes
The following categories of people are considered “high-risk” candidates for developing diabetes:
- Individuals who have overweight or obesity.
- Individuals who are 45 years of age or older.
- Individuals with first-degree relatives with diabetes .
- Individuals who are Black, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asia American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islanders.
- People who developed diabetes while they were pregnant or gave birth to large babies .
- Individuals with high blood pressure .
- Individuals with high-density lipoprotein below 25 mg/dl or triglyceride levels at or above 250 mg/dl.
- Individuals who have impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance.
- Individuals who are physically inactive engaging in exercise less than three times a week.
- Individuals who have polycystic ovary syndrome, also called PCOS.
- Individuals who have acanthosis nigricans, which are dark, thick and velvety skin around your neck or armpits.
In addition to testing the above individuals at high risk, the American Diabetes Association also recommends screening all individuals age 45 and older.
Read Also: Homemade Protein Shakes For Diabetics
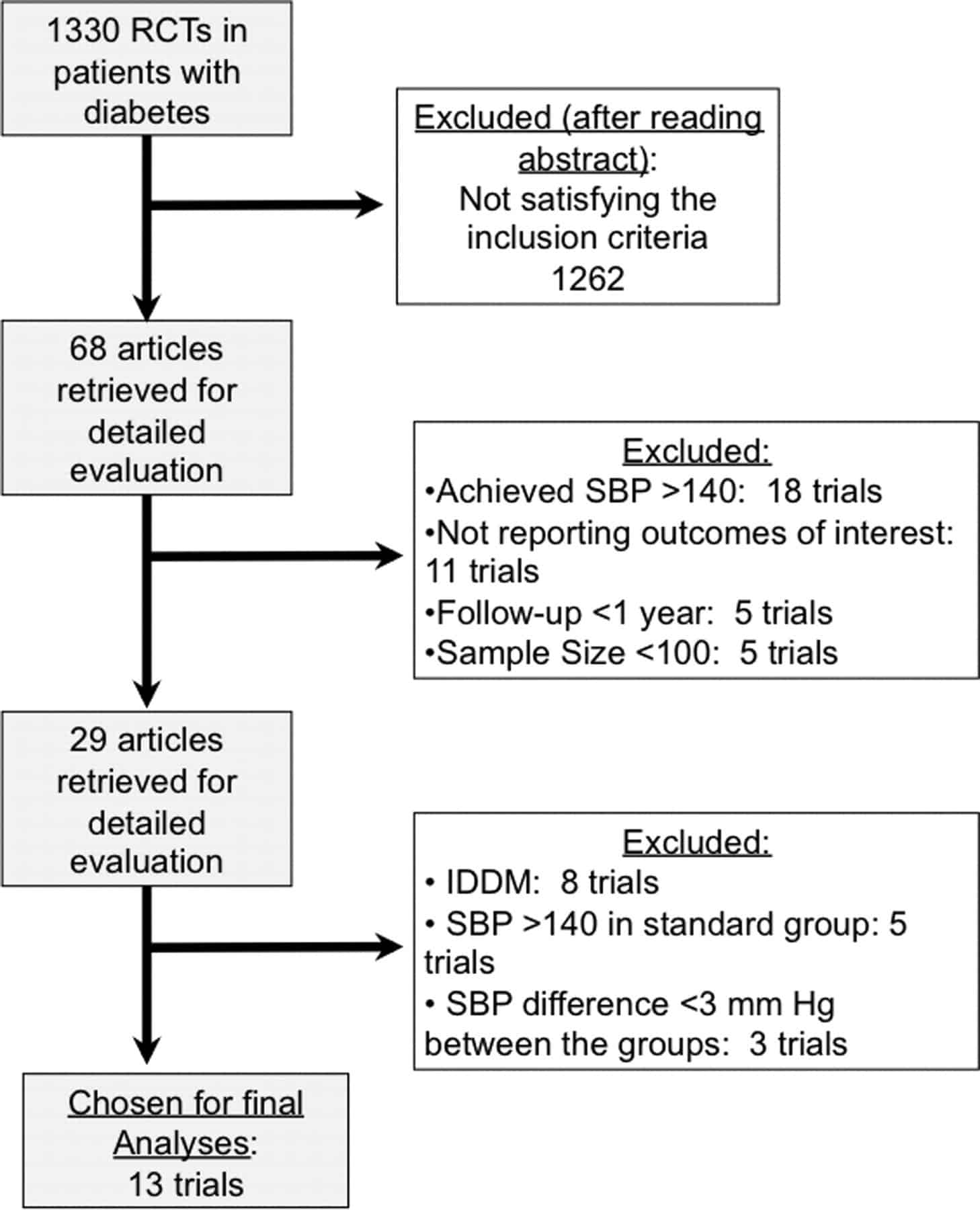
Key Question : Pediatric Population
All articles that met the general criteria and included children with IFG or IGT were collected . Of these, a subset of five articles met the criteria for diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment according to the criteria outlined in the methodology. These articles are included in the analysis of their respective sections above.
Four articles included within the analysis included participants 15 to 18 years of age, but the pediatric data were not presented separately. These studies were therefore excluded from the pediatric analysis. Nineteen studies were excluded for the following reasons: nine discussed cystic fibrosis,56-64 one discussed endemic fluorosis, one dealt with Turner’s syndrome, six related to type 1 DM risks, and no specific pediatric data could be extracted in two articles.
Thus, 13 of 36 articles had extractable pediatric data in articles relevant to either the prevalence, diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment of IFG and/or IGT. The information from these articles forms the basis of the analysis that follows.
