What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Your blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are a measurement that show how much glucose you have in your blood. Glucose is a sugar that you get from food and drink. Your blood sugar levels go up and down throughout the day and for people living with diabetes these changes are larger and happen more often than in people who don’t have diabetes.
Insulin And Blood Sugar
Insulin is an important hormone that helps regulate your blood sugar levels. The pancreas makes insulin. It helps control your blood sugar levels by assisting the cells that absorb sugar from the bloodstream.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body doesnt make insulin. This means you have to inject insulin every day.
If diet and exercise arent enough to manage blood sugar, those with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications to help keep blood sugar levels within target ranges.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body produces insulin, but may not use it properly or produce enough of it. Your cells dont respond to insulin, so more sugar keeps circulating in the blood.
Exercise can help the cells respond better and be more sensitive to insulin. The proper diet can also help you avoid spikes in blood sugar. This can help keep your pancreas functioning well since high blood sugar levels decrease pancreatic function.
Also Check: How Fast Can Diabetes Develop
Why You Should Measure Blood Sugar
As many as 1 in 3 adults in the US has prediabetes. This puts them at risk for developing type 2 diabetes. Among those, its also suspected that around 80% dont know they have it. Prediabetes often shows no symptoms at all for years.
This means that its important to get your blood glucose levels tested if you have any of the common for diabetes:
-
A family history of type 2 diabetes
-
Being older than 45
-
Having low levels of physical activity
If you fit into one or more of these categories, asking your health care provider for a simple blood test might help you avoid a lifetime of diabetes. It can also lower your risk for other conditions, such as heart disease, kidney conditions, eye problems, and stroke.
Its also crucial to keep track of blood sugar levels in diabetes to avoid serious complications of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia:
-
, such as coronary artery disease with chest pain, heart attack, stroke, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol
Read Also: Lisinopril For Kidney Protection In Diabetes
Several Factors May Cause A Persons Postprandial Blood Sugar To Remain Elevated
Smoking after the meal: Studies show that smoking raises blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. Extreme stress: Stress produces the bodys fight-or-flight response triggering the release of stress hormones such as cortisol. These hormones cause the body to release the glucose it has previously stored for energy. Eating or drinking after the meal and before testing the blood sugar: Continuing to eat will keep blood sugars closer to their immediate post-meal levels.
Studies show that 15 to 20 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, shortly after a meal may improve glucose metabolism and reduce postprandial glucose levels.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels
You might want to measure your blood sugar before meals to get a baseline, and then two hours after your meal to measure your “normal blood sugar level”. Your doctor might also suggest measuring blood sugar before bed to be sure you have been eating well throughout the day and can go to sleep with peace of mind.
