What Are Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are computerized devices which are quite handy due to their small size. These insulin pumps usually come in the size of a small cell phone. It comes with a flexible tube with a needle attached on one of its end.
This needle is inserted under your abdomen skin and secured with a tape. The insulin is administered through this the inserted needle.
Due to its compact size, you can easily attach the insulin pump on your belt, trousers, or even your bra. This makes it easy to keep the device concealed if you dont wish to make the pump visible to others.
How Do Insulin Pumps Work
The insulin pumps are designed in such a way that it will administer the required amount of insulin continuously throughout the day, based on the plan programmed by the insulin pump user. The programmed plan can be easily changed or modified by the user based on their requirement.
With the help of just few buttons, you can easily increase or decrease the amount of insulin being administered at any particular time. The main unit of the insulin pump is the insulin reservoir which can contain 176 to 300 units of insulin.
The insulin pump can administer the insulin two ways:
Basal Rate
In this method, the insulin pump can be programmed to administer the insulin in tiny and exact amounts throughout the day. This method helps you to maintain your sugar levels between your meals as well as overnight. The insulin pump can easily match the different basal rates throughout the day.
Bolus Dose
In this method, an additional insulin dose known as bolus dose can be administered to cover the meals that you are eating.
Type 2 diabetes patients using insulin pumps should monitor their blood glucose levels four times in a day.
There are also two different types of insulin pumps:
- The traditional pump which comes with a tube which connects the pump and the cannula. All the controls are available on the pump.
- A patch pump will wither have a tube or not and the pump is directly attached to the skin. You can control the pump through another wireless device.
Alberta Insulin Pump Therapy Program Information
For questions or concerns about coverage, including ketone testing equipment, please call Blue Cross customer services team at 1-800-661-6995. General inquiries can also be submitted online: .
- Alberta Health Insulin Pump Therapy Program for details on how to enroll.
- IPT Coverage for qualified candidates includes:
- Insulin pump every five years. Currently Medtronic or Omnipod Eros .
- Infusion sets: up to 100 per 100 days
- Insulin reservoirs: up to 100 per 100 days
- Serters: up to 1 per year
- IPT skin preparation : up to $100 per year
- Blood glucose test strips: up to 700 strips per 100 days
- Blood ketone test strips: up to 20 strips per 100 days
- Blood ketone test meter: up to 1 every 2 years
- Lancets: up to 700 units per 100 days
- Insulin syringes or pen tip needles: up to 100 per 100 days
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Omnipod Insulin Pump Cost
Omnipod is one of the most popular and most commonly used brands of insulin pumps. Omnipod insulin pumps are tubeless. Omnipod insulin pumps are very small and discrete, come in a variety of colors and can be worn on either the arm or a belt. Unlike many other brands, Omnipod records all the statistics of when and how much insulin is used to help doctors better treat the patient. Omnipod insulin pumps cost more than many other brands of tubeless insulin pumps. The average cost of an insulin pump made by Omnipod is around $7000. Omnipod also makes insulin pump cases.
