Tips For Avoiding High And Low Blood Sugars
Walking the tightrope of a life with diabetes is not easy.
We need to strive every day to make sure that we dont let our blood sugars go too high or too low, and that can be exhausting.
Here are some strategies to help keep your blood sugar in balance:
- Eat similar foods and meals that have predictable carbohydrate counts
- Cook food at home, so you know all of the ingredients in your meal
- Keep to a routine, and eat at the same times every day
- Get enough sleep!
- Double-check your insulin doses to make sure youre not taking too much, nor too little
- If youve counted carbohydrates for a meal and dosed insulin for those carbohydrates, eat everything
What Is A Rather Good Blood Sugar Level In The Morning
If youre planning to take your blood sugar readings in the morning before breakfast, it should be around 70 mg/dL to 100 mg/dL. This range is considered normal and is often reported by non-diabetic people. But if you take the glucose reading after breakfast, the readings can spike. Even in the morning, the normal diabetes level should not exceed 140 mg/dL. If it does, talk to your doctor.
What Are The Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
- Difficulty speaking
- Muscle weakness
If you are experiencing an extremely low blood sugar, which is anything less than 40 mg/dL, that is not responding to fast-acting glucose or glucagon, and you have taken fast-acting insulin within the previous 2 hours, call 911 and seek immediate emergency medical attention.
This condition can be life-threatening if not treated.
Don’t Miss: Blood Levels Diabetes Type 2
Is 135 Blood Sugar Level High In The Morning
Blood sugar levels exceeding 126 mg/dL in the morning indicate hyperglycemia. If you take the blood sugar reading on an empty stomach in the morning, and it still shows you glucose levels exceeding the 126 mg/dL mark, it highlights hyperglycemia. You should report it to your doctor and start timely treatment.
The Best Time To Check Blood Glucose After A Meal
Q: I was recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Should I check my blood glucose two hours from when I start eating or after I finish eating my meal? A: Most of the food you consume will be digested and raises blood glucose in one to two hours. To capture the peak level of your blood glucose, it is best to test one to two hours after you start eating. The American Diabetes Association recommends a target of below 180 mg/dl two hours after a meal. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommends a lower target: below 140 mg/dl two hours after a meal. Ask your doctor which target is right for you. Postmeal blood glucose monitoring is important because it helps you see how your body responds to carbohydrates in general and particular foods. Managing postmeal blood glucose can help reduce your risk of developing heart and circulation problems. Virginia Zamudio Lange, a member of Diabetic Living’s editorial advisory board, is a founding partner of Alamo Diabetes Team, LLP in San Antonio.Continue reading > >
Read Also: Free Insulin For Type 1 Diabetes
The Effects Of Protein And Fat
The rate at which food leaves your stomach, called gastric emptying, affects the amount of sugar in your blood after you eat. Protein and fat both slow down gastric emptying, which helps keep blood sugar lower shortly after a meal. In a study published in 2016 in the journal Diabetologica, people who ate high protein-foods before eating carbohydrates , experienced a rise in glucagon, which is thought to play a role in slowing down gastric emptying.
Read more:What Is a Healthy Blood Sugar Reading in the Morning?
Plus, says Palinski-Wade, “if you’re eating a meal that has a large amount of fat or protein, the fat, the protein or the fiber will slow down the absorption and conversion of the sugar, so the peak might be a bit delayed.” She suggests eating carbs with at least one good source of fiber, protein or fat. “Not only is it going to help with the release of blood sugar,” she says, “but it’s also going to help keep you more satisfied.”
When Is Blood Sugar Considered To Be Too High Or Too Low
Slight fluctuations in blood sugar levels are completely normal, and also happen every day in people who dont have diabetes, in response to the food they eat. Between around 60 and 140 milligrams of sugar per deciliter of blood is considered to be healthy. This is equivalent to a blood sugar concentration of between 3.3 and 7.8 mmol/l. Millimoles per liter is the unit that blood sugar is measured in. It describes the amount of a certain substance per liter.
If someone has readings over 7.8 mmol/l , they are considered to have hyperglycemia. These high blood sugar levels mainly occur if there isn’t enough insulin or the insulin doesn’t work properly. Without the effect of insulin, the organs can’t make good use of the sugar in the blood, so the sugar builds up. If type 1 diabetes is left untreated, blood sugar levels can increase to over 27.8 mmol/l . Such high levels tend to be uncommon in type 2 diabetes.
