What Should I Eat Before My Workout
Even when you time your workout perfectly with your insulin, you may need to eat extra carbohydrates to prevent lows. Everyones carbohydrate requirements for exercise are unique. Checking your blood sugar before, during and after exercise will help you develop your own plan.
And dont forget to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Its also a good idea to have hypoglycemic treatment, like glucose tabs or juice on hand during exercise.
After exercise
The effects of exercise dont stop when the physical activity or exercise is over. Delayed onset hypoglycemia can occur, dropping your blood sugar in the 6 to 15 hours after exercise. This is something to take into account when estimating your insulin dose before and immediately after exercise.
Test your blood sugar before, and then every few hours after exercise, and record what exercise you do and what food you eat in your blood sugar record book or with an app. This will make it easier to see trends and will also help you and your diabetes team to develop good diabetes management strategies.
If your blood sugar levels continue to fall after exercise, you may need to decrease your insulin doses before and after exercise. The amount by which you reduce your insulin will depend on your blood sugar trend. Your endocrinologist or diabetes team will be able to give you advice about insulin adjustment.
Life With Type 1 Diabetes As An Athlete
For ballerina Karz, exercise and diabetes wellness have shared a complex role in her life as shes worked to better understand what being an athlete with diabetes means and what a healthy level and approach to exercise looks like.
My biggest challenge proved to be my own psyche, the perfectionist part of me that wanted and needed to have a perfect performance and perfect blood sugar levels, she says. Not to mention the pressure I felt to perform well for my directors so I would continue to learn soloist roles
In time I learned it was more important not to risk dangerous lows, by having blood sugar levels a little on the higher side before the performance. And if the performance wasnt as perfect as my expectations, I had to learn that it was good enough.
Karzs narrative is similar to other elite-level athletes living with type 1 diabetes. Athletes with type 1 have excelled and are continuing to do so in numerous sports, including marathon running, triathlons, mountain climbing, cycling, football, baseball, basketball, yoga, swimming, skiing, and snowboarding. There have been NFL heroes, Olympians, and international sports champions all living with T1D.
Those who succeed do so safely, by working with an awareness of their individual bodies, blood sugar trends, and insulin needs in relationship to activity levels.
Keeping Active At Home
If you’re spending time at home, there are lots of ways to get active and keep moving that much more. How about doing:
- on-the-spot walking during TV ad breaks
- stretches for your arms and legs whilst sat in a chair
- hoovering your home or washing your car
- using cans of food as weights
- gardening – if you have a garden. If you dont, do you have any house plants you can water, prune and re-pot while standing up?
It might help to pop some music on while youre doing this, especially if youre not in the mood to move. It can stop you concentrating on the time and help you feel motivated. For more inspiration, watch Zahoor explain how he manages to move more around his home in this We Are Undefeatable video.
If you need to start off at an easier pace, try standing during a TV advert. If you can manage it, work towards standing for the whole advert break, then to walking on the spot during adverts. You can mix this up by doing stretches instead, or jogging on the spot while the ads are on. This will help you get your steps up.
Everyones different, and some people find video workouts helpful to keep them motivated and follow a routine. There are lots to choose from, but the NHS fitness studio might be a good place to start. Whether youre into aerobics, Pilates, even belly dancing – there are plenty of options for beginners and experts. But remember to warm your body up first. We recommend this warm-up video from the NHS.
You May Like: Is Bluechew Safe For Diabetics
Diabetes Exercise And Ketoacidosis
People with type 1 diabetes are at risk of developing a build-up of ketones if they are unwell or have forgotten to take their insulin.
If you have type 1 diabetes and you are unwell, avoid exercise until you feel better. If your BGL is above 15 mmol/L and you have positive blood or urine ketones, you need to clear the ketones from your blood before beginning exercise. Extra insulin is needed to clear ketones. Ask your diabetes health professional for an individual management plan.
People with type 2 diabetes are generally not at risk of developing dangerous levels of ketones and therefore do not need to check for them.