Tips For Using Insulin Pump Therapy
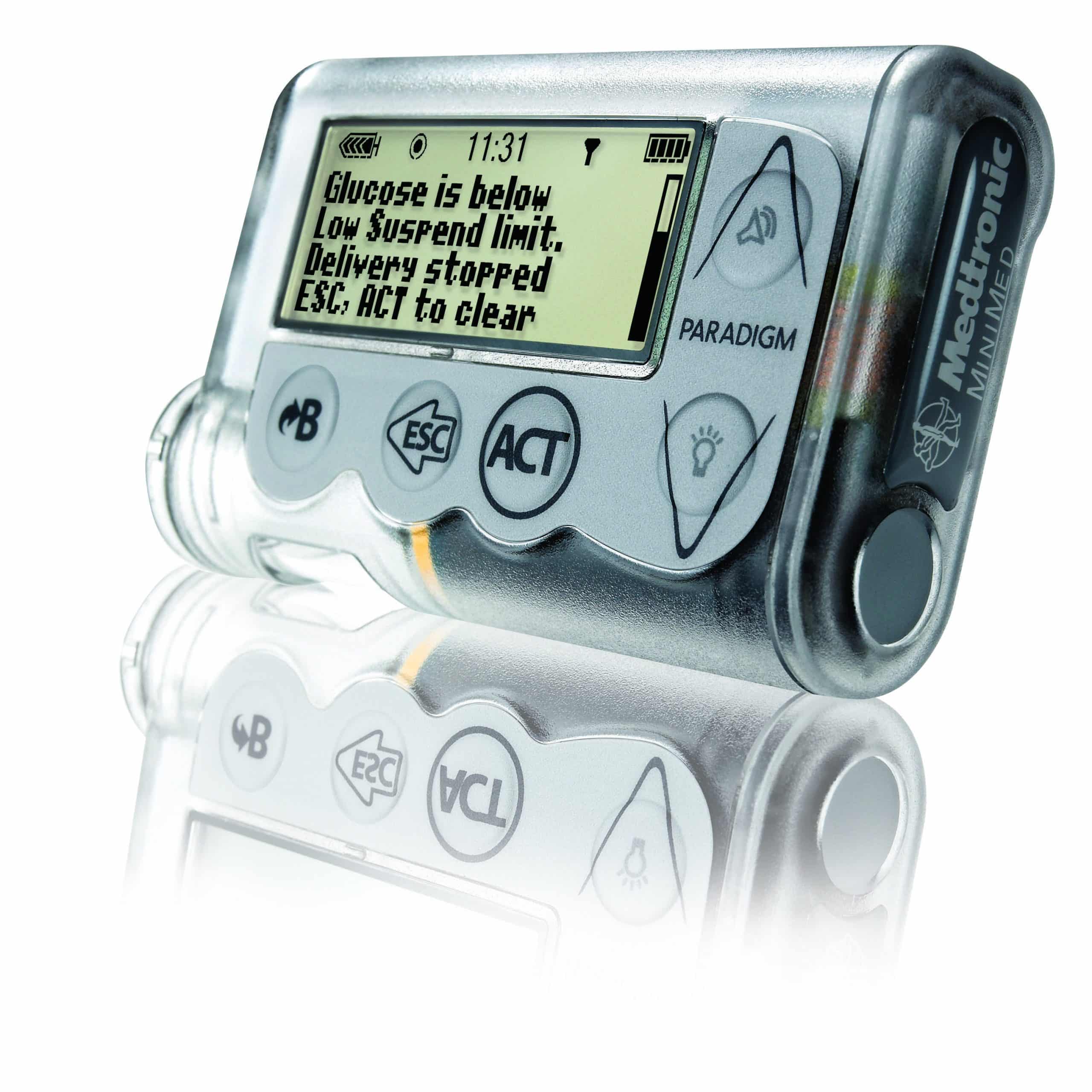
If used properly, insulin pumps and their related components are reliable and safe. But as with any technology, problems can sometimes occur. It’s important to be aware of potential problems and what to do if they arise, to maintain blood sugar levels and avoid side effects.
Tips for proper insulin pump therapy include:
- Watch for cannulas becoming kinked, or leakage in the reservoir or the infusion sets. Kinked cannulas and insulin leaks can lead to interruption of insulin flow, blockages, or mechanical failures.
- Check your pump for damage, such as a cracked display or jammed buttons.
- Make sure your battery is working, check the battery indicator and replace the battery as needed. Check for a loose or damaged battery cap to avoid unexpected power loss.
- Don’t expose your pump to water if it is not waterproof. Also avoid exposing the internal casing to water by changing the battery only in a dry area and making sure that the battery cover is not worn out or missing.
- Understand your personal settings. Be sure to adjust the program to account for changes in activity or diet.
- Change the infusion set according to the instructions for the infusion set you are using and the recommendations of your doctor or health care team.
- Pay attention to device alerts, such as beeps or vibrations. Make sure the volume is set high enough so that you can hear it.