Blood sugar levels below 3.3 mmol/l are considered to be too low. But, as you can see in the illustration below, there are no clear-cut borders between normal blood sugar levels and too high or too low blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar: Normal range between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia
Also Check: What Brand Of Glucose Meter Is Covered By Medicare 2022
Diagnosing And Treating Hyperglycemia
Diagnosing hyperglycemia is done by assessing symptoms and performing a simple blood glucose test. Depending on the severity of the condition and which type of diabetes the patient is diagnosed with, insulin and a variety of medication may be prescribed to help the person keep their blood sugar under control. Insulin comes in short, long and fast-acting forms, and a person suffering from type 1 diabetes is likely to be prescribed some combination of these.
Individuals who are either diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or are considered at risk for the disease are recommended to make alterations to their diet, lifestyle habits and exercise routine in order to lower blood sugar and keep it under control. These changes generally help to improve blood glucose control, individuals with type 2 diabetes may require medication eventually. These can include glitazones, acarbose, glucophage or sulphonylureas.
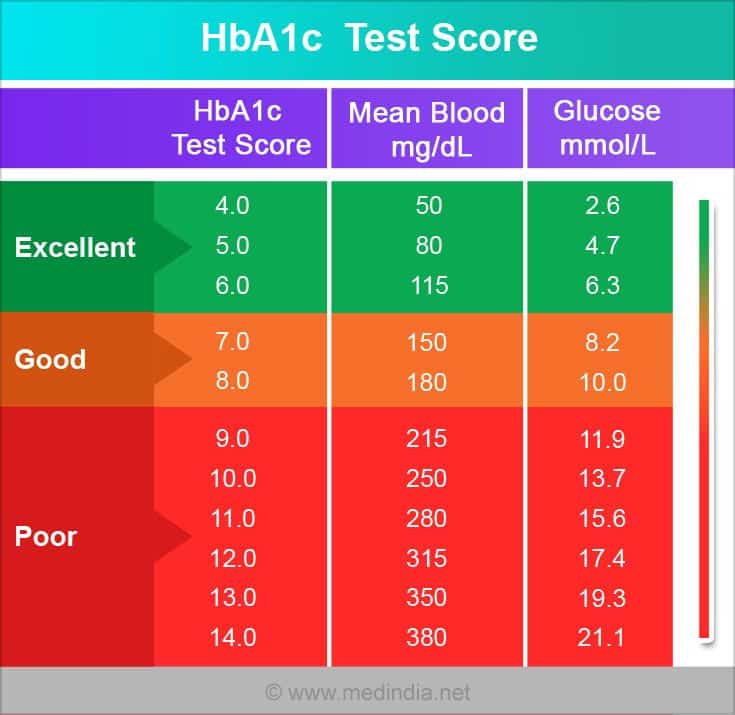
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting in seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Recommended Reading: Low Blood Sugar On Keto What To Do
Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Diabetics
The American Diabetes Association recommends that the blood sugar 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal be less than 180 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. This is typically the peak, or highest, blood sugar level in someone with diabetes. Again, this target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their health care provider.
Normal Blood Sugar 1 Hour After Eating
The ideal blood sugar level can vary from person to person. Ask your doctor what your ideal level is, although the ideal goal would be to achieve blood glucose levels similar to those without diabetes.