Effects Of Activity Type And Timing On Glycemic Balance
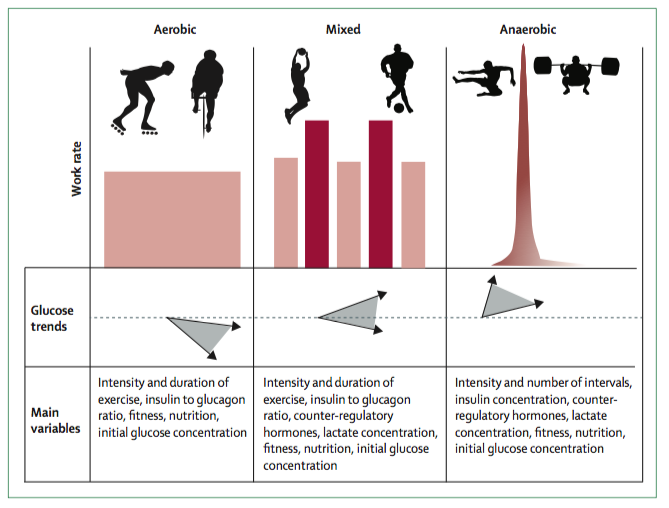
Blood glucose responses to physical activity in type 1 diabetes are highly variable . In general, aerobic exercise decreases blood glucose levels if performed during postprandial periods with the usual insulin dose administered at the meal before exercise , and prolonged activity done then may cause exaggerated decreases . Exercise while fasting may produce a lesser decrease or a small increase in blood glucose . Very intense activities may provide better glucose stability or a rise in blood glucose if the relative intensity is high and done for a brief duration . Mixed activities, such as interval training or team/individual field sports, are associated with better glucose stability than those that are predominantly aerobic , although variable results have been reported for intermittent, high-intensity exercise .
You May Like: Mens Low Cut Diabetic Socks
Balancing Act: Finding Your Blood Glucose And Peak Fitness Zone
Caution: Delayed Onset Hypoglycemia can occur typically 6 to 12 hours after exhaustive exercise, due to replenishment of muscle glycogen stores and enhanced insulin sensitivity. It is possible to prevent this by:
- Keeping records of your fitness regimen and the effects it has on your body
- Using a CGM or frequent blood testing to monitor your bodys response to activity
- Consuming slow-acting carbohydrates after activity
Similar recording and monitoring tactics can be used to prevent hyperglycemia . Some other options include:
- Bolusing 30 to 60 minutes prior to activity to offset rise of blood glucose, delayed bolusing or adding post-workout cool-down
- Incorporating relaxation, breathing, visualization tools to address pre-workout emotional stress
- Limiting pump disconnection time
- Administering rapid-acting insulin
Physical Activity In Youth With Type 2 Diabetes
Randomized trials evaluating exercise interventions in youth with type 2 diabetes are limited and inconclusive, although benefits are likely similar to those in adults. In the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth study , youth aged 1017 years with type 2 diabetes were stabilized on metformin and then randomized to metformin plus placebo, metformin plus rosiglitazone, or metformin plus lifestyle intervention and followed for a mean of 3.86 years. The lifestyle intervention included modest weight loss achieved through dietary energy restriction and increased physical activity , along with metformin use. The rate of glycemic failure was not significantly reduced in the lifestyle plus metformin group compared with metformin only or metformin plus rosiglitazone. Given the limited data in youth with type 2 diabetes, it is recommended that children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes meet the same physical activity goals set for youth in general : a minimum 60 min/day of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, including strength-related exercise at least 3 days/week.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Get Teeth Implants
Benefits Of Other Types Of Physical Activity
Flexibility and balance exercises are likely important for older adults with diabetes. Limited joint mobility is frequently present, resulting in part from the formation of advanced glycation end products, which accumulate during normal aging and are accelerated by hyperglycemia . Stretching increases range of motion around joints and flexibility but does not affect glycemic control. Balance training can reduce falls risk by improving balance and gait, even when peripheral neuropathy is present . Group exercise interventions may reduce falls by 28%29% . The benefits of alternative training like yoga and tai chi are less established, although yoga may promote improvement in glycemic control, lipid levels, and body composition in adults with type 2 diabetes . Tai chi training may improve glycemic control, balance, neuropathic symptoms, and some dimensions of quality of life in adults with diabetes and neuropathy, although high-quality studies on this training are lacking .
Diabetes Exercise And Foot Care
People who have had diabetes for a long time or those who have consistently high BGLs are at higher risk of developing foot problems. If you have nerve damage to your feet this makes you more prone to injury and to problems such as foot ulcers.
The health of your feet should be checked regularly by a podiatrist to make sure you are safe to do the exercise you are planning.
You can prevent foot injuries and infections by:
- wearing well-fitting socks and shoes check that shoes are long enough, wide enough and deep enough
- wearing the right shoe for the activity you are doing
- inspecting your feet daily
- having annual foot checks by a podiatrist
- reporting to your doctor any changes to your feet, such as redness, swelling or cuts or wounds, as soon as you detect them.
Read Also: Erectile Dysfunction Diabetes Type 2 Treatment
Disclaimers And A Green Light
The authors are careful to make a few important disclaimers, first and foremost that one-size recommendations do not fit all, so strategies should be built around exercise types and individual aims, and should take into account various factors including glucose trends, insulin concentrations, patient safety, and individual patient preferences based on experience.