You May Like: Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes In Child
Best Extended Use: Freestyle Libre 14
- Pros: Medicare cover is available for compatible smartphones, the company offers a free 14-day trial, and it does not require finger sticks.
- Cons: Some reviews have mentioned concerns with accuracy and irritation at the insertion site.
- Standout features: The product has long lasting sensors, and it can receive data through a smartphone.
- Administration: Self-applied sensor that syncs with the smartphone app.
- Suitability: People aged 18 and over with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
This CGM device can measure glucose levels every minute through its LibreLink app or a handheld reader and sensor.
According to the company, the FreeStyle Libre 14-day states this device can provide up to 14 days of accurate glucose readings due to its long lasting sensor, which users apply themselves. A person inserts this sensor just under the skin on the back of the upper arm.
Individuals can use their smartphones to track their glucose levels, receive alerts, and review trends. They can also set up the LibreLinkUp app to share their information with up to 20 people, such as family members or healthcare professionals.
The long lasting sensors help this device provide continuous coverage.
Limitations Of Studies Examining The Efficacy Of Insulin Pump Therapy In Patients With T2d
Read Also: Can Diabetic Neuropathy Be Treated
Medtronic: Minimed 630g System
Whats A Closed Loop For Diabetes
Insulin pumps are increasingly being combined with CGMs to create artificial pancreas or closed loop systems that automate blood sugar monitoring and insulin dosing.
Read all about the development of this so-called artificial pancreas technology here.
Whether the pump is connected to a CGM or not, the person wearing it still plays an important role in determining how much insulin they need and when they need it, especially around meals.
But no worries modern pumps are very intuitive and easy to use. And theres no age limit on using a pump they are used by children, all the way up to older adults.
Read on to learn about current insulin pumps in the United States approved by the Food and Drug Administration , some older models still in use, and a glimpse at next-gen insulin pump technology thats on the horizon.
Here is a rundown of the existing insulin pumps on the market in the United States and what they offer to people with diabetes:
Also Check: What Does It Mean If Your Glucose Is High
Is The Use Of Oral Or Other Injectable Antihyperglycemic Agents Recommended With Csii
The use of oral antihyperglycemic agents may be beneficial in type 2 diabetic patients treated with intensive insulin therapy in order to promote better glycemic control, reduce insulin requirement, and limit weight gain . Few studies have tested such a hypothesis in CSII-treated type 2 diabetic patients. An approach was proposed consisting of the maintenance of sulfonylurea together with CSII, with a titration of the oral antihyperglycemic agent aiming to control either fasting glucose or postprandial glucose level. Both strategies were safe and effective for lowering HbA1c . Metformin may be a helpful adjunct to CSII for long-term maintenance of HbA1c lowering together with weight gain limitation . In one study, CSII was provided overnight to type 2 diabetes patients not at goal on oral medications and effectively reduced fasting plasma glucose without occurrence of major hypoglycemia . Novel injectable antihyperglycemic agents such as glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs and mimetics have been recently combined with insulin therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with positive results on weight reduction and glycemic control . It is foreseeable that combination therapy with CSII in type 2 diabetes will bring similar advantages. No study on type 2 diabetes management has yet demonstrated the efficacy of oral antihyperglycemic agents or glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs in adjunct with CSII in a randomized controlled fashion.
Donât Miss: Is Jamun Good For Diabetes
Whats So Great About The Pump
The list is an important one, in large part because pumps provide more precise and tailored insulin delivery. As a result, they offer greater lifestyle flexibility. Tailored insulin delivery can help:
- The dawn phenomenon by matching your early-morning increase in insulin resistance, so you avoid high blood sugar.
- Post-meal glucose rise from slowly digested foods or gastroparesis .