Ideal blood sugar levels are usually found between these numbers:
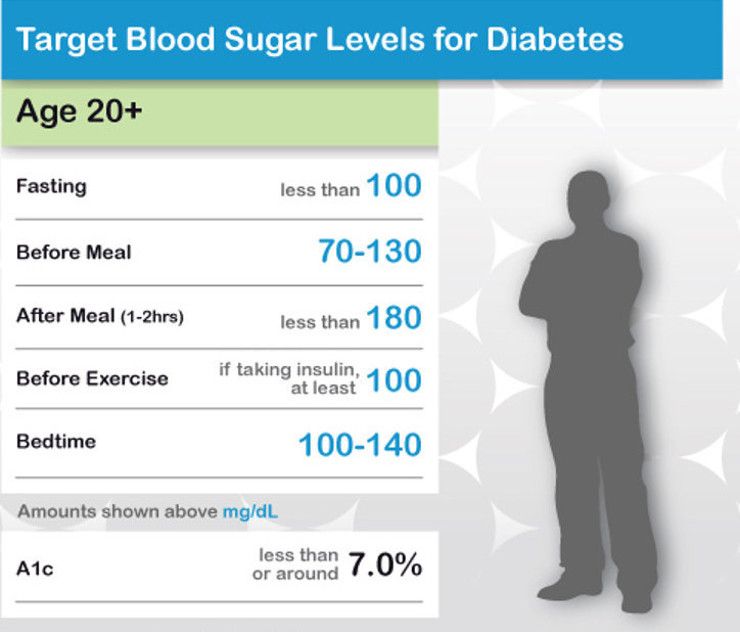
- 80 120 mg/dl, upon waking and before eating
- 180 or less, two hours after eating
- 100 140 mg / dl, at bedtime
Ask your doctor or healthcare professional when to get tested.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Meter Readings
Four Hours After Eating
If you’re generally healthy or are properly managing your diabetes, your blood glucose should fall between 90 and 130 milligrams per deciliter four hours after eating. If you do not have diabetes, your sugar could even go as high as 140 milligrams per deciliter after meals. Of course, if you do have diabetes, your blood glucose could rise even higher — 180 milligrams per deciliter or above, even several hours after eating.
Tests For Type 1 Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Prediabetes
All of us love to taste and try out different kinds of food. Food gives us energy and helps in sustaining our lives. It provides nutrients, macronutrients such as fats, carbohydrates and proteins and micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals to our body. All these are essential for the body to function well.
When we eat food, the body breaks down the food into glucose which is the main source of energy. This glucose enters the bloodstream and indicates the pancreas to let out a crucial hormone called insulin. Insulin is responsible to manage the glucose levels in the body. In persons with diabetes, the immune system attacks and destroys the cells of the pancreas which is liable to generate insulin. Therefore, the pancreas either stops producing insulin or is not able to use the insulin properly. A person can only know if he is diabetic only when the sugar levels are either too high or low. Some dont even have any symptoms and so tests are required to confirm the sugar levels of a person.
There are different types of diabetes like prediabetes, type 1, type 2 or gestational diabetes. The following blood tests are done to find out the type of diabetes in a person
You May Like: Which Is Better For Diabetics Stevia Or Splenda
Blood Sugar Levels Before And After Eating
Blood sugar levels in our bodies will fluctuate depending on various conditions and circumstances. Here are the different levels:
1. Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
According to the American Diabetics Association, normal blood sugar levels after meals should be 70 mg/dl 140mg/dl.This should be the reading 2 hours after a meal. If the levels are lower than 70mg/dl, it might mean that you have hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar is slightly higher than 140mg/dl, it does not necessarily mean that you have diabetes. However, you might need to have an oral glucose tolerance test later on to determine the severity of your elevated post-meal blood sugar.
2. Normal Levels of Fasting Blood Sugar
This blood sugar level is taken first thing when you wake up before your first meal. A normal level of fasting blood sugar lies from 70mg/dl to 92mg/dl. This is also the blood sugar level for a normal person who has not eaten for the past few hours.
3. Normal Blood Sugar Level for Type 1 Diabetics
American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets should lie between the following:
Before eating your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: 90-130mg/dl
After 1 to 2 hours after meals, your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: less than 180mg/dl
When going to bed, your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: 90-150mg/dl
4. Normal Blood Sugar Level for Type 2 Diabetics
American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar targets for people with type 2 diabetes:
- Adults: 70-130mg/dl
What Is Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Dry Mouth
For Children With Type 1
While some diabetes organizations may suggest lower targets, the generally recommended A1c level for children with type 1 diabetes is under 7.5%. However, , which involves a special wearable device that constantly monitors blood glucose, is thought to be a better approach. This is partly because only about a quarter of children with type 1 meet this A1c standard.
The target glucose level for newly diagnosed children using CGM is generally around 150 mg/dL, with some variation allowed during sleep hours .
Children who have been diagnosed for some time and already have an established treatment plan might have a more aggressive target of around 120 mg/dL. As with adults, time in range for children with type 1 diabetes is typically around 70% .