These are considered within the range of “normal” for blood sugar:
- Less than 140 mg/dl if you do not have diabetes.
- Less than 180 mg/dl if you have diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Pins And Needles Treatment
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
You May Like: On The Verge Of Diabetes
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: What Symptoms Will A Diabetic Experience
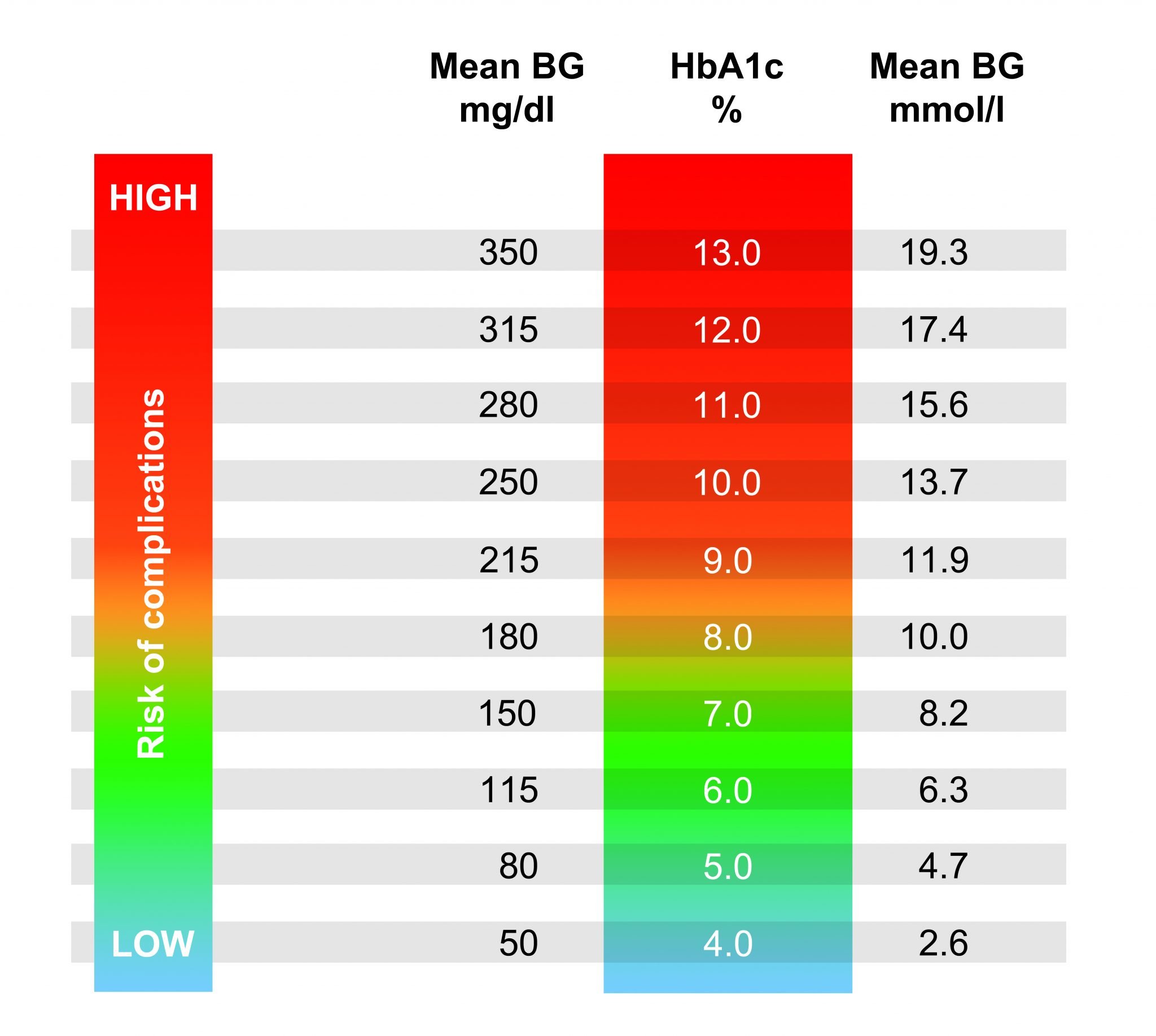
Blood Sugar Level Chart And Information
Synopsis:Information and printable chart showing diabetic blood sugar levels for persons with diabetes or pre-diabetes. The results of blood sugar tests vary by testing method and lab but generally doctors consider a fasting blood sugar of up to 100 mg/dL to be within the average range. A number of medical studies have shown a dramatic relationship between elevated blood sugar levels and insulin resistance in people who are not very active on a daily or regular basis.
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
Don’t Miss: What To Take To Lower Blood Sugar
What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is the sugar that is found in the blood. This sugar comes from the food we eat and this is the main source of energy for our bodies. Glucose can also be formed in the body and stored for later user. The blood carries this glucose to all the cells in the body to use it for energy.
Over time, if there is too much glucose in the blood, it can cause some serious health issues. Sometimes problems may arise if the sugar level is either too low or too high even without being a diabetic.
For People Without Diabetes
For people who dont have diabetes, an A1c test result lower than 5.7% is considered normal. If your level is between 5.7% and 6.4%, you may have what is sometimes called . This means that you have higher than normal blood glucose but dont meet the criteria to be diagnosed with diabetes.
An FPG test result of 99 mg/dL or lower means that youre within a safe range. A result between 100 to 125 mg/dL is in the prediabetes range, and you might need follow-up testing. A safe range for an OGT test result is around 140 mg/dL 2 hours after the test starts, while 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL is considered a prediabetic range.
If results suggest that you have prediabetes, your provider might order more tests and offer ideas for that can help bring your blood glucose levels down. The goal is tolower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, or to delay its onset as long as possible.
Don’t Miss: Will Losing Weight Lower Blood Sugar
High And Low Blood Sugar Levels With Diabetes In Adults
The chart below shows the dangerous level of blood glucose for diabetic patients. Red levels are indicators that require emergency treatment, while yellow levels indicate medical attention but not an emergency. So, it is clear that sugar levels greater than 250 mg/dl could be dangerous. It is recommended that you need to consult with the doctor immediately.
| Chart of High and Low Blood Sugar Levels in Diabetes |
|---|
| Blood sugar level status |
Also Check: Best Glucometers in India for 2022
High Sugar Levels Range in Adults
Monitoring Blood Sugar In Older Adults
Monitoring blood sugar regularly is crucial to diabetes management. You check your blood sugar with a device called a glucometer.