- Shift workers by adjusting the basal rates to your varying work schedule
- Frequent travelers by adjusting the basal and bolus rate to your travel schedule and time zone changes
- Prevent low blood sugars during physical activity and exercise by use of temporary basal insulin rate settings
- Extremely insulin sensitive people by delivering small doses of insulin
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Diabetes Permanently
Types Of Insulin Pumps
Insulin pump availability can vary depending on a variety of factors. Also, insulin pump manufacturers may introduce new pumps or enhanced models, and phase out older models.
Additionally, some pumps may be recommended for certain ages or types of diabetes. Its important to talk with your doctor about choosing a pump. This can ensure your pump of choice is the right option for you, your insulin needs, and your lifestyle.
Examples of commonly used insulin pumps include:
Types Of Insulin Pump
Your healthcare team will talk with you about the pump they think will work best for you, or which one you can get on the NHS if you are eligible.
Both are attached to your body by a tiny tube called a cannula, which goes just under your skin. Youll need to learn how to change the cannula yourself, which eventually becomes really easy.
You need to change your cannula or patch pump every two or three days and make sure you move to a different place every time you change it. This is really important because you can develop lipohypertrophy, which is where your body forms hard lumps that stop insulin working properly. You should also change sites to stop itching and rashes that form if you stick with the same site for too long.
A tethered pump is attached to your body by another small tube that connects to your cannula.
The pump itself usually has all the controls on it and can be carried on your belt, in a pocket, or in a body band. You can wear it under your clothes if you dont want it to be on show.
Tethered pumps can be different in things like colour, screen size and some have extra features like Bluetooth remotes.
Patch insulin pump
You attach patch pumps directly on to your body where youve chosen to place your cannula. People tend to put them on their legs, arms or stomachs.
Patch pumps have no extra tubing, which means the pump sits directly on your skin and it works by using a remote.
Also Check: Blood Glucose Level Chart For Ketosis
What Is The Level Of Satisfaction And Quality Of Life In Type 2 Diabetic Patients On Csii
In two randomized parallel-group studies, treatment satisfaction, diabetes impact, and diabetes satisfaction scores improved over time with both CSII and MDI treatments . The satisfaction score did not differ between MDI and pump in the older population , while the CSII group had greater improvement in overall treatment satisfaction compared with MDI in the younger population . The 36-Item Short Form Health Survey physical and mental composite score did not change significantly within and between groups in the older population . When CSII and MDI were compared in a crossover fashion, the satisfaction subscores were comparable between CSII and MDI . A multicenter observational study found after 1 year that health status evaluated in 61 patients on CSII was maintained in 75% and improved in 20% of the patients . Another 3-year study found an improvement of quality of life stated by the Diabetes Quality of Life and SF-36 questionnaires .
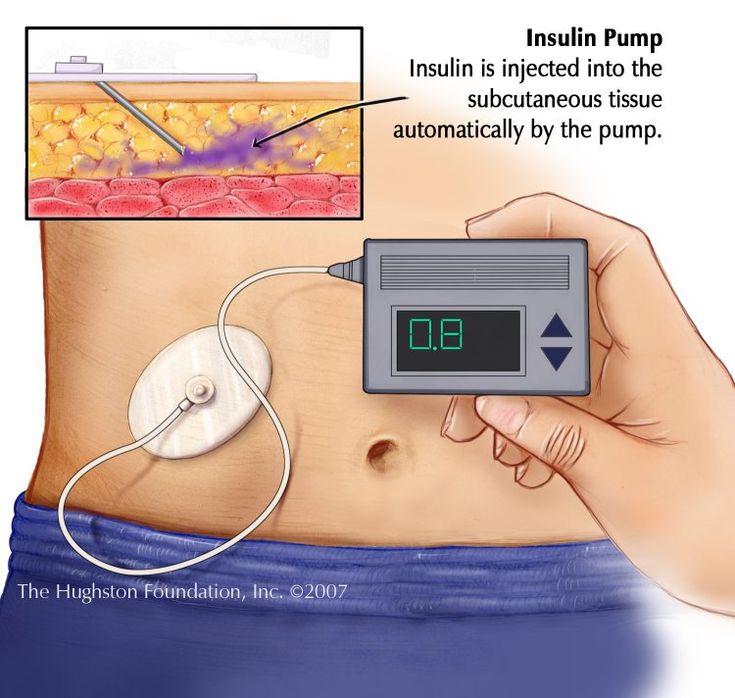
How An Insulin Pump Works
The device releases insulin almost the way your body naturally would: a steady flow throughout the day and night, called basal insulin, and an extra dose at mealtime, called a bolus, to handle rising blood sugar from the food you eat. You program the pump for both basal and bolus doses. If you eat more than normal, you can program a larger bolus to cover the carbs in your food. A bolus can bring down high blood sugar at other times, too.