What Should A Normal Blood Sugar Level Be One Hour After Eating
You should always consult with your doctor about what your target blood sugar levels should be, as itâs not always the same for everyone. If youâre looking for a standard benchmark, the American Diabetes Association recommends a target of below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after you eat. For people without diabetes, you should aim for a target below 140 mg/dL.
Read Also: Can Diabetics Eat Mac And Cheese
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
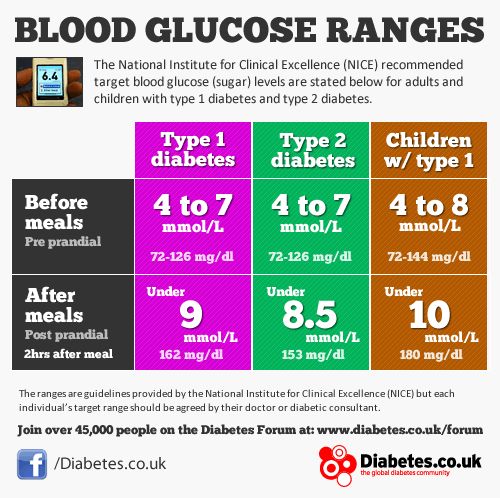
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
Blood Sugar Levels And Diabetes
The blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood. When we eat food, the body breaks down the food to form glucose, which is the main source of energy that is needed by the cells of the body. This glucose is sent to all the cells through the bloodstream as they need the glucose for energy. Diabetes is a problem within the body that causes blood glucose levels to rise higher than normal levels. This happens when the body is not able to produce a hormone called insulin in the required quantity or is not able to use the insulin properly.
Depending on the blood sugar levels, there are different types of diabetes. They are prediabetes, diabetes type 1, diabetes type 2 and gestational diabetes.
Also Check: How Lower Blood Sugar Fast
Target Blood Sugar Levels In Older Adults
When you’re over 65, you have different diabetic treatment goals than younger people. Having other health conditions and/or cognitive impairment affects your blood sugar targets.
If you’re in good health, you may be able to manage diabetes as if you were younger. If you have other health problems, less strict management can help you avoid hypoglycemia.
| Conditions Co-Occurring With Diabetes |
|---|
| 110200 mg/dL |
Summary Of Normal Glucose Ranges
In summary, based on ADA criteria, the IDF guidelines, a persons glucose values are normal if they have fasting glucose < 100 mg/dl and a post-meal glucose level < 140 mg/dl. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:
- Fasting glucose levels between 80-86 mg/dl
- Glucose levels between 70-120 mg/dl for approximately 90% of the day
- 24-hour mean glucose levels of around 89-104 mg/dl
- Mean daytime glucose of 83-106 mg/dl
- Mean nighttime glucose of 81-102 mg/dl
- Mean post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99.2 ± 10.5 to 137.2 ± 21.1 mg/dl
- Time to post-meal glucose peak is around 46 minutes 1 hour
These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in nondiabetic individuals.
Recommended Reading: Blood Sugar Too Low Symptoms
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be High
Based on the ADA guidelines above, if your blood sugar is above 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it is considered above the normal range. What might cause your glucose or blood sugar to rise? Consider the following factors:
- Consuming more carbohydrates or a larger meal than usual
- Not taking enough insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Reduced physical activity
- Side effects from medications like steroids or antipsychotics
Monitoring Blood Sugar In Older Adults
Monitoring blood sugar regularly is crucial to diabetes management. You check your blood sugar with a device called a glucometer.
First, you prick a fingertip with a small needle called a lancet. Then you place a drop of blood on a test strip in the glucometer. After a few seconds, you’ll get a number.
Generally, blood sugar should be checked before meals and at bedtime. Your healthcare provider may want you to check more or less often.
The following chart outlines what blood sugar levels should be for older adults in the hours following a meal as well as when levels are either too high or too low.
| Level | |
|---|---|
| 0-70 mg/dL | 0-60 mg/dL |
Cognitive decline and chronic illnesses can make it hard to follow your diabetes care plan. That can happen even if you’ve successfully managed it for years.
In these situations, your healthcare provider may:
- Prescribe a lower dose of medication
- Involve your caregivers in monitoring
- Carefully watch you for low blood sugar
Read Also: Healthy Diet For Diabetes And High Cholesterol