First, you prick a fingertip with a small needle called a lancet. Then you place a drop of blood on a test strip in the glucometer. After a few seconds, you’ll get a number.
Generally, blood sugar should be checked before meals and at bedtime. Your healthcare provider may want you to check more or less often.
The following chart outlines what blood sugar levels should be for older adults in the hours following a meal as well as when levels are either too high or too low.
| Level | |
|---|---|
| 0-70 mg/dL | 0-60 mg/dL |
Cognitive decline and chronic illnesses can make it hard to follow your diabetes care plan. That can happen even if you’ve successfully managed it for years.
In these situations, your healthcare provider may:
- Prescribe a lower dose of medication
- Involve your caregivers in monitoring
- Carefully watch you for low blood sugar
Also Check: Low Blood Sugar Early Pregnancy
Other Severe Symptoms Of Hyperglycaemia Include:
- Blood vessel damage
Mild hyperglycaemia, depending on the cause, will not typically require medical treatment. Most people with this condition can lower their blood sugar levels sufficiently through dietary and lifestyle changes.
Those with type 1 diabetes will require the administration of insulin , while those with type 2 diabetes will often use a combination of injectable and oral medications , although some may also require insulin.
What To Expect After Meals
Food affects blood sugars, and most people who monitor their blood sugars notice their readings rise — and can be more challenging to control — after meals. If you do not have diabetes or prediabetes, your blood sugars may rise only slightly after meals — typically not exceeding 140 mg/dL when checked 2 hours after the start of a meal. If you have diabetes, ADA recommends post-meal blood sugars stay below 180 mg/dL. If your readings exceed this, you may be able to improve them. For instance, blood sugar can often be reduced by eating smaller meals, choosing healthful, high fiber foods, increasing physical activity, and by taking prescribed diabetes medications on time. If your readings are consistently above target, work with your doctor and diabetes care team to discuss solutions.
You May Like: Strict Diet For Diabetes Type 2
When To See A Healthcare Provider
If your test results reveal that you have type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, it is vital to speak to your doctor about establishing a comprehensive treatment plan.
This plan should include diabetes self-management education and support services, as well as clear steps you can take to ensure that you are in the best state of health. However, if you have prediabetes or want to prevent diabetic issues, you should modify your lifestyle and avoid the outcome of the condition.
Maintaining blood glucose levels within your target range is the main objective. Your doctor will specify your desired range. The type of diabetes, age, and presence of problems all affect the target level. For example, your blood sugar levels will be lower if you have gestational diabetes than in other forms of diabetes.
As per research, physical exercise is crucial for managing diabetes. Find out from your doctor how many minutes you should exercise per week. Nutrition is also vital. You must also keep an eye on your cholesterol and blood pressure.
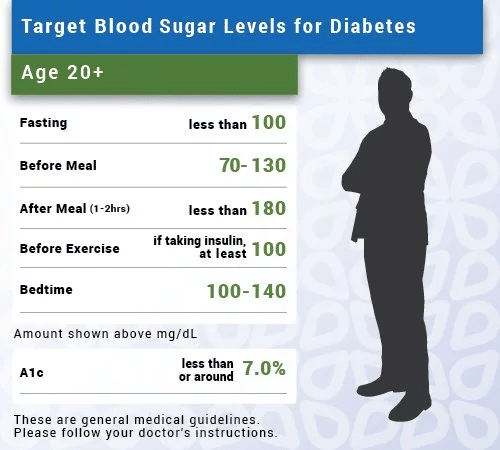
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels by Type |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Also Check: How To Lower High Blood Sugar Without Insulin
Problems Caused By High Blood Sugar
Its not usually a serious problem if your blood sugar is sometimes slightly high for a short time.
But high blood sugar can cause serious problems if it stays high for a long time or gets to a very high level.
It can lead to:
- life-threatening conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis
If you have high blood sugar, your doctor or care team may ask you to test your blood or pee to check for ketones. A high level of ketones is a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
You May Like: What Is Glucose Test For
When To See A Doctor
Knowing when to see your endocrinologist is important in the life of any person with diabetes and even their caretakers. Learn all about the blood sugar levels and their normal ranges to be able to understand what to look out for. In case of frequent lows, unmanageable highs, traces of ketones in the urine, continuous blurred vision, etc. visit your doctor. Ideally, you should be visiting them every 3 months after your HbA1c test.
How Do You Control Random Blood Sugar
It is highly important to keep your sugar level normal. The dedication and hard work required to do so would be highly beneficial in the short and long term too. Ensuring that you are taking the right steps to keep these levels in check can be done in the following ways:
- Eating healthily and on time
- Taking the required dose for the number of carbs you are consuming
- Planning and managing sick days well.