The pump is about the size of a smartphone. You attach it to your body using an infusion set: thin plastic tubing and either a needle or a small tapered tube called a cannula you put under the skin. The place where you put it in — your belly, buttock, or sometimes thigh — is called the infusion site. Some pumps come with inserters for easier placement even in hard-to-reach areas.
Insulin pumps use short-acting and rapid-acting insulin, but not long-acting, since the pump is programmed to deliver a small amount continuously to keep your blood sugar levels even.
You May Like: Watch That Measures Blood Sugar
How Does An Insulin Pump Work
The American Diabetes Association states that insulin pumps are small, computerized devices. They deliver insulin in a steady and continuous dose, or basal rate, which the user programs. They also deliver insulin as a surge dose, or bolus, under the users direction.
The insulin enters the body through a thin tube that attaches to a needle, which goes under the skin. People refer to the tube and needle together as an infusion set.
Donât Miss: Desserts For Type 1 Diabetes
The Road To Developing An Insulin Pill
The obstacle to oral insulin administration is the fact that insulin is a protein that is digested in the stomach before it reaches the bloodstream.
For insulin to work, it must get past the stomach and into the bloodstream still intact, to be transported to the insulin receptors on fat, muscle, and liver cells.
In recent years, there have been many research efforts to overcome this challenge.
For example, in a 2019 study , an MIT-led research team developed an ingestible, self-orienting capsule containing a small needle that could inject insulin directly into the stomach wall.
Other researchers have focused on insulin mimetics molecules that mimic insulins ability to activate the human insulin receptor, which in turn, triggers blood glucose uptake. Yet this is not an easy feat.
Peter R. Flatt, Ph.D., professor of biological and biomedical sciences at Ulster University, explained to Medical News Today that, insulin has a complex structure which has defeated chemists trying to make a small molecule mimetic that can be taken orally.
Daniel J. Leahy, Ph.D., professor of molecular biosciences at the University of Texas at Austin, noted to MNT:
It has been difficult to make an insulin-supplanting pill as insulin is a protein that would be digested in the gut, and any insulin-mimicking pill would have to survive being digested as well as be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Recommended Reading: 2 Hour Glucose Tolerance Test
The Effects Of Csii Therapy Combined With Glucose Lowering Agents
Combination of insulin treatment with insulin sensitizers or with incretin-based treatments might enable attainment of similar, or possibly better, glycemic goals than insulin treatment alone, but with lower insulin needs, less weight gain, and less hypoglycemia . Several studies have assessed the benefits obtained with the combination of CSII and glucose lowering agents in patients with T2D. Combination of sitagliptin with CSII for 2 weeks enabled attainment of similar glycemic targets versus CSII alone, but with lower glycemic variability and improved beta cell function , . A study which randomized poorly controlled patients to CSII alone or CSII with the combination of exenatide for 3 days demonstrated increased glycemic variability with exenatide but reduced glucose AUC in an OGTT . A study assessing the benefit of the addition of liraglutide therapy to CSII versus CSII alone demonstrated faster attainment of euglycemia with liraglutide and improved beta-cell function over 12 weeks of therapy. Glycemic variability was not reported in this study . Longer and larger trials may be needed to fully demonstrate the effect of the combination of various anti-diabetic drugs with CSII in patients with T2D and its’ possible contribution to reducing glycemic variability, improving beta cell function, and better and faster attainment of glycemic targets.