Most studies addressed the prevalence of IFG or IGT in various at-risk populations and in the population at large. Two studies compared IFG and IGT diagnosis in children. Four studies examined longitudinal followup of a cohort of children and addressed the prognosis of IFG or IGT. One study examined treatment in an open-label trial with metformin.
Prevalence
Finally, 11 of 21 adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome had abnormal OGTT results .
What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose comes from food. As you eat, food is broken down into sugar and sent to the blood. The insulin is what helps the sugar go into the cells. Once this happens, the sugar is either used for energy or stored away.
Glucose is known as the bodys main energy source. Too much glucose in the blood, or if it is not absorbed properly, can create both short- and long-term health issues. To keep a healthy blood sugar level, it’s important to:
You May Like: How To Check If I Have Diabetes
What Does Impaired Fasting Glycemia Mean
Impaired fasting glycemia means that the body cannot regulate glucose as efficiently as it should be able to.
Glucose is usually carried around the body where it is absorbed and made into energy.
Insulin regulates the concentration of glucose in the blood.
IFG occurs when this process isnt functioning as effectively as it could, and effects millions of people in the UK.
What Is Impaired Fasting Glucose
Impaired fasting glucose< sup> 3< /sup> is defined as glucose values of 100 to 125 mg/dL when you first wake up and before youâve eaten anything for the day. Prediabetes is the same thing as impaired fasting glucose and itâs a sign that glucose is not being used efficiently in the body.
Letâs start with how things should work. The cells in our bodies rely on glucose as a primary source of energy. It powers everything from your muscles to your organs to your brain and keeps it all running smoothly.
While your liver can make small amounts of glucose, the majority comes from carbohydrate-rich foods like fruits, veggies, grains, treats, and starches. Carbs are eventually broken down into glucose, which travels throughout your body in your bloodstream. Whatever isnât used by the cells for energy is stored in your liver, muscles, or fat cells.
Regulating glucose is criticalâyour body carefully monitors how much stays in your blood versus how much is taken in by your cells. When glucose rises, insulin is released from your pancreas.
Insulin is the hormone that signals that itâs time to get sugar out of the blood. Once it moves into your cells, your blood sugar drops, and insulin should decrease as well.
Ideally, your glucose should stay low while you sleep, but as it gets closer to morning, blood sugar can rise slightly as part of a normal wakening response. This is known as the dawn phenomenon.
Don’t Miss: What Is Normal Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms Of Impaired Fasting Glycaemia
IFG has no symptoms and can often go undiagnosed for years. Although there are no symptoms, many people diagnosed with IFG are overweight. Nine out of 10 people with IFG have high blood pressure, raised cholesterol levels or a family history of the condition.
IFG can increase your risk of type 2 diabetes. Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms, but if you do have symptoms they might include:
- passing more urine than normal
- re-occurring infections
If you have any of these symptoms, you should talk to your GP.
What Do The Test Results Mean
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 3.6mmol/l and 6mmol/l, this means that your blood glucose level is normal.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is 7mmol/l or higher, this is likely to mean that you have diabetes. Diabetes is a long-term condition where the body is not able to control the amount of glucose in the blood.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 6.1mmol/l and 6.9mmols/l, you may have IFG.
You May Like: Insulin Pump Basal Rate Calculator
Diagnosis Of Impaired Fasting Glycaemia
Both IFG and diabetes are both diagnosed by testing glucose levels in the blood. The first test you will have is a fasting plasma glucose test. You will be asked not to eat anything for eight to 10 hours before a blood sample is taken. What do the test results mean?
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 3.6mmol/l and 6mmol/l, this means that your blood glucose level is normal.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is 7mmol/l or higher, this is likely to mean that you have diabetes. Diabetes is a long-term condition where the body is not able to control the amount of glucose in the blood.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 6.1mmol/l and 6.9mmols/l, you may have IFG.
Depending on the results of this test you may also be asked to have a two-hour plasma glucose test . If you have this test, you will also be asked not to eat anything for eight to 10 hours before the blood sample is taken. After the blood sample is taken you will be asked to swallow a drink containing a known amount of glucose. Another blood test is then taken two hours after the first to see how your body has dealt with the glucose you swallowed.
About Impaired Fasting Glycaemia
Impaired fasting glycaemia means that your body isn’t able to regulate glucose as efficiently as it should.Glucose is a simple form of sugar found in foods and sugary drinks it’s absorbed as a natural part of digestion.
One function of your blood is to carry glucose around your body. When glucose reaches body tissues, such as muscle cells, it’s absorbed and converted into energy. The glucose concentration in your blood is automatically regulated by a hormone called insulin.
The amount of glucose in your blood changes throughout the day. Its higher and lower depending on what youre eating and drinking.
Blood glucose levels can be measured in a laboratory by testing a blood sample. This is usually done when you have not eaten for eight hours and is called a fasting blood glucose test.Its estimated that seven million people in the UK have IFG.
You May Like: How Much Does Type 1 Diabetes Cost Per Year
Whats The Difference Between Impaired Fasting Glucose And Prediabetes Or Diabetes
Impaired fasting glucose and prediabetes are the same thing. Both mean that your body is not handling glucose efficiently. But diabetes is a more serious diagnosis.
The following are the ranges for prediabetes and diabetes< sup> 7< /sup> based on fasting glucose:
- Normal: less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL and above
All three conditions share the same foundational principle that something happens in the body to interrupt the normal regulation of glucose and insulin.
People with diabetes often need medications in addition to lifestyle changes to help manage their blood sugar. However, people with impaired fasting glucose can still reverse progression.