- Exercising regularly to ensure proper metabolic health.
- Not forgetting the doses of insulin.
Don’t Miss: Cvs Health True Metrix Blood Self-monitoring Glucose Meter
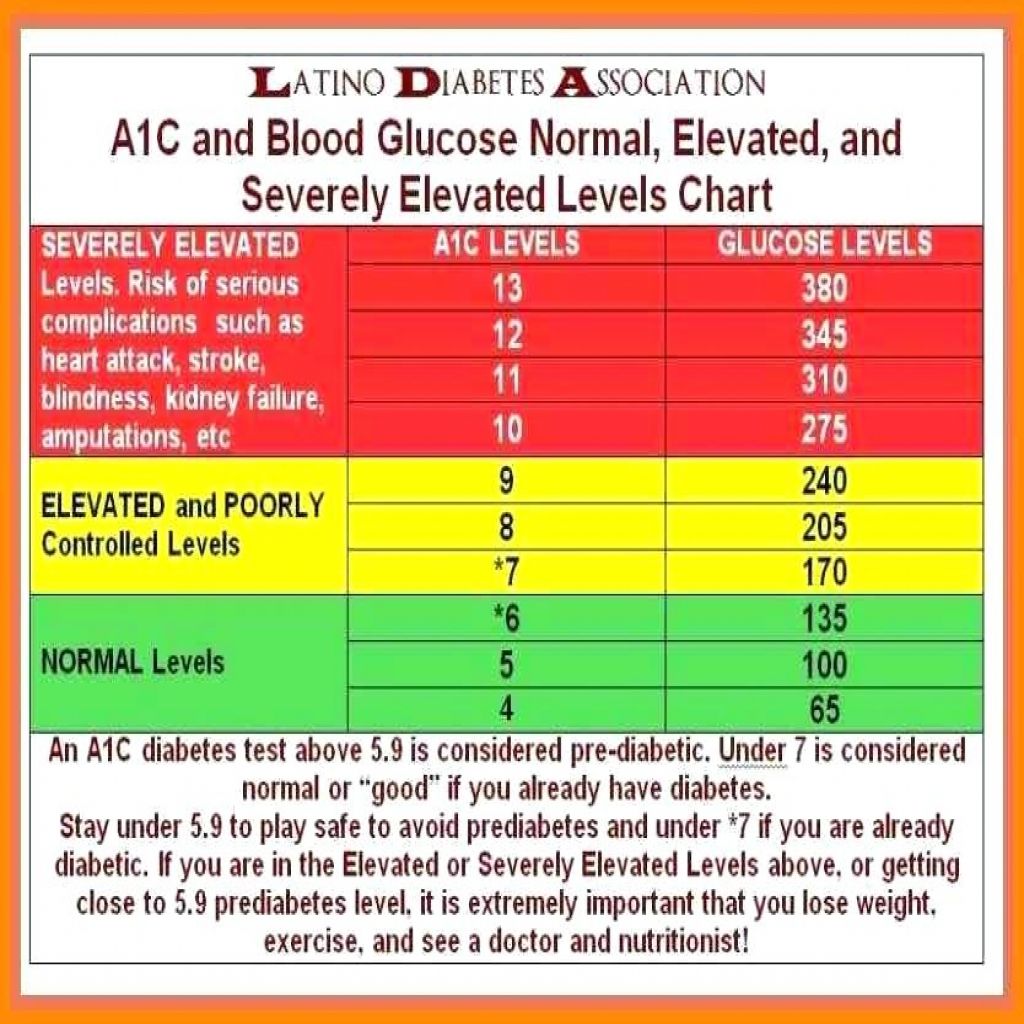
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Children With Diabetes According To Age
Summary
Don’t Miss: Onetouch Ultramini Blood Glucose Monitoring System
Diabetes: Blood Sugar Levels
Topic Overview Keeping your blood sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems such as diabetic eye disease , kidney disease , and nerve disease . Some people can work toward lower numbers, and some people may need higher goals. For example, some children and adolescents with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, people who have severe complications from diabetes, people who may not live much longer, or people who have trouble recognizing the symptoms of low blood sugar may have a higher target range. And some people, such as those who are newly diagnosed with diabetes or who don’t have any complications from diabetes, may do better with a lower target range. Work with your doctor to set your own target blood sugar range. This will help you achieve the best control possible without having a high risk of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Canada suggests the following A1c and blood glucose ranges as a general guide.Continue reading > >