The other main disclaimer is the simple fact that there are VERY FEW studies from which they were able to draw. Several small observational studies and a few clinical trials have been published to date that help to inform the consensus recommendations presented here. More studies are needed to determine how to best prevent exercise-associated hypoglycemia and how to manage glycemia in the recovery period after exercise.
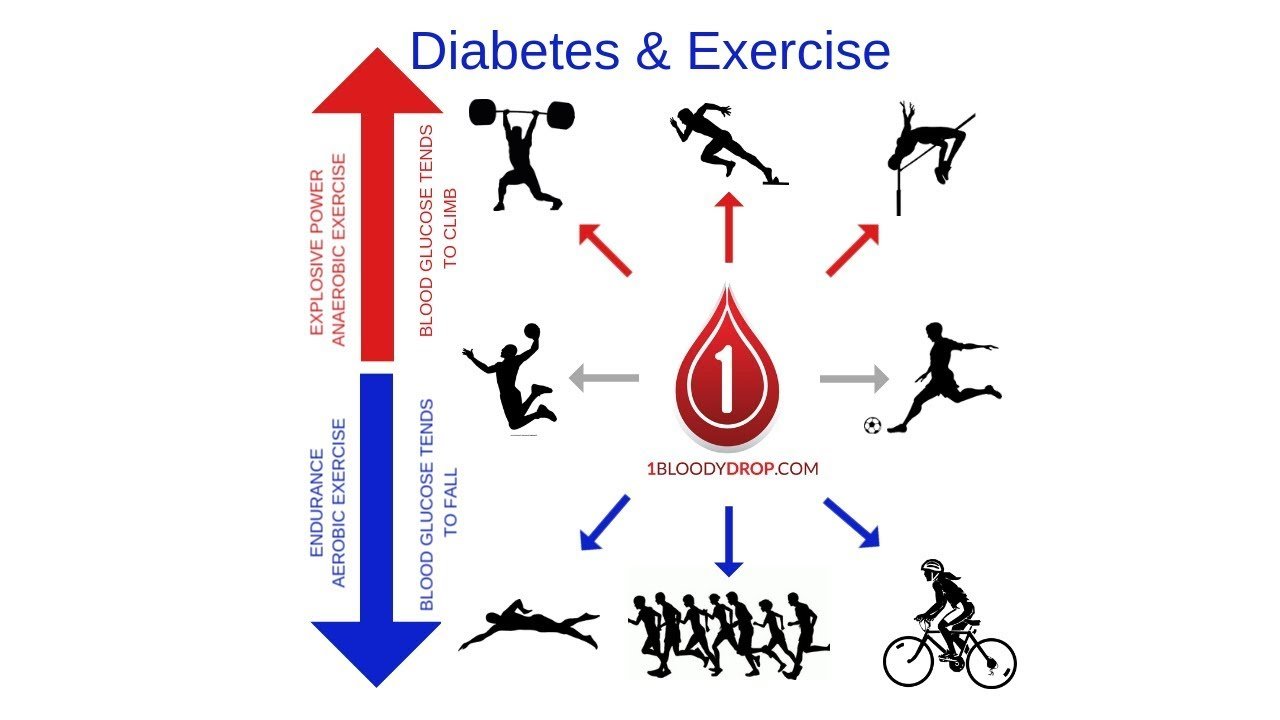
They also state what seems obvious to most of us: In general, aerobic exercise is associated with reductions in glycemia, whereas anaerobic exercise might be associated with increase in glucose concentrations. Both forms of exercise can cause delayed-onset hypoglycemia in recovery.
Still, they make a big point of saying that despite concerns around fluctuating BG levels, exercise is highly recommended! Active adults with type 1 diabetes tend to have better chance of achieving their levels, blood pressure targets, and a healthier BMI than do inactive patients less diabetic ketoacidosis and reduced risk of severe hypoglycemia with coma.
Gotcha, good news.
Best Type Of Exercise When You Have Diabetes
There isnt one type of activity thats best for everyone with diabetes – its about finding what works for you. This can depend on lots of things, like what you enjoy, where you are and how much time you have. Try to think about how activity can fit in with your life, not the other way around.
Were running free physical activity classes for people living with diabetes, both online and face-to-face with coronavirus safety measures in place. and start your journey to move more.
In general, its best to try and do a mixture of different types of activity. This is because different types of activity have different benefits, and use different parts of your body.
For example, swimming can make you breathe harder and raise your heart rate. This is good for your heart health because your heart has to work harder to pump blood around the body. When you have diabetes, keeping your heart healthy is even more important because youre more at risk of complications, including heart disease.
Gardening, however, can help with strength, and doing something like digging can help the body use insulin better.
Some people can find that doing the same thing can get boring after a while, so weve put together a list of ideas to give you inspiration or to help you get started.
And weve also teamed up with Sport England and other charity partners to help promote moving more across the UK in the We Are Undefeatable campaign.
Don’t Miss: Free Stuff For Type 1 Diabetes
Pattern Recognition And Learning
For an exercise calculator or a closed-loop AP system to work effectively, access to real-time data about physiological variables like heart rate, movement , and possibly other biometric data like blood lactate levels during more intense training, is likely a necessity.111 Beyond just receiving these data, it would benefit from having the capacity to analyze and integrate these inputs into algorithms that would identify regimen changes in real time and be able to predict such a change prior to the start of the PA, enabling the system to take preventive actions to help to maintain glycemia and optimize performance outcomes.
For real-time learning to take place with a calculator or for any integrated system, it should be able to collect and analyze data in real time, use algorithms developed using mathematical modeling that can adapt to new input from users and associated devices, and decrease variability in outcomes over time with more relevant and individualized recommendations for diabetes regimen management.65,66 Ideally, such systems or machines would also be able to quantify or integrate users more subjective responses to them, thereby enhancing their perceived value.112 For that to be the case, technologies will eventually have to advance to be even more accurate and adaptable than they currently are to integrate analyses from multiple sources, participants and types of PA, along with having adaptive machine learning to allow for personalization of advice.
Add Variety For The Best Outcome
Practise different types of exercise to experience maximum health benefitsaerobic and resistance training as well as stretching and balance training. People with diabetes often develop poor balance and joint stiffness, says Riddell. Yoga and stretching can help with both of these. While it can sometimes be inconvenient to include dumbbell curls, push-ups, and other resistance exercises to your day, keep in mind that just 20 minutes of resistance training twice a week can lead to major improvements in body weight and blood sugar levels, says Riddell.
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
Types Of Exercise And Physical Activity
Aerobic exercise involves repeated and continuous movement of large muscle groups . Activities such as walking, cycling, jogging, and swimming rely primarily on aerobic energy-producing systems. Resistance training includes exercises with free weights, weight machines, body weight, or elastic resistance bands. Flexibility exercises improve range of motion around joints . Balance exercises benefit gait and prevent falls . Activities like tai chi and yoga combine flexibility, balance, and resistance activities.
Physical Activity And Sports In Youth And Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
Youth experience many health benefits from physical activity participation . A meta-analysis of 10 trials in youth < 18 years of age with type 1 diabetes found significant improvements in A1C in exercisers , and exercising more than three sessions/week for longer and doing both aerobic and resistance exercise may be beneficial . In adults, regular physical activity has been associated with decreased mortality . There is insufficient evidence on the ideal type, timing, intensity, and duration of exercise for optimal glycemic control.
Recommended Reading: Healthy Diet Plan For Diabetic Patient
Use Technology For Tracking
With a cell phone app or an activity tracker watch, you can track your steps, minutes of exercise, heart rate intensity, carbohydrates, and more, says Michael Riddell, a professor in the School of Kinesiology and Health Science at Torontos York University, and a co-author of the chapter about physical activity and diabetes in the Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. Another useful piece of technology: the continuous glucose monitor , which is a tiny sensor placed under the skin. Users check the CGM as theyre exercising and then can make adjustments to their snacking pattern or change their insulin infusion rate well before they develop either low or high blood sugar, says Riddell.
The Benefits Of Any Kind Of Exercise
Sure, there are more things to think about and prepare for when exercising with type 1 diabetes. But there are also extra benefits! In addition to getting stronger, improving heart health, decreasing stress, aiding weight management and loss and improving general mental health, those with type 1 diabetes can see these benefits:
- Muscles are better at absorbing glucose when they are contracted. This increased glucose uptake by your muscles increases insulin sensitivity the opposite of insulin resistance, a problem when the body requires more insulin to process glucose.
- Exercise slows carbohydrate absorption, better using the glucose it has and reducing the insulin you need. This counteracts after-meal hyperglycemia.
Type 1 diabetes should never hold you back from your fitness goals. There are no exercises specifically for people with diabetes, any workout you want to do is possible. There will be highs and lows as you figure out what works for you, but dont let them get you down! Youve got this!
T1D athlete Maddie Maloney uses a combination of yoga and meditation to get in the right headspace for exercise. Watch her explain how she does it.
Also Check: Urine Test For Diabetes Type 2
What Should I Eat Or Drink Before And After I Exercise
You should drink lots of water before, during and after you exercise. You should also eat snacks that are high in carbs and protein.
Below are some examples of snacks you can eat before and after you exercise. Carb counts can be different, depending on the brand. Read the nutrition labels before you exercise:
| Snack |